CCNA – OSPF Questions
Here you will find answers to OSPF Questions
Note: If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial
Question 1
Which of the following statements below best describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
A – It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router
B – It is locally significant
C – It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database
D – All routers in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information
Answer: B C
Question 2:
Why R1 can’t establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with R3 according to the following graphic? (Choose two)
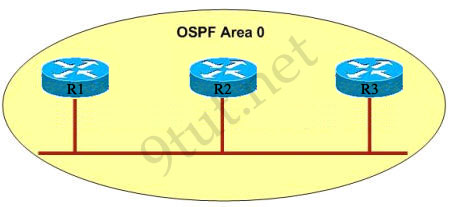
A – Configure EIGRP on these routers with a lower administrative distance
B – All routers should be configured for backbone Area 1
C – R1 and R3 have been configured in different areas
D – The hello and dead interval timers are not configured the same values on R1 and R3
Answer: C D
Explanation:
A is not correct because configure EIGRP on these routers (with a lower administrative distance) will force these routers to run EIGRP, not OSPF.
B is not correct because the backbone area of OSPF is always Area 0.
C and D are correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
- Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag
Question 3:
Which items are correct about the routing protocol OSPF? (Choose three)
A – Support VLSM
B – Increase routing overhead on the network
C – Confine network instability to one area of the network
D – Allow extensive control of routing updates
Answer: A C D
Explanation:
Routing overhead is the amount of information needed to describe the changes in a dynamic network topology. All routers in an OSPF area have identical copies of the topology database and the topology database of one area is hidden from the rest of the areas to reduce routing overhead because fewer routing updates are sent and smaller routing trees are computed and maintained (allow extensive control of routing updates and confine network instability to one area of the network).
Question 4:
Which three features are of OSPF routing protocol? (Choose three)
A – Converge quickly
B – OSPF is a classful routing protocol
C – Identify the best route by use of cost
D – Before exchanging routing information, OSPF routers find out neighbors
Answer: A C D
Question 5:
OSPF routing uses the concept of areas. What are the characteristics of OSPF areas? (Chose three)
A – Each OSPF area requires a loopback interface to be configured
B – Areas may be assigned any number from 0 to 65535
C – Area 0 is called the backbone area
D – Hierarchical OSPF networks do not require multiple areas
E – Multiple OSPF areas must connect to area 0
F – Single area OSPF networks must be configured in area 1
Answer: B C E
Explanation:
I used to think the answers should be C D E and here is my explanation:
OSPF can use an active interface for its router ID, so a loopback interface is not a must -> A is incorrect.
OSPF Area is a 32-bit number so we can use up to 232 – 1 = 4294967296 – 1 (since Area 0 is the first area). Remember that only process ID is a 16-bit number and ranges from 1 to 65535 -> B is incorrect.
F is incorrect too because single area OSPF netwoks must be configured in Area 0, which is called the backbone area.
For answer D, it is a bit hard to guess what they want to say about “hierarchical” but we should understand “Hierarchical OSPF networks” as “OSPF networks”. D is correct bercause we can only have one area (area 0 – the backbone area) for our networks.
But TT commented on 01-11-2010:
Especially to note on choice B, D, and E:
Choice B: we all know that The areas can be any number from 0 to 4.2 billion and 1 to 65,535 for the Process ID. As choice B specifies ‘area’ (be aware, it’s not saying ‘process id), there is no reason to say that we cannot assign numbers from 0 to 65535 for area # (it is using ‘may be’, not ‘have to be’ or ‘ought to be’). Hence, we do not worry about assigning ’0′.
Choice E: as Area 0 is the backbone, we all understand that any areas in a OSPF network have to be connected to it. And actually this is implicitly saying that multiple areas form a hierarchical OSPF network, as Area 0 being a root and others being its leaves.
Choice D: when it specifies ‘Hierarchical’, at least 2 areas should be required to form such topology (of course that includes Area 0)
Although Choice B is not an absolutely accurate statement since it not only can be assigned up to 65535, it is still a correct answer. And again, it specifies ‘area’, not ‘process id’, so ’0′ can be included. Finally, it would be meaningless to call OSPF a hierarchical network if no more than one area is present.
