New CCNA – Drag and Drop 3
Here you will find answers to CCNA Drag and Drop Questions – Part 3
Question 1
Drag the security features on the left to the specific security risks they help protect against on the right. (Not all options are used)
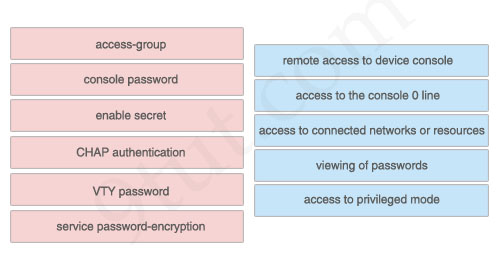
Answer:
1) VTY password: remote access to device console
2) console password: access to the console 0 line
3) access-group: access to connected networks or resources
4) service password-encryption: viewing of passwords
5) enable secret: access to privileged mode
The unselected left-box – CHAP – is used to verify the identity of the peer by means of a three-way handshake.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. PC-A is sending packets to the FTP server. Consider the packets as they leave RA interface Fa0/0 forwards RB. Drag the correct frame and packet address to their places in the table.
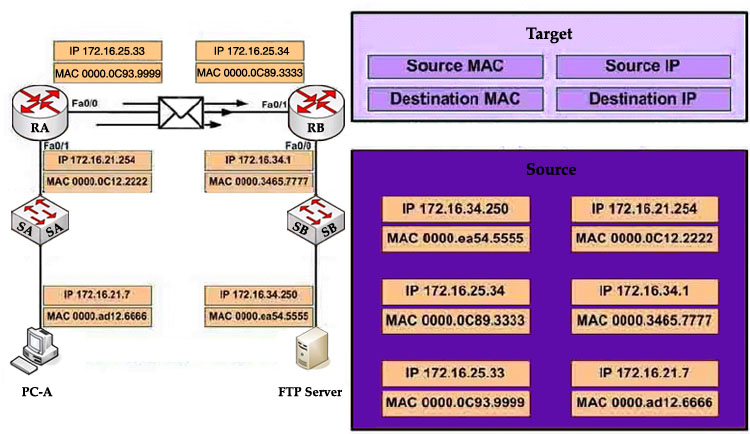
Answer:
Source MAC: 0000.0C93.9999
Destination MAC: 0000.0C89.3333
Source IP: 172.16.21.7
Destination IP: 172.16.34.250
Explanation
Remember these rules:
The IP addresses (of source and destination) of a packet never change during the transportation through the network. For example if PC-A wants to send a packet to PC-Z then the source and destination IP addresses of the packet will be the IP addresses of PC-A and PC-Z no matter how many devices they go through.
The MAC addresses, conversely, will change while passing the devices. The source MAC address is the address of the last sender and the destination MAC address is the address of the next device.
Question 3
As a network administrator, you are required to configure the network security policy. And the policy requires that only one host be permitted to attach dynamically to each switch interface. If that policy is violated, the interface should shut down. Which two commands must the network administrator configure on the 2950 Catalyst switch to meet this policy? Please choose appropriate commands and drag the items to the proper locations.
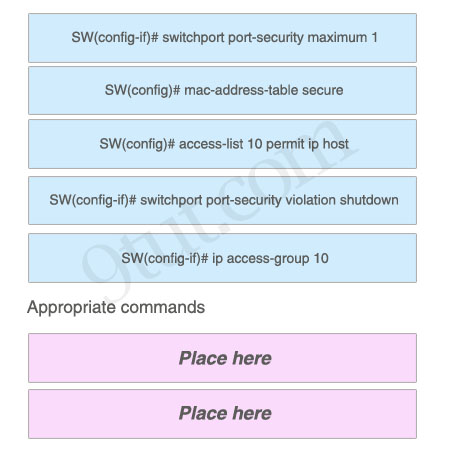
Answer:
Appropriate commands:
SW(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1
SW(config-if)# switchport port-security violation shutdown
Question 4
The left describes boot sequence, while the right describes the orders. Drag the items on the left to the proper locations.
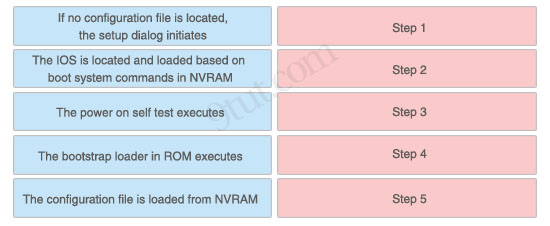
Answer:
1) Step 1: The power on self test executes.
2) Step 2: The bootstrap loader in ROM executes.
3) Step 3: The IOS is located and loaded based on boot system commands in NVRAM.
4) Step 4: The configuration file is loaded from NVRAM.
5) Step 5: If no configuration file is located, the setup dialog initiates.
Explanation
When a router boots up, it performs a series of steps, called the boot sequence, to test the hardware and load the necessary software. The boot sequence consists of the following steps:
1) Power on self test (POST): tests the hardware to verify that all components of the device are operational and present.
2) The bootstrap loader in ROM executes: The bootstrap loader is a program in ROM that is used to find where a valid Cisco IOS image is located.
3) If a valid Cisco IOS image is located, it is loaded.
4) IOS loads configuration file. Once the IOS image is loaded, it will search for a valid startup configuration in NVRAM.
5) If a valid startup configuration file cannot be found, the router will load the System Configuration Dialog (sometimes called setup mode). This mode allows you to perform the initial configuration of the router.
Question 5
Drag and Drop question. Drag the items to the proper locations.
Routing has been configured on the local router with these commands:
Local(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1
Local(config)# ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2
Local(config)# ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.3.3
Drag each destination IP address on the top to its correct next hop address at the bottom.
