CCNA – OSPF Questions 2
Here you will find answers to OSPF Questions – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true about the loopback address that is configured on RouterB? (Choose two)
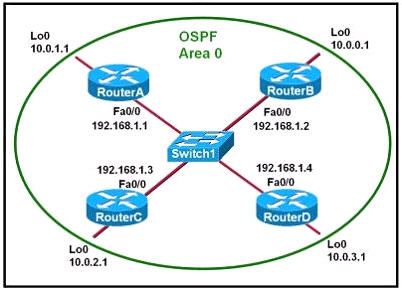
A. It ensures that data will be forwarded by RouterB.
B. It provides stability for the OSPF process on RouterB.
C. It specifies that the router ID for RouterB should be 10.0.0.1.
D. It decreases the metric for routes that are advertised from RouterB.
E. It indicates that RouterB should be elected the DR for the LAN.
Answer: B C
Explanation
A loopback interface never comes down even if the link is broken so it provides stability for the OSPF process (for example we use that loopback interface as the router-id) -> B is correct.
The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
-> The loopback interface will be chosen as the router ID of RouterB -> C is correct.
Question 2
Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A C D
Explanation
Each of routers running link-state routing protocol learns paths to all the destinations in its “area” so we can say A is correct although it is a bit unclear.
Link-state routing protocols generate routing updates only (not the whole routing table) when a change occurs in the network topology so B is not correct.
Link-state routing protocol like OSPF uses Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest path -> C is correct.
Unlike Distance vector routing protocol (which utilizes frequent periodic updates), link-state routing protocol utilizes event-triggered updates (only sends update when a change occurs) -> D is correct but E is not correct.
Question 3
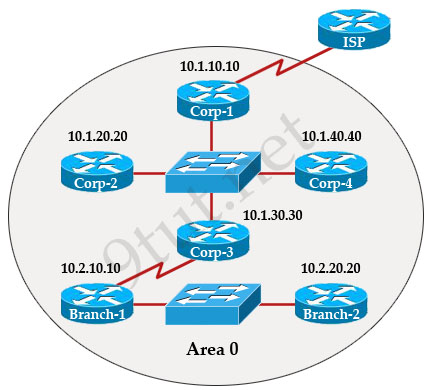
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance.
As part of examining the router resources the OSPF DRs need to be known.
All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router.
Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two)
A. Corp-1
B. Corp-2
C. Corp-3
D. Corp4
E. Branch-1
F. Branch-2
Answer: D F
Explanation
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40) & Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
Question 4
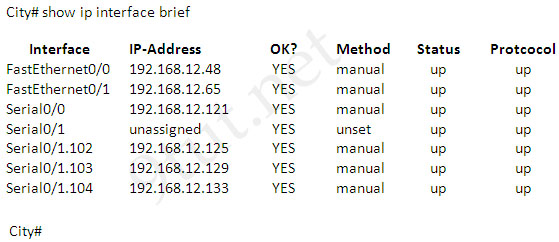
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.
Question 5
When running OSPF, what would cause router A not to form an adjacency with router B?
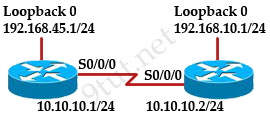
A. The loopback addresses are on different subnets.
B. The values of the dead timers on the routers are different.
C. Route summarization is enabled on both routers.
D. The process identifier on router A is different than the process identifier on router
Answer: B
Explanation
To form an adjacency (become neighbor), router A & B must have the same Hello interval, Dead interval and AREA number.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. The network is converged. After link-state advertisements are received from Router_A, what information will Router_E contain in its routing table for the subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96?
