New CCNA – RSTP
Note: If you are not sure about Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, please read our Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol RSTP Tutorial.
Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (Choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconvening time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expands the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
E. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
F. RSTP uses the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
Answer: A B D
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit:
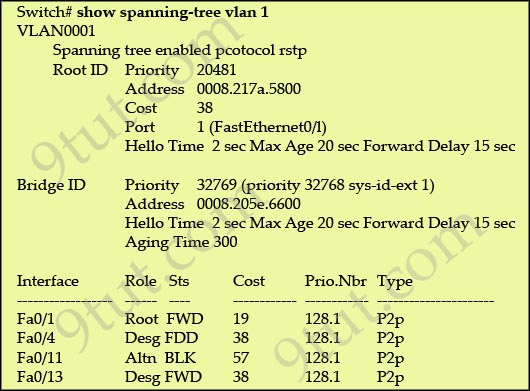
Why has this switch not been elected the root bridge for VLAN1?
A. It has more than one internee that is connected to the root network segment.
B. It is running RSTP while the elected root bridge is running 802.1d spanning tree.
C. It has a higher MAC address than the elected root bridge.
D. It has a higher bridge ID than the elected root bridge.
Answer: D
Explanation
As we can see from the output above, the priority of the root bridge is 20481 while that of the local bridge is 32769.
Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
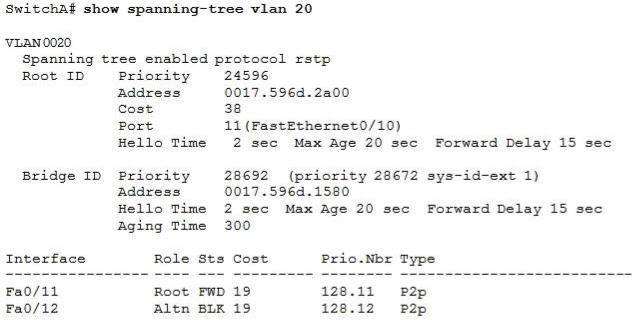
A. The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20.
B. VLAN 20 is running the Per VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol.
C. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.1580.
D. SwitchA is not the root bridge, because not all of the interface roles are designated.
Answer: D
Explanation
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge -> A is not correct.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST -> B is not correct.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00 -> C is not correct.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge -> D is correct.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. The output that is shown is generated at a switch. Which three of these statements are true? (Choose three)
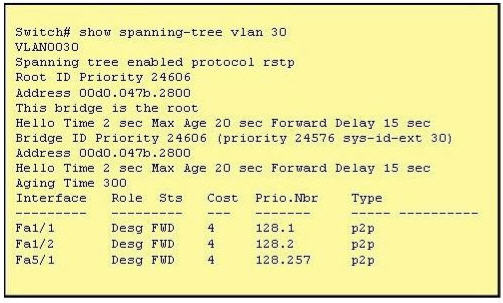
A. All ports will be in a state of discarding, learning or forwarding.
B. Thirty VLANs have been configured on this switch.
C. The bridge priority is lower than the default value for spanning tree.
D. All interfaces that are shown are on shared media.
E. All designated ports are in a forwarding state.
F. The switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs on this switch.
Answer: A C E
Explanation
From the output, we see that all ports are in Designated role (forwarding state) -> A and E are correct.
The command “show spanning-tree vlan 30″ only shows us information about VLAN 30. We don’t know how many VLAN exists in this switch -> B is not correct.
The bridge priority of this switch is 24606 which is lower than the default value bridge priority 32768 -> C is correct.
All three interfaces on this switch have the connection type “p2p”, which means Point-to-point environment – not a shared media -> D is not correct.
The only thing we can specify is this switch is the root bridge for VLAN 3o but we can not guarantee it is also the root bridge for other VLANs -> F is not correct.
Question 6
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 7
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
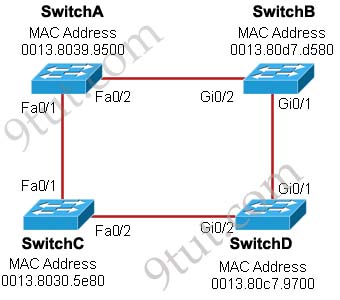
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again
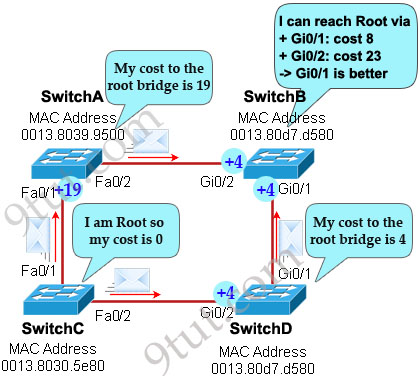
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
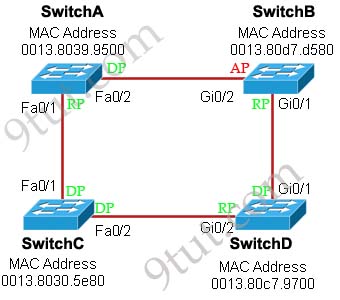
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. At the end of an RSTP election process, which access layer switch port will assume the discarding role?
