CCNA – IP Routing Questions
Here you will find answers to IP Routing Questions
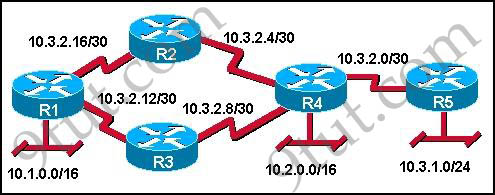
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Assume that the routing protocol referenced in each choice below is configured with its default settings and the given routing protocol is running on all the routers. Which two conditional statements accurately state the path that will be chosen between networks 10.1.0.0 and 10.3.2.0 for the routing protocol mentioned? (Choose two)
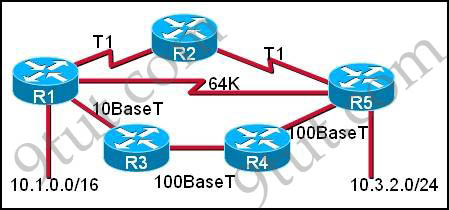
A. If OSPF is the routing protocol, the path will be from R1 to R3 to R4 to R5.
B. If OSPF is the routing protocol, the path will be from R1 to R2 to R5.
C. If OSPF is the routing protocol, the path will be from R1 to R5.
D. If RIPv2 is the routing protocol, the path will be from R1 to R3 to R4 to R5.
E. If RIPv2 is the routing protocol, the path will be from R1 to R5.
Answer: A E
Explanation
First we need to know the speed of these links:
+ T1: 1.544 Mbps
+ 10BaseT: 10 Mbps
+ 100BaseT (often referred to as FastEthernet): 100Mbps
OSPF chooses the best path via bandwidth while RIP only uses hop count (the sum of routers to reach the destination).
Therefore if OSPF is used, it will choose the path R1 -> R3 -> R4 -> R5 because these links have much higher speed than other paths -> A is correct.
But if RIP is used it only counts the number of routers to reach the destination (the less the better) so it will choose path R1 -> R5 (hop count: 1) -> E is correct.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Which three statements are true about how router JAX will choose a path to the 10.1.3.0/24 network when different routing protocols are configured? (Choose three)
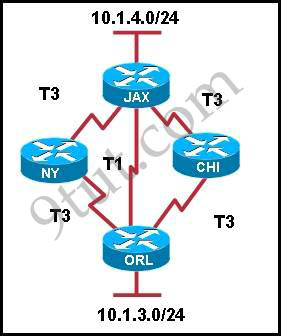
A. By default, if RIPv2 is the routing protocol, only the path JAX-ORL will be installed into the routing table.
B. The equal cost paths JAX-CHI-ORL and JAX- NY-ORL will be installed in the routing table if RIPv2 is the routing protocol.
C. When EIGRP is the routing protocol, only the path JAX-ORL will be installed in the routing table by default.
D. When EIGRP is the routing protocol, the equal cost paths JAX-CHI-ORL, and JAX-NY-ORL will be installed in the routing table by default.
E. With EIGRP and OSPF both running on the network with their default configurations, the EIGRP paths will be installed in the routing table.
F. The OSPF paths will be installed in the routing table, if EIGRP and OSPF are both running on the network with their default configurations.
Answer: A D E
Explanation
First we need to know the speed of these links:
+ T1: 1.544 Mbps
+ T3: 45 Mbps (each T3 line consists of 28 T1 lines)
RIP chooses the path with minimum hop count to reach the destination so it will choose JAX-ORL path -> A is correct.
EIGRP, by default, calculates metric via bandwidth & delay (metric = bandwidth + delay). Delay parameter can be ignored in this case so EIGRP will choose the path via metric. Both the path JAX-CHI-ORL and JAX- NY-ORL have the same metric (each includes two T3 lines) so EIGRP will use these paths -> D is correct.
EIGRP has lower Administrative Distance than OSPF (EIGRP: 90 < OSPF: 110) which is better -> EIGRP will be preferred to OSPF -> E is correct.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator must establish a route by which London workstations can forward traffic to the Manchester workstations. What is the simplest way to accomplish this?
