CCNA – Operations 3
Here you will find answers to Operations Questions – Part 3
Question 1:
Your company wants to reconfigure a Catalyst 2950. which actions must be taken to erase the old configuration? (Choose three)
A – Erase flash
B – Restart the switch
C – Delete the VLAN database
D – Erase the startup configuration
Answer: B C D
Question 2:
If the subnet mask is 255.255.255.224, which of the following addresses can be assigned to network hosts? (Choose three)
A – 15.234.118.63
B – 92.11.178.93
C – 134.178.18.56
D – 192.168.16.87
Answer: B C D
Explanation:
The addresses can be assigned to network hosts are the addresses that satisfy these conditions:
+ They don’t belong to network addresses
+ They don’t belong to broadcast addresses
The last octet of the subnet mask is 224, which is 1110 0000 in binary form, so the increment is 32. This is the value we need to find out the network addresses and broadcast addresses when using the 255.255.255.224 subnet mask.
Network addresses: x.x.x.0, x.x.x.32,x.x.x.64,x.x.x.96,x.x.x.128,x.x.x.160,x.x.x.192,x.x.x.224
Broadcast addresses: x.x.x.31, x.x.x.63, x.x.x.95, x.x.x.127, x.x.x.159, x.x.x.191, x.x.x.223
(Notice we don’t care about the first three octets because the first three octets of the subnet mask are all 255)
From that we learn 15.234.118.63 is one of the broadcast addresses. Other answers are correct because they are neither network addresses nor broadcast addresses.
Question 3:
An administrator issues the command “ping 127.0.0.1″ from the command line prompt on a PC host named PC1. If an ICMP reply is received, what does this confirm?
A – The PC host PC1 has connectivity with a local host
B – The PC host PC1 has connectivity with a Layer 3 device
C – The PC host PC1 has a default gateway correctly configured
D – The PC host PC1 has connectivity up to Layer 5 of the OSI model
E – The PC host PC1 has the TCP/IP protocol stack correctly installed
Answer: E
Explanation:
If you are having problems with your network then issue the command “ping 127.0.0.1″ to prove the network card and the TCP/IP software is working correctly. Address 127.0.0.1 is reserved for the test loop back purpose.
Question 4:
Study the exhibit carefully, can you tell which three description are correct about the ways used by the router R1 to choose a path to the 10.1.3.0/24 network when different routing protocols are deployed? (Choose three)
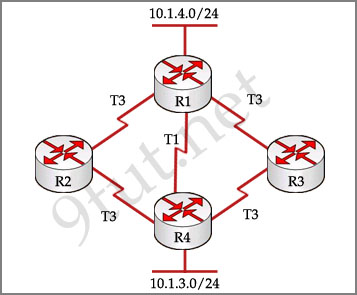
A – When RIPv2 is the routing protocol, only the path R1-R4 is to be installed into the routing table by default
B – When RIPv2 is the routing protocol, the equal cost paths R1-R3-R4 and R1-R2-R4 are to be installed in the routing table
C – If both EIGRP and OSPF are working on the network with their default configurations, the EIGRP paths will be installed in the routing table
D – By default, if EIGRP is the routing protocol, the equal cost paths R1-R3-R4 and R1-R2-R4 will be installed in the routing table
Answer: A C D
Explanation:
RIP is a distance vector routing protocol and it uses hop count as the metric for path selection so only the path R1-R4 (with only 2 hops) will be installed into the routing table.
If both EIGRP and OSPF are used, the EIGRP paths will be installed in the routing table because the default administrative distance of EIGRP is 90 while that of OSPF is 110. Therefore these routers will choose EIGRP because it has lower administrative distance value (Notice that a lower value for the administrative distance indicates the more reliable route).