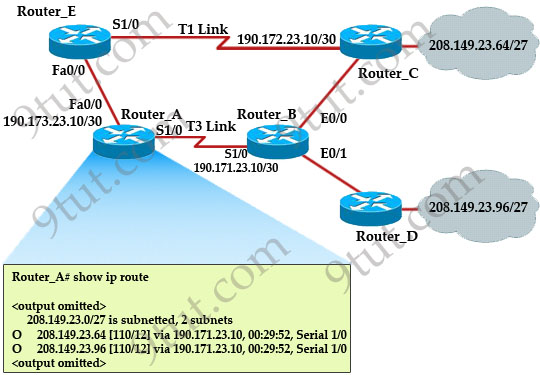
A. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, FastEthernet0/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
B. 208.149.23.64[110/1] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/3] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
C. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
D. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, Serial1/0
Answer: A
Explanation
Router_E learns two subnets subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96 via Router_A through FastEthernet interface. The interface cost is calculated with the formula 108 / Bandwidth. For FastEthernet it is 108 / 100 Mbps = 108 / 100,000,000 = 1. Therefore the cost is 12 (learned from Router_A) + 1 = 13 for both subnets -> B is not correct.
The cost through T1 link is much higher than through T3 link (T1 cost = 108 / 1.544 Mbps = 64; T3 cost = 108 / 45 Mbps = 2) so surely OSPF will choose the path through T3 link -> Router_E will choose the path from Router_A through FastEthernet0/0, not Serial1/0 -> C & D are not correct.
In fact, we can quickly eliminate answers B, C and D because they contain at least one subnet learned from Serial1/0 -> they are surely incorrect.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this RouterD?
RouterD# show ip interface brief

A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.316
Answer: C
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 8
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (choose two)
A. Router(config)#router ospf 1
B. Router(config)#router ospf 0
C. Router(config)#router ospf area 0
D. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
E. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
F. Router(config-router)#network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: A D
Explanation
In the router ospf
command, theranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number -> A is correct but B is not correct.
To configure OSPF, we need a wildcard in the “network” statement, not a subnet mask. We also need to assgin an area to this process -> D is correct.
Question 9
Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
A. Bandwidth, Delay and MTU
B. Bandwidth
C. Bandwidth and MTU
D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay and Load
Answer: B
The well-known formula to calculate OSPF cost is
Cost = 108 / Bandwidth
so B is the correct answer.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. Why are two OSPF designated routers identified on Core-Router?
| Neighbor_ID | Pri | State | Dead Time | Address | Interface |
| 208.149.23.194 | 1 | Full/DR | 00:00:33 | 190.172.32.10 | Ethernet1 |
| 208.149.23.60 | 1 | Full/BDR | 00:00:33 | 190.172.32.10 | Ethernet0 |
| 208.149.23.130 | 1 | Full/DR | 00:00:39 | 190.172.32.10 | Ethernet0 |
A. Core-Router is connected more than one multi-access network
B. The router at 208.149.23.130 is a secondary DR in case the primary fails.
C. Two router IDs have the same OSPF priority and are therefore tied for DR election
D. The DR election is still underway and there are two contenders for the role.
Answer: A
Explanation
OSPF elects one DR per multi-access network. In the exhibit there are two DR so there must have more than one multi-access network.
Question 11
What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 16
B. 2
C. unlimited
D. 4
Answer: D
Explanation
The default number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router is 4. We can change this default value by using “maximum-paths” command:
Router(config-router)#maximum-paths 2
Note: Cisco routers support up to 16 equal-cost paths. In detail, the default number of maximum paths is 32 for Cisco CRS-1 routers and 16 for Cisco XR 12000 Series Routers. The range is from 1 to 32 for Cisco CRS-1 routers and 1 to 16 for Cisco XR 12000 Series Routers.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios_xr_sw/iosxr_r3.7/routing/configuration/guide/rc37ospf.html)
Question 12
What is the OSPF default frequency, in seconds, at which a Cisco router sends hello packets on a multiaccess network?
A. 10
B. 40
C. 30
D. 20
Answer: A
Explanation
On broadcast multiacess and point-to-point links, the default is 10 seconds. On NBMA, the default is 30 seconds.
Question 13
What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 120
B. 100
C. 90
D. 110
Answer: D
Question 14
What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C



hw we can separate the zone?in qtn 3
@Ranjitha
Q3.
You can call it zone, but a better word is segments.
Q. How do we separate the zone-segment?
Ans. According to IP address and subnets. And each segment will elect a DR.