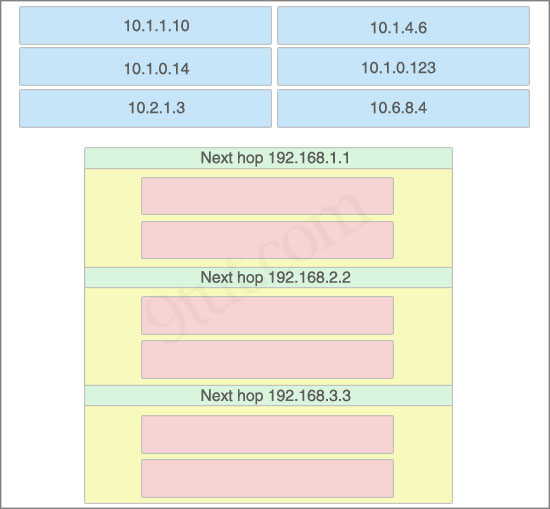
Answer:
Next hop 192.168.1.1:
+ 10.2.1.3
+ 10.6.8.4
Next hop 192.168.2.2:
+ 10.1.0.14
+ 10.1.0.123
Next hop 192.168.3.3:
+ 10.1.1.10
+ 10.1.4.6
Explanation
If we have many entries matching for next hop ip address then the router will choose the one with most specific path to send the packet. This is called the “longest match” rule, the route with the most bits in the mask set to “1″ will be chosen to route packet.
For example, the destination IP address of 10.1.0.14 will match two “ip route” commands:
ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2
ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.3.3
But the first command is more specific (10.1.0.0/24 is more specific than 10.1.0.0/16) so the packet will be routed to 192.168.2.2.
Note: The IP address 10.1.1.10 only matches the second command “ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.3.3″. It does not match the command “ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2″ because the third octet is different (10.1.1.10 is different from 10.1.0.0/24).
Question 6
If a Cisco router has learned about network 10.1.1.0 from multiple sources, the router will select and install only one entry into the routing table. Indicate the order of preference that the router will use by dragging the routes on the left to the order of preference category on the right.
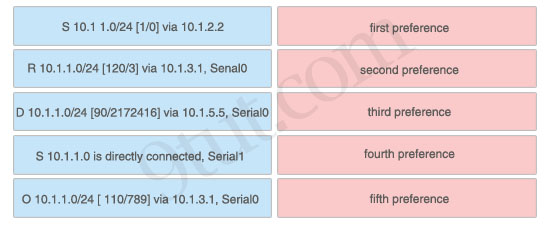
Answer:
1) First preference: S 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial1
2) Second preference: S 10.1 1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.2.2
3) Third preference: D 10.1.1.0/24 [90/2172416] via 10.1.5.5, Serial0
4) Fourth preference: O 10.1.1.0/24 [ 110/789] via 10.1.3.1, Serial0
5) Fifth preference: R 10.1.1.0/24 [120/3] via 10.1.3.1, Senal0
Explanation
Administrative distance is the first criterion that a router uses to determine which routing protocol to use if two protocols provide route information for the same destination. It is a measure of the trustworthiness of the source of the routing information. The smaller the administrative distance value, the more reliable the protocol.
In this question, notice that the destination of all routes is 10.1.1.0/24 so we need to use Administrative distance of each routing protocol to specify the priority of each route. Below lists the Administrative Distance default values of popular routing protocols:
+ Directly connected: 0
+ Static route: 1
+ EIGRP (symbolize by “D”): 90
+ OSPF (symbolize by “O”): 110
+ RIP (symbolize by “R”): 120



i can’t understand Q5 ..any one can help?
@ A.Zidan
Local(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1
Local(config)# ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2
Local(config)# ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.3.3
Just see above lines
ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2
means i care about 10.1.0.X (so all ip having 10.1.0.x are sent to 192.168.2.2)
ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.3.3 means i care about 10.1.X.X (all IP having 10.1.X.X are sent t0 192.168.3.3)
GOT IT THANK YOU @SAVMORE :)
Thanks @savmore
Thanks @savmore!!
got q3 on 2/20 passed
would anyone pls send me the latest dumps : s.mahdiamiri@outlook.com
i’ll take the exam next month
Q2, Q5
Hi Guys do u have any latest dumps…..
9tut is enough to pass the ccna exam.
Hi, please i dont understand Q5. can you explain more. thank for you savmore, but i dont understand
Hello Caudrick:
Routing table shows 2 subnets and 1 default route
1st subnet is 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 = 10.1.0.0/24
It means, you are taking care about 24 bits/3 octets of the IP address: 10.1.0
In other words, every packet which begins with 10.1.0.X will be forwarded to 192.168.2.2.
If you have a closer look, there are 2 packets matching:
+ 10.1.0.14
+ 10.1.0.123
2nd subnet is 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 = 10.1.0.0/16
It means, you are taking care only about 16 bits/2 octets of the IP address: 10.1. You dont take care, what is further.
In other words, every packet which begins with 10.1.X.X (and not matching first subnet) will be forwarded to 192.168.3.3.
+ 10.1.1.10
+ 10.1.4.6
YOU CAN’T PUT HERE THESE IP 10.1.0.14 / 10.1.0.123 BECAUSE THEY MATCH THE FIRST NETWORK (BASED ON LONGEST MATCH RULE)
Last one is “default route” used for packets not matching any of networks above. Put the remaining ones:
+ 10.2.1.3
+ 10.6.8.4
I hope, all is clear now. If not, take pen, paper, write those network binnary and follow the longest match rule.
Without simulation is it possible to pass for exam
each sim carry 100 marks….so its impossible to clear without sim
Q2 & Q5 today
Thank you savmore..it was helpful
Hi Tomas. Your explanation was great! :D