Question 5:
Which two statements describe characteristics of IPv6 unicast addressing? (Choose two)
A. Global addresses start with 2000::/3
B. Link-local addresses start with FE00:/12
C. Link-local addresses start with FF00::/10
D. There is only one loopback address and it is ::1
E. If a global address is assigned to an interface, then that is the only allowable address for the interface.
Answer: A D
Explanation:
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses:
| Loopback address | ::1 |
| Link-local address | FE80::/10 |
| Site-local address | FEC0::/10 |
| Global address | 2000::/3 |
| Multicast address | FF00::/8 |
From the above table, we learn that A and D are correct while B and C are incorrect. Notice that the IPv6 unicast loopback address is equivalent to the IPv4 loopback address, 127.0.0.1. The IPv6 loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, or ::1.
E is not correct because of anycast addresses which are indistinguishable from normal unicast addresses. You can think of anycast addresses like this: “send it to nearest one which have this address”. An anycast address can be assigned to many interfaces and the first interface receives the packet destined for this anycast address will proceed the packet. A benefit of anycast addressing is the capability to share load to multiple hosts. An example of this benefit is if you are a Television provider with multiple servers and you want your users to use the nearest server to them then you can use anycast addressing for your servers. When the user initiates a connection to the anycast address, the packet will be routed to the nearest server (the user does not have to specify which server they want to use).



regarding Q4 why the answer include option D
i think for option D the tow route will be in the topology table as feasible successor and in addition how do i know that cost of R1-R3-R4 is same as R1-R2-R4 in Eigrp what if the bandwidth and the capacity of link is different in R3 than R2
i think answer should be A B C
also the RIPV2 will see the cost of path as equal to each other because the cost path for both will be 3 hop same cost
answer B – wrong. rip route will be only R1-R4, because metric is hop count.
Your comment under Q3 “If you are having problems with your network then issue the command “ping 127.0.0.1″ to prove the network card and the TCP/IP software is working correctly” is not 100% correct.
It does prove that the TCP/IP stack is installed and working – but you can remove all NICs and still get a reply with ping from 127.0.0.1 – so pinging 127.0.0.1 cannot prove that the NIC is working correctly (I have just checked this on an old PC to prove the point).
Hi all!
which option is valid Ip address
( inValid means either incorrect format or but format is ok but using some other puposes: i.e loopback, site-local,global-address,multicast address,..
honestly I do not know the mean but by common sense I think both should be cosidered as invalid, am I correct?)
A.2001:0000:130F::099a::12a
I believe both uppercase /lower case are existed- I mean characters)
B.2002:7654:A1AD:61:81AF:CCC!
C.FEC0:ABCD:WXYZ:0067::2A4
D.2004:1:25A4:886F::1
E .(not in dump) ABCD::DEFG:3400:9ASD:EFG
Ans: D
why not ? B and C
what you think about E?
Please answer it.
Thanks
Hi Jhon,
Hexadecimal number ends with F
10 = A, 11 = B, 12 = C, 13 = D, 14 = E, 15 = F
So the options u have given :-
A. Here “a” is there – Invalid
B. ! in last block i.e. CCC! – Invalid
C. WXYZ in 3rd block – Invalid
E. DEFG in 2nd block – Invalid
Hope I u understood the explanation.
Hi all,
Would you please help me with this question?
A national retail chain needs to design an IP addressing scheme to support a nation wide network.
The company needs a minimum of 300 sub-networks and a maximum of 50 host address per subnet working with one class B address. Which of the following subnet masks will support an appropriate addressing scheme: (Choose two answers)
A-255.255.255.0
B-255.255.255.128
C-255.255.252.0
D-255.255.255.224
E-255.255.255.192
F-255.255.248.0
I chose D, E because D will give us 30 host per subnet , E will give us 62 host per subnet, and the maximum required hosts per subnet is 50.
but the answer is B,E.
Please tell me the correct answer.
Thanks a lot.
@ Mohamed
Address is of class B, so default mask is:
255.255.0.0 or /16. This is fixed. We can not go back (I mean lower than 16: 15, 14… etc) in the network bits.
Default mask:
255.255.0.0
11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000
Solving for Subnets
——————-
Subnets required: 300
So network bits we need to borrow from host portion = n = ?
300 can be achieved using what power of 2?