In the above example, there are two segment, which means we going to have two DR.
10.1.x.x is one segment, and 10.2.x.x is the other segment. All under one area though…
Study the above topology slowly, step by step, and also read the explanation given for better understanding…
@koffy…todd lammle page 471..in that selecting dr and bdr…will u pls read that………and giv me rply…and thanks for your explanation
@Ranjitha
I’m sorry, but I don’t have access to Todd Lamme, so I might not be able to read the chapter you are referring me to. Thanks.
Can someone explain question 6 to me clearer than the explanation given because I did not understand that
does support ospf unequal cost-path
@Queston 8.
The question asks:
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0?
First, we don’t have to worry about the area. Is given in the question………”Area 0″
To configure OSPF, We need a process identifier or Process ID(It is only locally significant) Can be choosen from any number between 1 to 65535.
OSPF unlike other routing protocols uses wild card when advertising its network or in its network statements not the subnet mask.
Option A is where we issue the process ID(In Global config mode)
Router(Config)# router ospf 1…………….this take us into config-router mode to issue our network statements in area 0
Option D is where we issue our network statement in area 0(In config-router mode)
Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.225 area 0……this is a Class C address. The focus is on the forth octet…./24
Conversion……..192.168. 16. 0
255.255.255.255
———————–
0 0 0 255
I hope this helps.
@Q 8
Conversion………192.168. 16 . 0
………………………255.255.255.255
……………………..———————–
…………………….. 0 . 0 . 0 . 255
@koffy
will we want to memorize this cost value for east interface type???
or any easier method 2 find that??
@bakky
What question are you referring to. Your question is not clear. Thanks.
Fast Ethernet(Fa)……..cost is 1
Ethernet(E)…………….cost is 10
E1………………………cost is 48
T1………………………cost is 64
T3………………………cost is 2
128kbps……………….cost is 781
64kbps…………………cost is 1562
56kbps…………………cost is 1785
i asked about this. shold i want 2 memorize the cost value for each????
@bakki
Yes, if you can. It will be helpful, if you can get yourself thoroughly familiarize with these OSPF link cost.
All the best.
what is ospf maximum cost path in cisco roter and non cisco?
hi friends next month i am going to write a ccna exam so if u ‘ve a new dump please
send to this mail id sathish.kaman@gmail.com
@razi
There is no such a thing. Is irrelevant.
There is a typo in the explanation:
“For FastEthernet it is 10^8 / 100 Mbps = 10^8 / 10,000,000,000 = 1.”
Instead of:
“For FastEthernet it is 10^8 / 100 Mbps = 10^8 / 100,000,000 = 1.”
Question 4… How do you know it is a /26??
@Dave
/26 is increment of 64/128/192/256
Mathematically….64+64(128)+64(192)+64(256)………..increment of 64
128…64…32…16….8…..4…..2……1
128-192-224-240-248-252-254-255
/25../26../27../28../29../30../31../32
Follow this illustration, and you will be able to figure out the “hows” and the “whys”
I hope this help.
Q.6
Hi,
Am a bit confused by above question whose choices are;
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.316 and the answer given as C.
In a situation where where you have choices on classes A, B and C, how do you choose the higher ip address as the router’s ID?
@Ngoroko
First of all you choose between two loopback addresses: 10.154.154.1 and 192.168.5.316
second one is higher so that will be router ID
Class C address is higer than any class B or A address. Same goes for class B compared to class A
Hope I understood your question right
@Ngoroko
You meant Q7 not Q6
Classes of address A,B,C is less relevant when choosing a router ID
The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
The reason option C is chosen is because is the highest loopback address.
I hope this help.
@Koffy,
Thanks bro. Think its now sinking and will definitely with additional practice.
@koffy,
pls in your explanation of q6 on sept. 17 you said TI cost is 64 ,but 9tut explanation of the same q6 says TI cost is 66. Pls which is correct?
@usGhana
The table I posted on sept.17 is the standard. Table for OSPF LINK COST(metric).
It is more like a guide or reference table.
But, you are right bro. It might be a typo.