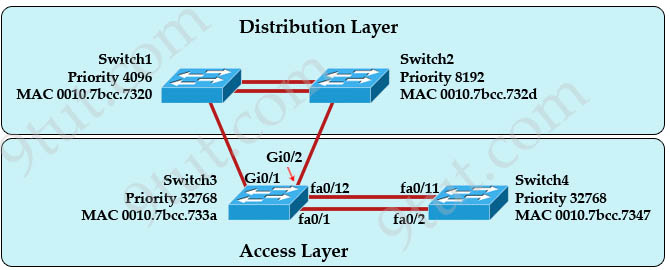
A. Switch3, port fa0/1
B. Switch3, port fa0/12
C. Switch4, port fa0/11
D. Switch4, port fa0/2
E. Switch3, port Gi0/1
Answer: C
Explanation
In this question, we only care about the Access Layer switches (Switch3 & 4). Switch 3 has a lower bridge ID than Switch 4 (because the MAC of Switch3 is smaller than that of Switch4) so both ports of Switch3 will be in forwarding state. The alternative port will surely belong to Switch4.
Switch4 will need to block one of its ports to avoid a bridging loop between the two switches. But how does Switch4 select its blocked port? Well, the answer is based on the BPDUs it receives from Switch3. A BPDU is superior than another if it has:
1. A lower Root Bridge ID
2. A lower path cost to the Root
3. A lower Sending Bridge ID
4. A lower Sending Port ID
These four parameters are examined in order. In this specific case, all the BPDUs sent by Sswitch3 have the same Root Bridge ID, the same path cost to the Root and the same Sending Bridge ID. The only parameter left to select the best one is the Sending Port ID (Port ID = port priority + port index). In this case the port priorities are equal because they use the default value, so Switch4 will compare port index values, which are unique to each port on the switch, and because Fa0/12 is inferior to Fa0/1, Switch4 will select the port connected with Fa0/1 (of Switch3) as its root port and block the other port -> Port fa0/11 of Switch4 will be blocked (discarding role).
If you are still not sure about this question, please read my RSTP tutorial.



Question 4 – why is answer A not correct too – one can conclude from the fact that fa0/11 has the root port role (and the RSTP protocol is used) that SwitchA is not he root bridge for VLAN 20
In the question it says : ” The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20″
so a root bridge can never have a root port
q1,and q2 was on today mine exam paper got 100%
q1,4,6,9 yesterday. passed! tnx 9tut!
Question 6. Answer should be C, D
Passed yesterday with score 1000 Thank God
The exam was 51 questions, only one drag and drop about cable types, all questions are very easy just similar to 9tut.
The lab simulations were Eigrp , ACL1 (similar to 9tut exactly) and ACL2 (modification 3 but with host B to access the finance server)
Good luck for everyone, just be relaxed its very very easy :)
questions 2,3 were in it
Please help ! Anyone knows dumps and questios for SPNGN 640-878 please write me to my mail digital_score@yahoo.com Thanks in advance
My exam today was 99% of what I learned from 9tut
Passed my CCNA exam today (18th Mar)… Q1 in exam
Q 8 answer is not acceptable.. as to why we need to cost calculate. It clearly shows the highest MAC address is Switch B hence the Alternative Port is G0/2 of Switch B. Also cost calculation exaple MAC address of SW D is wrong. Please correct me if i am wrong. Please also note that I do understand cost calulation happens only when MAC and Priority are same.
Ants.
Have my exam today, let’s pray !
Q2,5
Wrote my exam and got a score of 903/1000
In question 5, why option A is not correct/why is it correct or true? could that be because all ports on switch have to be in either of 3 states. ie. either discarding learning or forwarding. It seems the make wordings of this option lil tricky deliberately.
q8 bullshit expl. how FEGE = GE?
Please help! Is there an error in explanation Q9 ?
“and because Fa0/12 is inferior to Fa0/1″, maybe must says
“and because Fa0/12 is superior to Fa0/1″ ?
Thks.
I agree with you KKP , Q5 option A is not make sense Because of (discarding state)
What are the steps to decide who will be designated n who will be non designated….?
hey
regarding Q8, for DP we first see the path cost and then the mac address right ?
so between sw A and sw B shouldnt swb g0/2 be dp as it has lower path cost ??
PLEASE HELP
how to find the mac address
Passed the exam on 13 april with 1000 marks…….this is the best site
Q8:
I think that cost from root bridge C to switch D equal 19 not 4 as you mentioned, as port F0/2 connected to switch D is a Fastethernet port not Gigaethernet port … or what do you think ??
note : that will not change a thing in the answer as the link between switch D and switch B is actually Gigaethernet but between switch B and A is Fastethernet Link so answer still the same ???!!!