Answer: 9
So 2^n = 2^9 = 512
So we need to borrow 9 more bits from host portion (Zeroes) and include them in network part (Ones)
New subnet mask:
11111111.11111111.11111111.10000000
which is 255.255.255.128 (Option B)
Solving for Hosts
—————–
Hosts required: 50
So how many bits do we need to reserver for hosts = h = ?
50 can be achieved using what power of 2?
Answer: 6
Total IP address = (2^h) = (2^6) = 64
Nodes assignable addresses = (2^h)-2 = 62 (Subtracted 2 for network and broadcast ID)
Now write new subnet mask with only 6 bits for hosts and assign rest to the network:
11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000
i.e., 255.255.255.192 (Option E)
Option D is incorrect because if maximum required hosts are 50, there is no harm in having some extra hosts available to you i.e., 62 but solving for 30 hosts DOES NOT FULFILL the requirement. You MUST always solve for networks and hosts demanded in the question. You can always have more but you can never ever provide less than what was required. Hope that explains.
Cheers
@UthmanHassan
Thank you very much & have a nice day
i got my exam yesterday and passed with 974. especial thanks for the 9tut. pass4sure & testinside dumps are still valid. sims are eigrp,vtp & access-list only the ip addresses are changed. in access-list the the pc also changed. again thanks for the 9tut and all of the contributors
if any one need help from me pls email to
hasy_001@yahoo.com
about IPv6 :
address A.2001:0000:130F::099a::12a is invalid because it has two :: notations.
Hi 9tut,
I am new to 9tut and want to participate in its forum,
I have to understand one question, but i couldnt find where i can post my question.
please guide me
There is an easy way of finding out the answer for Q.2
If the subnet mask is 255.255.255.224, which of the following addresses can be assigned to network hosts? (Choose three)
A – 15.234.118.63
B – 92.11.178.93
C – 134.178.18.56
D – 192.168.16.87
1st we should subtract 224 from 256….then we get 32..so the increament is 32.
32+32=64…….therefore….1st network address is 32..1st address is 31 and the broadcast address is 63(64-1)..the assignable host address are therefore..31 to 62… for the 1st network that is 32..
32+32=64
64+32=96
32 (network address) 64 (network address)
31 (1st assignable address) 65 (1st assignable address)
62 (last assignable address) 94 (last assignable address)
63 (broadcast address) 95 (broadcast address)
therefore the answers are within these ranges of the two networks…
ip address 92.11.178.93 is in the 92.11.178.64 network….
ip address 134.178.18.56 is in the 134.178.18.32 network
ip address 192.168.16.87 is in the 192.168.16.32 network
Answer: B C D
correction to my post…
ip address 192.168.16.87 is in the 192.168.16.64 network
@ hasy
plz give me dumps and tell me how i prepare for exam,on Feb 1stweek.so plz help me
dkd_nvs@yahoo.co.in
Mr. Hassan,
If you are borrowing 6 bits, why is your mask reflecting that you are borrowing 10 bits?
You’re default mask is 255.255.0.0 and you are showing 255.255.255.192 as your answer
?
I know you explained this in great detail but this half does not make sense to me.
Could someone please break this down for me or explain in another way?
Hosts required: 50
So how many bits do we need to reserver for hosts = h = ?
50 can be achieved using what power of 2?
Answer: 6
Total IP address = (2^h) = (2^6) = 64
Nodes assignable addresses = (2^h)-2 = 62 (Subtracted 2 for network and broadcast ID)
Now write new subnet mask with only 6 bits for hosts and assign rest to the network:
11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000
i.e., 255.255.255.192 (Option E)
Option D is incorrect because if maximum required hosts are 50, there is no harm in having some extra hosts available to you i.e., 62 but solving for 30 hosts DOES NOT FULFILL the requirement. You MUST always solve for networks and hosts demanded in the question. You can always have more but you can never ever provide less than what was required. Hope that explains
is it enough to study these question or we have to get some other dumps
Q. 5 explanation site local is FEF0::/10 or FEC0::/10 ??
Hi 9tut
I think in Q4 answer is just A and C. default bandwidth for all serial links is 1544. and with the default values the R1-R4 will be installed on routing table, but when the B.W configured correctly, then R1-R2-R4 and R1-R3-R4 will be installed on routing table. Am I right?