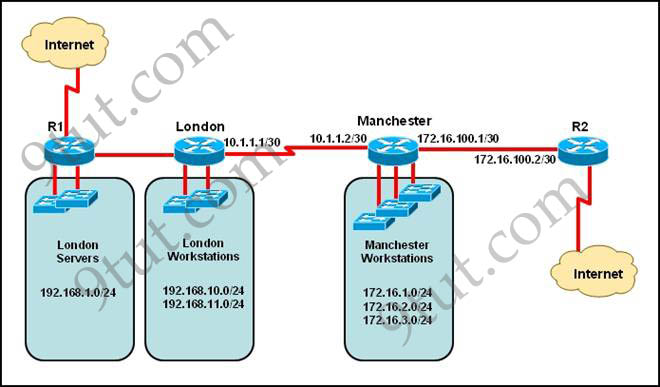
A. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise all routes to Manchester.
B. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise summarized routes to Manchester.
C. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on Manchester to advertise a default route to the London router.
D. Configure a static default route on London with a next hop of 10.1.1.1.
E. Configure a static route on London to direct all traffic destined for 172.16.0.0/22 to 10.1.1.2.
F. Configure Manchester to advertise a static default route to London.
Answer: E
Question 4
Which command is used to configure a default route?
A. ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 0.0.0.0
B. ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.2.1
D. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
Answer: D
Explanation
The simple syntax of static route:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network
+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network
+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router
+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
In the statement “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1″:
+ 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0: refer to any network
+ 172.16.2.1: the next-hop-IP-address
Question 5
If IP routing is enabled, which two commands set the gateway of last resort to the default gateway? (Choose two)
A. ip default-gateway 0.0.0.0
B. ip route 172.16.2.1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
C. ip default-network 0.0.0.0
D. ip default-route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
Answer: C E
Question 6
What must be set correctly when configuring a serial interface so that higher-level protocols calculate the best route?
A. bandwidth
B. delay
C. load
D. reliability
Answer: A
Explanation
Higher-level protocols (OSPF, EIGRP) calculate the best route mainly based on bandwidth so it must be set correctly -> A is correct.
Question 7
Which destination addresses will be used by Host A to send data to Host C? (Choose two)
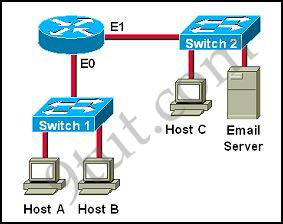
A. the IP address of Switch 1
B. the MAC address of Switch 1
C. the IP address of Host C
D. the MAC address of Host C
E. the IP address of the router’s E0 interface
F. the MAC address of the router’s E0 interface
Answer: C F
Explanation
While transferring data through many different networks, the source and destination IP addresses are not changed. Only the source and destination MAC addresses are changed. So in this case Host A will use the IP address of Host C and the MAC address of E0 interface to send data. When the router receives this data, it replaces the source MAC address with it own E1 interface’s MAC address and replaces the destination MAC address with Host C’s MAC address before sending to Host C -> C and F are correct.
Question 8
Which routing protocols can be used within the enterprise network shown in the diagram? (Choose three)
A. RIPv1
B. RIP v2
C. IGRP
D. OSPF
E. BGP
F. EIGRP
Answer: B D F
Explanation
RIPv1 & IGRP can not be used in this network because they do not support Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) -> A and C are not correct.
BGP is a complicated routing protocol between different network (usually very big) or different Autonomous System. For example BGP can be used between two Internet Service Providers (ISP). The above network is very small in an enterprise so BGP is not a suitable choice -> E is not correct.
RIPv2 supports VLSM and can be used in networks which have less than 15 routers -> B is correct.
OSPF and EIGRP can be always used in most of enterprise networks -> D F are correct.