—————————————————————————————————-
I reviewed the question and think it is a more suitable solution with choice B than choice D, surely it is a tricky question!
Question 6:
Part of the OSPF network is shown below:
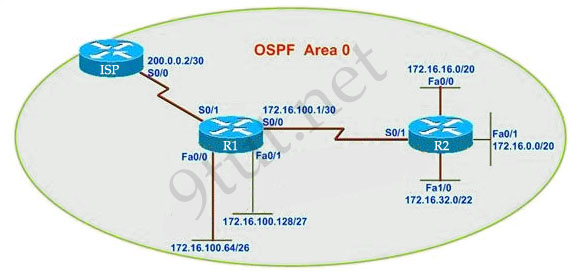
Configuration exhibit:
R1 routing commands:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0
router ospf 1
network 172.16.100.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 172.16.100.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 172.16.100.128 0.0.0.31 area 0
default-information originate
You work as a network technician, study the exhibits carefully. Assume that all router interfaces are operational and correctly configured. In addition, assume that OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2. How will the default route configured on R1 affect the operation of R2?
A – Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately
B – Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R1 will be dropped
C – Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately because of the lack of a gateway on R1
D – The network directly connected to a router R2 will not be able to communicate with the 172.16.100.0, 172.16.100.28 and 172.16.100.64 subnetworks.
E – Any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in the routing table of router R2 will be directed to R1. R1 will then send that packet back to R2 and a routing loop will occur
Answer: E
Explanation:
First, notice that the more-specific routes will always be favored over less-specific routes regardless of the administrative distance set for a protocol. In this case, because we use OSPF for three networks (172.16.100.0 0.0.0.3, 172.16.100.64 0.0.0.63, 172.16.100.128 0.0.0.31) so the packets destined for these networks will not be affected by the default route.
The default route configured on R1 “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0″ will send any packet whose destination network is not referenced in the routing table of router R1 to R2, it doesn’t drop anything so answers A, B and C are not correct. D is not correct too because these routes are declared in R1 and the question says that “OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2″, so network directly connected to router R2 can communicate with those three subnetworks.
As said above, the default route configured on R1 will send any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in its routing table to R2; R2 in turn sends it to R1 because it is the only way and a routing loop will occur.



Please send me latest dumps.
s_abhishek@y7mail.com
thanks alot
Can someone help me with the latest dumps plz
eng.falahrofifanalmajali@yahoo.com
plz i waill go to exam next week soo any one can send me a copy from lastversion & what about testinside plz anyone have any advices or exam send me @ fadyfarouk_86@hotmail.com
guys see there anyone who wrote an exam this week
@9tut:
This question from Rouges Pierre posted on July 14th, 2011 is very interesting but nobody has answered it yet. Quote it again:
Can someone help me with this one?
http://i54.tinypic.com/2im2p0z.jpg
Refer to the exhibit. Why was RouterA not elected as the designated router?
A. The OSPF process ID of RouterA is lower than the process ID of the elected DR.
B. RouterA has a lower OSPF priority value than the router elected as DR.
C. The interface address of RouterA is a higher value than the interface address of the DR.
D. RouterA is not advertising the interface with address 221.130.149.10.
Every dump I have seen indicates that answer D is correct. However, I think the exhibit clearly indicates that 221.130.149.10 is advertised and the reason RouterA is not elected DR is answer B. RouterA has a lower OSPF priority… exhibit indicates priority is 1.
Any thoughts? It is driving me crazy.
Base on the output, we know that Router A is the BDR with priority 1 and has the router ID higher than the DR; the type of network is broadcast. That can be concluded that the DR has a higher priority number. In the identification of neighborship process, the Hello packet is included the router ID so answers D is not correct. I have the same opinion with Rouge Pierre. Please correct me.
@hai
wow, nice question!
came across this on the net, it’s from testking:
“On broadcast and non-broadcast multi-access networks, a designated router and backup designated router are elected.
The election is done by first choosing the routers with the highest priority value or, if the priorities are same, choosing the routers with the highest router ID.