Hi 9tut… About Q5 – the given answers are correct,
But in the explanation part,
I think the most recent RFC revision says that site-local addresses start with FC00::/7 (FD00::/8 to be used while FC00::/8 to be used by “authorities”) and not FEC0::/10 anymore.
FYI
:)
quoting wikipedia
“In 1995, RFC 1884 reserved the block fec0::/10 for site-local addresses, that could be used within a “site” for private IPv6 networks. However, insufficient definition of the term site lead to confusion over the resulting routing rules. RFC 3879 (September 2004) deprecated this address range, and postulated solutions to its problems. In October 2005, RFC 4193 was published, reserving the address block fc00::/7 for use in private IPv6 networks, and defining the associated term unique local addresses. ”
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unique_local_address
hi
can sm1 send me the latest dump on phathu6@webmail.co.za.
am planning 2 take my exam in 2 weeks tym.
tanks
Just dropping in to thank the Lord, 9tut.com and ankitc (on the forums) for helping me through my exams today! I passed with a score of 894/1000. Got VTP, EIGRP and ACL2 sims.
This site is amazing and very worthwhile to go through these sims, questions and answers.
plz plz someone send me latest dumps of ccna640-802 as iwill take the exam the nxt week
@ doda_zeta@yahoo.com
look for the site http://pass for sure
@Odoyl
Odoyl wrote on January 28th, 2011
Mr. Hassan,
If you are borrowing 6 bits, why is your mask reflecting that you are borrowing 10 bits?
You’re default mask is 255.255.0.0 and you are showing 255.255.255.192 as your answer.
—————
Sorry. I was away for too long. Odoyl I sincerely hope that you would have figured it out by now and have become certified as well but for newcomers that could get stuck at same place, I’ll explain it anyways.
While solving for 50 hosts, I’m NOT BORROWING 6 BITS, I’m RESERVING 6 BITS FOR HOSTS.
Cheers
Im gonna take the CCNA exam on 9 July 11. Can any kind soul send the latest dump to my email add: aken31@hotmail.com. thanks alot. Greatly appreciated!
can someone please email the latest dump to me at pakhtarao@yahoo.ca
thanks in advance
this site rocks!
can someone please email the latest dump to me at nikos_g_s@hotmail.com..thanks!!!!
HI, 9tut thanks a lot
Hi 9Tut and a big thanks this site is better than pass4sure that rarely explains answers.
Can anyone help I have seen a questionon p4sure about dada transfer being slow betwean source and destination the QOS requested by the tarnsport layer is not being mantained at which layer should the trouble shooting begin? I thought transport, as this is where windowing etc is but they have the answer down as network, now I just thought network was responsible for logical addressing can anyone explain the answer?
TIA
Where can i download the latest dump? Taking the exam in coming weeks.
gio_perez1980@yahoo.com
iam going to exam next week . can some email the latest dump to me at ‘ crosbymorris @yahoo.co.uk
Inregards to Q3. issuing the command “ping 127.0.0.1″ and getting a ICMP reply back means your network is functional in terms of connectivity. This is local I suppose.
In one other question under Troubleshooting 1. Q9. A ping (127.0.0.1) to the local host IP address was successful, but a ping to the gateway and a remote server was unsuccessful. The answer to this problem is “A local physical layer problem exists.
Does this two scenarios complement each other or contradict each other. I hope I’m making some sense in this comparison. Anyway share some light on this? Thanks.
@koffy
the class A IP range of 127.0.0.0~127.255.255.255 (127.0.0.1 included) is reserved for loopback
what does this mean?
the command *ping 127.0.0.1* tests if the device has the TCP/IP stack installed correctly. that’s it. only local importance.
regarding your second question:
*ping 127.0.0.1* works <- device has TCP/IP stack installed
*ping 10.0.0.35* works <- same as pinging 127.0.0.1 because this is the IP of the computer on the network
*ping 10.0.0.1* fails <- the problem is on the LAN
*ping 10.5.75.250* fails <- the LAN problem is preventing packets to go to/get back from the remote address
options:
A. A remote physical layer problem exists. <- ruled out because the default gateway is unreachable
B. The host NIC is not functioning. <- it is working as it is able to perform a loopback test
C. TCP/IP has not been correctly installed on the host. <- false, the successful loopback test means the TCP/IP stack is installed correctly.
