CCNA – TCP/IP Model & Operation
Here you will find answers to TCP/IP Model & Operation Questions
Question 1
An inbound access list has been configured on a serial interface to deny packet entry for TCP and UDP ports 21, 23 and 25. What types of packets will be permitted by this ACL? (Choose three)
A. FTP
B. Telnet
C. SMTP
D. DNS
E. HTTP
F. POP3
Answer: D E F
Explanation
The access list denies packet entry for TCP & UDP -> all the services on ports 21, 23 and 25 are disabled. Services on these ports are FTP (port 21), Telnet (port 23), SMTP (port 25). Other services are allowed so D E F are the correct answers.
Question 2
What are two characteristics of Telnet? (Choose two)
A. It sends data in clear text format.
B. It is no longer supported on Cisco network devices.
C. It is more secure than SSH.
D. It requires an enterprise license in order to be implemented.
E. It requires that the destination device be configured to support Telnet connections.
Answer: A E
Explanation
Telnet, part of the TCP/IP protocol suite, is a virtual terminal protocol that allows you to make connections to remote devices, gather information, and run programs. Telnet is considered insecure because it transfers all data in clear text -> A is correct.
The destination device needs to support Telnet connection. For example, if a device doesn’t support TCP/IP protocol suit then maybe we can’t telnet to it.
Question 3
An administrator issues the command ping 127.0.0.1 from the command line prompt on a PC. If a reply is received, what does this confirm?
A. The PC has connectivity with a local host.
B. The PC has connectivity with a Layer 3 device.
C. The PC has a default gateway correctly configured
D. The PC has connectivity up to Layer 5 of the OSI model
E. The PC has the TCP/IP protocol stack correctly installed.
Answer: E
Explanation
The address 127.0.0.1 is called loopback address. When we ping 127.0.0.1, in fact we are testing if the TCP/IP protocol suite is installed on our device.
Note: The address 127.0.0.1 does not have anything related with the NIC card. We still ping 127.0.0.1 even if we don’t have the NIC card.
Question 4
Where does routing occur within the DoD TCP/IP reference model?
A. application
B. internet
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B
Explanation
The picture below shows the comparison between TCP/IP model & OSI model. Notice that the Internet Layer of TCP/IP is equivalent to the Network Layer which is responsible for routing decision.

Question 5
A host is attempting to send data to another host on a different network. What is the first action that the sending host will take?
A. Drop the data.
B. Send the data frames to the default gateway.
C. Create an ARP request to get a MAC address for the receiving host.
D. Send a TCP SYN and wait for the SYN ACK with the IP address of the receiving host.
Answer: B
Explanation
Before sending data, the sending host checks if the destination host is inside or outside the local network. If it is outside the local network, the data will be sent to the default gateway.
Question 6
A TCP/IP Transfer is diagrammed in the exhibit.
A window size of three has been negotiated for this transfer. Which message will be returned from the receiver to the sender as part of this TCP/IP transfer?
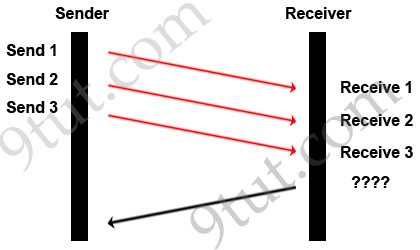
A. Send ACK 1-3
B. Send ACK 3
C. Send ACK 4
D. Send ACK 4-6
E. Send ACK 6
F. Send ACK 7
Answer: C
Explanation
In response, the receiver replies with an ACK. The acknowledgment number is set to one more than the received sequence number. The ACK means “I have got all messages up to sequence number n-1 so please send me the message for sequence number n”.
Question 7
What is the purpose using the traceroute command?
A. to map all the devices on a network.
B. to display the current TCP/IP configuration values.
C. to see how a device MAC address is mapped to its IP address.
D. to see the path a packet will take when traveling to a specified destination.
E. to display the MTU values for each router in a specified network path from source to a destination.
Answer: D
Question 8
A network admin wants to know every hop the packets take when he accesses cisco.com. Which command is the most appropriate to use?
A. path cisco.com
B. debugcisco.com
C. trace cisco.com
D. traceroute cisco.com
Answer: D
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Host A pings Host B. What source MAC address and source IP address are contained in the frame as the frame leaves R2 destined for host B?
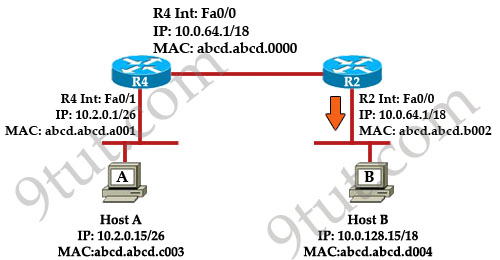
A. abcd.abcd.a001
B. abcd.abcd.b002
C. abcd.abcd.c003
D. 10.2.0.15
E. 10.0.64.1
F. 10.0.128.15
Answer: B D
Explanation
When packets are sent from Host A to Host B, the source and destination IP addresses are never changed and they are the IP addresses of Host A & Host B. Only the MAC addresses will be changed to reflect the device of the current network. In this case, when the frame leaves R2 destined for host B. It will have:
+ Source IP: IP of Host A - 10.2.0.15 (never changed)
+ Destination IP: IP of Host B – 10.0.128.15 (never changed)
+ Source MAC: MAC of Fa0/0 of R2 – abcd.abcd.b002
+ Destination MAC: MAC of Host B – abcd.abcd.d004
Question 10
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two)
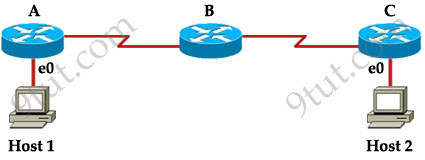
A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The last known good router will try to inform you that the destination cannot be reached (with a Destination Unreachable message type) so from that information you can learn how far your packets can travel to and where the problem is.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. The switch in the graphic has a default configuration and the MAC table is fully populated. In addition, this network is operating properly. The graphic represents selected header information in a frame leaving host A. What can be concluded from this information?