Mr Muhammad, you are totally right , because The root Bridge (Switch C) is connected with with its FastEthernet 0/2 to The interface gigabitethernet 0/2 of (switch D) ,so they will auto negotiate for the speed of the link to be 100Mbps so they can get along with each others,meaning the cost of 19.
Dear instructor
about the Question 9 you explained that –(In this question, we only care about the Access Layer switches (Switch3 & 4). Switch 3 has a lower bridge ID than Switch 4 (because the MAC of Switch3 is smaller than that of Switch4) so both ports of Switch3 will be in forwarding state).– ,it actually don’t matter Because we don’t Verify this parameter first , in fact it is ,the lower path cost to the Root, Imagine that Switch 4 will always need Switch 3 to get to the Root Bridge anyway, meaning Let’s Assume you are right ,and it is just happened that The bridge ID of Switch 4 is lower than Switch 3,that means both ports of Switch4 will be in forwarding state,and one port of Switch 3 Will be blocked,that means if we decided to put a hub in between this link,and connect a computer to this hub,And this computer want to get to some device connected to Switch 1,the Computer frame will be forwarded to Switch 4 and Then Switch port send it back To switch 3,So whats is the point.
A lot of people confuse between electing the root bridge procedure and choosing the best path to get to it.
So the answer i think will be
A lower path cost to the Root
. A lower Sending Bridge ID
A Lower Sending port priority
A lower Sending port number.
Q5,7,9
**Q9**
Im really confused about this one… If SWITCH C is the Root Bridge, wouldn’t the ports on Switch C be Designated Ports? If so, How can answer E be correct?
SORRY… I MEANT *****Q8******* ^^^^^^^^
Classic, it is F not E!
Can anyone please help me with the last version of the VCE Simulator? I can´t open many VCE files with the version that I have. Please my e-mail is cliche0025@gmail.com. Thanks.
Instructor – please adjust your explanation for Question 8. You arrived at the correct answer but with a faulty explanation.
The only true “Gigabit” link is between SwitchB and SwitchD. All the rest are “FastEthernet” links, because the ports coming off of SwitchA and SwitchC are all FastEthernet.
Therefore, in your illustration, SwitchD will actually advertise it’s root cost as 19 (not 4, as you specify).
SwitchB will compare those two advertisements (they are equal), and then add another 19 to the cost from SwitchA (since that is a FastEthernet link), while adding another 4 to the cost from SwitchD (since that is a true Gigabit link) – giving it a choice of either using Gi0/2 as it’s root port (with a cost of 38) or Gi0/1 as it’s root port (with a cost of 23).
Then, as you said, SwitchB will choose Gi0/1 as it’s root. (but with a cost of 23, not 8 as you specified)
Finally, SwitchA will set it’s port Fa0/2 to Designated/Forwarding (since it has the lower root cost) and SwitchB will set it’s port Gi0/2 to Alt/Discarding on that same link.
I hope this helps to clarify things for those who were asking.
Hi Guys, please send me the latest dumps via my email polarbeer2000@hotmail.com. I really appreciate any other study material you will recommend. Tkx
Hello Guys,
Please share the latest dumps if you have on zameer.ise@gmail.com. I’m planning to take up test next week.
Thank You
Hello, Please help for Q5
I do not agree with the explanation for why answer F is incorrect. In RSTP, all VLANs in the network share the SAME root bridge.
Further, answer choice A seems incorrect to me – it implies that the final state of the ports on the switch will be either discarding, learning or forwarding. However, in a root bridge the final state of all ports is FORWARDING.
How can one justify that A is correct and F is not. I am worried I will have to remember to give an incorrect answer to this question if it appears on the actual exam.
Please help in correcting my logic if I am wrong. Also, if anyone who says they had this quesiton on the exam, how similar was it? Were the output and answer choices exactly the same? Please let me know
Thank you!!
Q8
For those who are confused with this question, you can follow this order
1.Determine the Root Bridge by using smallest bridge ID
2.Determine the root ports by using the path cost
– You can use Bridge ID if you have a tie
3.Determine the designated ports by using the smallest bridge id…
This is from Todd Lamle tho this explanation contradict from that of Jeremy of CBT nugget…
Q9:
Most of the explanation is wrong.
Ports are blocked when a redundant path is detected. Bridge IDs only come into play when it’s not immediately obvious which side should do the blocking (ie. they both have an equal-cost path to root)
In this case S4 isn’t advertising a competing path to S3 (since it has none) thus S3 won’t do any blocking. The IDs are completely irrelevant.
S4 however receives BPDUs from S3 on two ports advertising equal cost paths to root so it knows it needs to block one and it uses port prio/port id to determine which.