The router ID is chosen by the highest IP address on any loopback interface or, if no loopback interfaces are configured, the highest IP address on any active physical interface.
Note: Referring to the exhibit of the “show ip protocols” command: Router ID is:
221.130.149.10 but this network is not advertised using network command on OSPF.
OSPF does not need to route this network in order for it to be used as the router ID, so the other router must have a higher priority value, or it has been simply up longer since this election process is not preemptive (this was not one of the choices).”
you are right, option B is correct
@hai @xallax: Yes, I agree with both of you. The router ID of this router is 221.130.149.10 while the DR’s router ID is 208.149.23.194 which is smaller. The most suitable answer should be B – RouterA has a lower OSPF priority value than the router elected as DR.
@xallax and 9tut:
Thanks for your explains. I was been confused between advertising and Hello process in the manner of network address and router ID, but your note is clear me out. (that means the exhibit of the “show ip protocol” must have the network 221.130.149.10 if the router A has advertised it).
Regarding to expand this question, can I assume that the non-DR and non-BDR routers in this network have the priority number 1 with routers’ID lowered than 221.130.149.10? Because the priority number of router A is 1, and it is the BDR.
@hai
i’d say that the other routers, if any, have a priority of 0
or
they have the same priority of 1, but their IDs have lower values than that advertised by router A.
@xallax:
Thanks Xallax. But
Be careful with the priority number 0. I remember that a router with the priority 0 does not involve in the neighboring establishment process. Am I right?
I wonder that thing above because in the Cisco CCNA ICND2 book wrote by Wendell Odom, chapter 11, example 11-6 on page 422, the “show ip ospf neighbor” command give the output as following:
R2#show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Address Interface
1.1.1.1 1 FULL/BDR 10.1.1.1 Fas 0/0
3.3.3.3 1 2way/Drother 10.1.1.3 Fas 0/0
4.4.4.4 1 FULL/DR 10.1.1.4 Fas 0/0
Why router 3 is not a BDR? It has the same priority number with all other routers and the second highest router ID.
@hai
Neighbor ID Pri State Address Interface
1.1.1.1 1 FULL/BDR 10.1.1.1 Fas 0/0___________let’s call this R1
3.3.3.3 1 2way/Drother 10.1.1.3 Fas 0/0________let’s call this R2
4.4.4.4 1 FULL/DR 10.1.1.4 Fas 0/0____________let’s call this R3
R2 should’ve been the BDR. Maybe it came online after the DR/BDR election took place…
i m not able to understand Q.1.
plz send latest dumps . i m havin exam next week.
amolia.virgo@gmail.com
thanku….
@pallavi
A – It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router
try turning on OSPF without it, you won’t be able to. it’s not OPTIONAL
B – It is locally significant
yep. nobody else will know it except the router on which it is configured
C – It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database
yes. you can run multiple OSPF processes on the same router
D – All routers in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information
nope. this question is trying to make you think of EIGRP and AS.
have my exam month end…any advice from anyone on the SIMs to expect?
On # 6, what is the effect of router configuration mode command default-information originate on the entire configuration. Thanks in advance for your feedback.
9tut, you’ve been doing a wonderful job here.
@Toumany, I’m planning to write my ccna exam soon also, can u send me the pass for sure too?
@resolved: The “default-information originate” is used to advertise a default route to other routers in the domain.
hey people :)
what muter ID will OSPF use ? the highest IP address ? or the highest loopback ip address ?
@abed: Please read http://www.9tut.com/ospf-routing-protocol-tutorial
In short:
The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router and is chosen using the following sequence:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
+ The router ID can be manually assigned
can someone direct me where i can get cisco ios’s to download?
I have GNS3 and needs the ios to simulate.thanks.
@ EDDIE
u can download Packet tracer that simulates IOS softwares ;)
@9tut
very nice questions thnx :)
Can sombody send me latest CCNA dump?
because i’ll take ccna exam next week.
my mail :malindagc@hotmai.com
thanks>
Can someone please be generous enough to send me the latest dumps.
Testing 12/16
Thank you in advance
Can someone please be generous enough to send me the latest dumps.