@9tut
Can you take a second look at the link cost in your explanation on Q6. T1 cost is 64 not 66. Thanks.
@Koffy: Yes, the cost of T1 is 64, not 66 (Cisco routers don’t use floating-point math, so they drop the numbers after the decimal). Thanks for your detection. I updated it.
Can you please send me CCNA ICND2 dump at rizeed@gmail.com. PLEASE urgently..
@koffy
thanks for the quick response
Q 14
What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
—-I agree with option C. but how can A be correct. because hello packets are only used to establish neighbor adjacencies. I think F is the right answer.DR’s monitor
the state of link changes and update it to other DROTHERS. (routers other than DR & BDR)
can anyone please…………… help me out in Q14.
@uday:If you have CCNA 7th edition Todd Lammle book with you (or if you can find it anywhere on internet easily), here is something for you.
Go to page 456 and at (almost) bottom of the page there is written:
Hello packets and LSAs build and maintain the topological databases.
& the book is Indian version.
Question 3
Where you see two zones? Where in question say that? If you not see that(Im not see that),you are have a ansver: Brabch2 – DR, Branch1 – BDR.
@Dharamjeet Brar:
Thank you dud……….
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
Very nice questions 9tut thanks
awesome website :)
send me latest dumps plz
hossam.saber4@gmail.com
thanks in advance
q3)
the choices E & F are correct rather than D & F. because In a network running Ospf each area has a DR and a BDR. The highest router id becomes the DR and the 2nd highest becomes the BDR. as in the question it is asked for 2 answers. those two are branch1 and branch2 because they have the higher router id’s. what is the point of dividing the area into zones when all the routers are confined to one single area.
If anyone is so strong that D & F is the right answer then please justify……… to correct the mistake.
@uday: D&F – right choice.
Link between Corp-3 and Branch1 is a Serial (point to point).But OSPF is electing DR/BDR in _broadcast_ and _non-broadcast multi-access networks_ only (such as Ethernet and Frame relay.) So in this case OSPF will start 2 independent elections for routers in the Corp zone and for routers in the Branch zone.
The highest Router id is elected as DR (Master) and the second highest becomes the BDR (Slave) ready to take over in case of anything!!!
In quiz 3, Highest ip DR and the second BDR respectively
Thanks
@DimS
Thanks this question was ridiculous without a proper answer………….
i want to do ccsp any one know good ins, in india
plz help me
@Uday
Q14 this regarding hello and LSA packets
Initially hello multicast are used to discover the neighbours and they will added in neighbour table
when two dirctly connected router are neighbours they start exchange topology table (LSA packet)
Once all routers have same topology table ,they are said to in full state,after this multicast hellos are use to keep alive (whether the neighbour is alive or dead)
Hi, Guys, I hav exam tom, Can anybody tell me OSPF Q.2, what is correct answer, D&F or E&F? (Doubtful about this Answer)
Hi, Guys, I hav exam tom, Can anybody tell me OSPF Q.2, in this Q.No.3 about Corp & Branch… what is correct answer, D&F or E&F? (Doubtful about this Answer) & Which Sim r most Important, Thanks
@Sagitarrius81
The answer to Q3 are option D & F
Corp-4 for the 10.1…………subnet or segment
Branch-2 for the 10.2………subnet or segment.
Read above explanation for additional understanding. Thanks.
Q7 & 13 was there in today’s exam.
please i want to find out some thing very important about the exam if i use the ? sign for the lab is it allowed i mean to find help or find out more about the config am trying to work on i would really love to know please.
please i want to find out some thing very important about the exam if i use the ? sign for the lab is it allowed i mean to find help or find out more about the config am trying to work on i would really love to know please
Thanks a lot to Mikka n Koffy… for very good explaination about Cost calculations…
please need answer vlan generally decrease collision domain true of false with explanations thanks you
9tut,
Would appreciate your help here … did some research but so far its just making my understanding worse … I saw the links on Cisco, but still not clear.
What is the similarity / difference between:
1) redistribute static
2) default-information originate
3) ip default-network
Thanks!!