(But notice that EIGRP is a Cisco-proprietary routing protocol so it can be used in Cisco routers only)
Question 9
Which routing protocols will support the following IP addressing scheme? (Choose three)
Network 1 – 192.168.10.0 /26
Network 2 – 192.168.10.64 /27
Network 3 – 192.168.10.96 /27
Network 4 – 192.168.10.128 /30
Network 5 – 192.168.10.132 /30
A. RIP version 1
B. RIP version 2
C. IGRP
D. EIGRP
E. OSPF
Answer: B D E
Explanation
RIPv2, OSPF and EIGRP are classless routing protocol which support VLSM.
Question 10
Refer to the graphic. A static route to the 10.5.6.0/24 network is to be configured on the HFD router. Which commands will accomplish this? (Choose two)
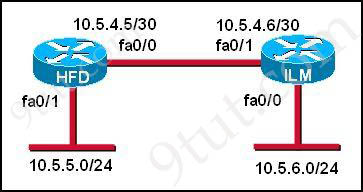
A. HFD (config) #ip route 10.5.6.0 0.0.0.255 fa0/0
B. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 0.0.0.255 10.5.4.6
C. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0
D. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 10.5.4.6
E. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.4.6 0.0.0.255 10.5.6.0
F. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.4.6 255.255.255.0 10.5.6.0
Answer: C D
Explanation
The simple syntax of static route:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network
+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network
+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router
+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
In the statement “ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0″:
+ 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0: the destination network
+fa0/0: the exit-interface



thakns 9tut very nice
very good :*
9tut thank you for all the questions. i really appreciate all your effort specially to those who are really focus in cisco certifications. more power. XD
9tut, I appreciate the exam type questions that you are posting on this website.
Thanks,
resolved
planning to take exam on tomorrow morning……any unexpected recent changes in ccna exam…can anyone help??
Q10. the answer was wrong for the exit interface,
C. HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/0
Ans:HFD(config)# ip route 10.5.6.0 255.255.255.0 fa0/1
cause this is the exit interface base on the exhibit.
@Vince: Answer C is correct. Please notice that the exit-interface is the local interface on that router so fa0/0 is correct.
It seems Q1 has wrong answer: OSPF chooses the best path via bandwidth. T1 is much higher than 10baseT or 100baseT, therefore the path should be R1, R2, R5. Answer B , not A!
@new
seems to be little confused about T1 & 10baseT speeds
T1>>> 1.544 Mbps
10baseT> 10 Mbps
100baseT>100Mbps
how can T1 higher than 10???
hope to be this useful to u :)
So useful Questions thnx 9tut :) :)
@new
@Eng-Support
There is a rule when it comes to OSPF chosen best path. OSPF uses bandwidth.
This is the rule “The slower the link the more bandwidth it consumes, and the faster the link the less bandwidth it consumes.
The idea of OSPF chosen best path base on the bandwidth is actually to conserve bandwidth or overhead. In order to so, OSPF chooses the faster or fastest link.(Link state)
And, by the way, between T1, 10baseT, and 100baseT.
T1 is the slowest link, followed by 10baseT, and then 100baseT.
My advise is read some more about OSPF and its characteristic. Thanks.
thanks 9tut!!!!!!!!
thanks a lot!
i will be taking exams come monday 12 can someone send me the latest dumb on ccna
please comment Q5 – its true?
please can some one explain me question 3 ???
@9tut
is option C correct for Q5? tested on packettracer and couldn’t get it to define any routes as default.
@bakki
you are asked for the simplest way. a static route is the simplest way
@xallax: option C of Q5 is the correct answer. For more information you can read here:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094374.shtml
“Use the ip default-network and ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 commands to set the gateway of last resort on Cisco routers that have ip routing enabled”
You should test it on GNS3, not Packet Tracer.
@9tut
so “ip default-network 0.0.0.0″ is correct?
i thought it had to be “ip default-network NETWORK_ADDRESS”
thank you for the reply :)
@ Vince
T1 is 1 mbp
Remember, the serial links are slower than ethernet links, by this, at the moment you never saw 100 mbps of internet speeds, that are being supplied by your ISP.