Testing 12/16
Thank you in advance
jmf54321@gmail.com
pls somebody help me by exp.qtn 6….?
@ranjitha
it has been already explained by 9tut…
wud be thankful to u frds,
if u cud send me latest dumps on etc2013@gmail.com
am going 2 face ccna exam on monday(12 dec),,
q6 – there is no routing loop!
Please note: there is no mention of a default route for R2.
The the default route (0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0) on R1 is not within the advertised OSPF networks listed. Even if it where: I tried using GNS3 to advertising 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 and still could not get OSPF to share the default route, yet all other routes did share.
My conclusion…
Router R2 will obtain a full routing table, (NOT including a default route) from R1.
However packets originating from r2 without a destination route in the routing table will be dropped before leaving the router with an ICMP “destination unreachable” response
Packets originating from r1 will forward out its default route to r2 where it will be dropped also with an ICMP “destination unreachable” response (remember there is no default route to r1)
I have found any mention anywhere that OSPF shares default routes.
Correct me where I’m wrong.
Q6 – How come that a loop can be created? I thought that OSPF is a no loop routing protocol.
Could you double-check and confirm what should be a correct answer, please?
Maybe A ?
Thanks
@lucia67: If only OSPF is running then there will have no loop. But this is between OSPF and static route so a loop can occur.
@9Tut. Thank you very much. I understand now.
Bruno:
I totally agree with you. I have bought the Boson CCNA exam, which contains more than 300 questions, and even the worst question over there is better than questions in this Cisco test.
There are a lot of unnecessary questions here, I don’t understand why they don’t use Boson or Odom’s tests, which is said to be “official exam certification library”.
Question concerning graphic http://i54.tinypic.com/2im2p0z.jpg
D. RouterA is not advertising the interface with address 221.130.149.10.
The answer is D….because during the election process, RouterA had not advertised that interface, and the DR election proceeded without that advertisement. The wording of the answer should say “RouterA had not” rather than “RouterA is not” but the correct wording gives away the answer! JMHO.
In Question 6 the explanation said;
“…the default route configured on R1 will send any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in its routing table to R2; R2 in turn sends it to R1 because it is the only way and a routing loop will occur.”
Following the Routing Theory, when a Router doesn’t have a route for some network, he’ll discart the packet. So R2 will discart the packet.
May someone help me?
Q6
I don’t understand how will R2 use default route received from R1 since that route sends everything that’s not specified in the R2 routing table to R1?
Can someone please explain?
Thanks
correction
Q6
I don’t understand how will R2 use default route received from R1 since that route sends everything that’s not specified in the R1 routing table to R2?
Can someone please explain?
Thanks
@maja
There’s a loop in the topology. You should take one step back and analyze what is causing the loop, and that will eliminate some of the questions you are asking.
This topology does not have ” a route of last resort” set yet, OR actually “route of last resort” is not properly configured. Therefore causing a routing loop.
Dears
kindly anyone send to me the last damp (test inside, pass4sure ….etc) for urgent as i gonne exam the next month ……….. mail: mohamed.zaied@tedata.net
If you set the router with priority 0, than it will never ever be DR
with “ip ospf priority 0″
By default, all routers are set to 1. So if all are set to one, they will pick the router with highest ip address. loopback has a higher priority than interfaces.
1. priority
2. loopback address
3. interface
default-information original is used in OSPF only to put the gateway of last resort route into the ospf routing table
I need latest dump, anyone pls :) send to nzetenia@gmail.com thanks
Can you please send me CCNA ICND2 dump at rizeed@gmail.com. PLEASE urgently..
please send me the lastest dump plzzzzz
my email c.vasco_9@hotmail.com, please i will take the ccna exam I need the last dump
dont understand question 1
@furqan
process identifier (OSPF ID) is not propagated across the network and it is used by the router to separate OSPF processes apart (same like windows does with PID numbers)
Latest dump http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2011-07-09.by.Collisio.486q.vce.file.html
can anybody send me the latest dumps ….. becoz next week i’ve my ccna exam !!!!!! plz
noreenali2010@gmail.com
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!