D. A local physical layer problem exists. <- only option left standing.
Thanks xallax.
Yes there should realize the reader to RSS my feed to RSS commentary, quite simply
regarding to Q#4::
Study the exhibit carefully, can you tell which three description are correct about the ways used by the router R1 to choose a path to the 10.1.3.0/24 network when different routing protocols are deployed? (Choose three)
A – When RIPv2 is the routing protocol, only the path R1-R4 is to be installed into the routing table by default
B – When RIPv2 is the routing protocol, the equal cost paths R1-R3-R4 and R1-R2-R4 are to be installed in the routing table
C – If both EIGRP and OSPF are working on the network with their default configurations, the EIGRP paths will be installed in the routing table
D – By default, if EIGRP is the routing protocol, the equal cost paths R1-R3-R4 and R1-R2-R4 will be installed in the routing table
Why and how B and D are correct answers???
@cisco craze:
B – is incorrect answer. RIPv2 use hop count when choosing a route: the less hop count the better a route. Route R1-R4 has hop count = 1, routes R1-R2-R4 and R1-R3-R4 have hop count = 2.
D – correct answer. EIGRP is using bandwidth and delay as a metric when choosing a route. T3 links have better bandwidth then T1 (T3 ~ 45 Mbs, T1 ~ 1.544 Mbs). And EIGRP can use up to 4 equal cost path by default.
Can some body send me latest dump of ccna
chaudaryimran@hotmail.com
For Explanation on the Q5,the Site local address name and and the ipv6 address was deprecated,and has now been replaced by Unique local Address with address FC00::/8
Friends…can some one send me the latest & Valid dumps for CCNA @kiganto@yahoo.com
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
Q4
A – in the route table on R1 hop will be 1 (i think)
Q.2
If the Subnet mask is 255.255.255.224, which of the following addresses can be assigned to network hosts? (Choose three)
A – 15.234.118.63
B – 92.11.178.93
C – 134.178.18.56
D – 192.168.16.87
1st we should subtract 224 from 256….then we get 32..so the increament is 32.
32+32=64-1 to get the broadcast address.Hence the 1st network address is 32..1st address is 31 and the broadcast address is 63(64-1)..the assignable host address are therefore..31 to 62… for the 1st network that is 32..
32+32=64
64+32=96
32 (network address) 64 (network address)
31 (1st assignable address) 65 (1st assignable address)
62 (last assignable address) 94 (last assignable address)
63 (broadcast address) 95 (broadcast address)
therefore the answers are within these ranges of the two networks…
i p address 92.11.178.93 is in the 92.11.178.64 network….
i p address 134.178.18.56 is in the 134.178.18.32 network
i p address 192.168.16.87 is in the 192.168.16.32 network
Meaning B, C and D are correct.l
Thanks to all.
olesimbe@yahoo.com
Hi All,
I am taking the exam on April 8, 2012. Can someone send me the latest dumps to my email rshiva62@gmail.com.
Hi all
May exam is on April as well. If you please do me favour and guide me for best and working dum on exam collection.
Will appreciate if u plz send me on my mail zaaaam7@gmail.com
Please can anyone who really understand Q2 explain it to me correctly because i see answer C and is where I am getting confuse .e mail info to ramabolu@hotmail.com
thanks
@tazze
subnet mask is 255.255.255.224
possible subnets:
.0 ~ .31
.32 ~ .63
.64 ~ .95
.96 ~ .127
increases by 32 as you can see
A – 15.234.118.63
broadcast address, not suitable for a host
B – 92.11.178.93
usable IP address on the .64 ~ .95 subnet
C – 134.178.18.56
usable IP address on the .32 ~ .63 subnet
D – 192.168.16.87
usable IP address on the .64 ~ .95 subnet
thanks 9tut!=D