9tut is def building my confidence. Hopefully I’ll be ready by next month.
thanks 9tut just cleared ccna 14 dec
@ deepak singh jasrotia (sanoora) thanks for me providing a guide line
hi guys,
am new in this site and has fallen in love with. am intending to seat for ccna in a few weeks time. my problem now is that i cannot find a site to download a Qemu host for practice. i’ve tried many but to no avail. pls help and keep doing this good work.
Thx 9tut, your website is very helpful. Keep up the good work.
@bakki
just review about subnetting
/22 accomplished the condition to cover 4 networks in the 3rd octet of 172.16.X.0, where X is from 0 to 3 subnet.
@Ngoroko
there are lots of Qemu host images that you can download from gns3.net website.
there are also qemu hosts for vbox that you can use as a switch.
best paper
Hi guys. I’m just wondering,
are these two hosts on the same network? do they communicate within the LAN without a router?
PCA: 192.168.1.1/24
PCB: 192.168.1.2/25
@XYZ
Thanks for the your advice. will visit and the download asap.
when we used ospf or Eigrp if network link was failure.we can identify the link failure using keep alive meassge…but my question is when we use static route how we can identify link failure ?what should we do that?plz anyone help me……….
@ragul
Static route are manually configured and injected into routing table by network admin. Should something go wrong with the static route, the network admin would have to fix it manually.
Router#show running-config
I hope this helps.
can somebody pls explain further q3 for me ?
@usGhana
Between London and Manchester is a serial link(point-to-point)
Therefore configuring a static route(most reliable route) on London to direct all traffic destined for 172.16.0.0/22 via 10.1.1.2., which will service 172.16.1.0/24….172.16.2.0/24…..172.16.3.0/24 Manchester workstations.
I hope this helps.
@koffy
tanx alot
Q5. it should be ” ip default-network NETWORK-ADDRESS”
hi all,thanks for the information you are sharing on this site its really helpfull.I sitting for my ccna 640-802 exam next week,if anyone does have latest dumps please may you kindly assist me,you can send them to canvarlp2p@yo.co.zw
thank you
someone could explain Q3?
@dan123
Between London router and Manchester router is a serial link(point-to-point)
Therefore configuring a static route(most reliable route) on London will direct all traffic destined for 172.16.0.0/22 via 10.1.1.2., which will service 172.16.1.0/24….172.16.2.0/24…..172.16.3.0/24 Manchester workstations.
I hope this helps.
@koffy
you said “172.16.0.0/22″ why /22?
@dan123
that is the summarized network.
if you want the neighboring router to show up several subnets in one then you use summarization.
as you can see nobody is using the 172.16.0.0/24 so we can include that in a bigger summarization.
172.16.0.0 /24
172.16.0.1 /24
172.16.0.2 /24
172.16.0.3 /24
what is the range for these 4 networks? 172.16.0.0 ~ 172.16.3.255.
if you were to have a subnet with all these IP addresses what would the subnet mask be? 255.255.252.0 or /22
can anybody explain that why is the E answer??????
f IP routing is enabled, which two commands set the gateway of last resort to the default gateway? (Choose two)
A. ip default-gateway 0.0.0.0
B. ip route 172.16.2.1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
C. ip default-network 0.0.0.0
D. ip default-route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.1
answer C E
@suhail
If option C is the default network, then you going to need a route to that default network leading to remote network or ISP. This is called the “ip route” gateway of last resort to the default network. Option E.
Hope this explains it and also helpful.
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
plz send me latest dumbs nikhilnneverlasting@gmail.com
Hi everyone, can anyone help me please.. I’ll be having my exam this feb 15. Please send me the latest dump of the exam if you have. Appreciate much. here is my email add: dlanz19@yahoo.com
Q5)
what is the meaning of gateway of last resort? how come the answers are c and e? can anyone please help me out in this?
@uday
that is the default network. it’s the place where packets are sent if no other entry is matched in the routing table.
9tut wrote this 2 months ago regarding that question:
“Use the ip default-network and ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 commands to set the gateway of last resort on Cisco routers that have ip routing enabled”
@xallax
thank u for ur clear explanation xallax………………….