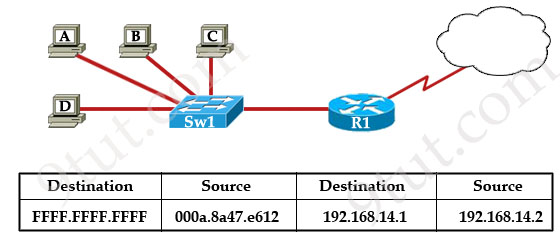
A. The MAC address of host A is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
B. The router will forward the packet in this frame to the Internet.
C. The switch will only forward this frame to the attached router interface.
D. All devices in this LAN except host A will pass the packet to Layer 3.
Answer: D
Explanation
This frame is leaving host A so host A is the source of this frame. In this frame, the MAC destination is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF which is a broadcast address so Sw1 will flood this frame out all its ports except the port it received the frame -> Hosts B, C, D and the interface connected to Sw1 on R1 will receive this frame. When receiving this frame, they will pass the packet to Layer 3 (because they consider broadcast address “everyone, including me”). At Layer 3, the Destination IP will be checked and only the host (or the interface on the router) with correct IP will respond to Host A while others keep silence -> D is correct.
Just for your information, maybe you can ask “this is a broadcast message so why router R1 doesn’t drop it?”. Suppose this is an ARP Request message. In fact, R1 drops that packet but it also learns that it is an ARP Request so R1 looks up its routing table to find a route to that destination. If it can find one, it will send an ARP Reply back for host A”.



Hi 9tut, Can you review question 8.
Question asks what command is the most appropriate. The tool used is traceroute however the command entered is tracert cisco.com. What do you think?
@ccent certified
tracert is on windows machines
it is asking for a network admin. that leads you to switches and routers, right?
cheers :)
latest dumps :-
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.PrepKing.640-802.v2012-01-03.by.DHARANI.615q.vce.file.html
&
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2011-07-09.by.Collisio.486q.vce.file.html
Hi,
For Q5, true answer should be “C”, Sending host first attempts to send a ARP request to resolve MAC address of the destination host if it is an unknown host. Am I wrong??
@Ilter
Q5.
Option B
Send the data frame to default gateway.
Please, read above explanation for better understanding.
That’s awsome..!
Hw i get a confident on ccna exam.
@Ilter
host will look at his ip and will notice that they are not in the same network ..then host will send the the frame direct to his gateway…
it possible to make an arp before ..but not to get the mac of the receiving pc but the mac of the gateway…
Q5
This question is to examine the ARP working principle.
When Host A doesn’t know the MAC address of Host B, the ARP request will be broadcast so that all hosts on
the LAN can see this request. If the IP is not local, the router will check its routing table to see whether there is
a route to the destination network. If there is, the router will reply with its own MAC address.
So C is correct.
for packet tracert
when send icmp request to another network
host send ARP & ROUTER check the network for des in route table
if finded router reply with arp request to source host with mac address to router (default gatway) and router send arp again to destination network for finded to mac address for destination host wen destination host reply and send mac address to router (arp reply)
router forward icmp request drom host 1 (source) to host 2 (destination)
correct answer is c
but one moment
HOST 1 sent ARP request for default gatwey to get mac address for router not for get mac address for des host mmmmmmmmmmmmm when this B correct
A little more guidance for Question 5
Normally it would be correct, but when the computer is turned on it will have the IP address configured and the default gateway in its local arp table. You can confirm this by typing in arp -a in a cmd prompt and it will display your gateway address and MAC. The first step it will take when it is being processed is that it will check the destination IP address and it will notice it is in a different network. It does this because as the data is being process to get sent out it goes from the top down (Layer 7 to Layer 1) and as it is being processed when it comes in the goes from the bottom up (Layer 1 to Layer 7). The IP address is at Layer 3 so that would get processed before the Layer 2 MAC address. This would allow it to see the different network and the host computer would then send it to its defaut gatway to get processed. I hope this explains it better for you guys.
@ oreoz u got d brains!! Perfect!
I have a question regarding Question 9. How come the source MAC address is not the the MAC address of the port on R2 connecting to R1 like the question below?
Host A is communicating with a server. What will the destination MAC address of the frames sent by Host A to the server?
Router
e0 / \ e1
/ \
Hub Switch
| |
Host A Server
Answer was the MAC address of Router interface e0. Please explain as I am confused.
for question 5 the answer is C. The first action host will take is to send an ARP request. This ARP request will be received by all in the LAN segment. Router will check whether it is for different LAN and respond with its MAC address. Then host address the MAC address of the Router as destination address.
Q1, Q10 as is, and Q9 with a little change in address scheme, were in today’s exam.
Q11– the broadcast packets get dropped at layer 3? and only the host with the correct IP will respond? –oooo — this is an arp request because it has destination IP address
which network protocol that DNS use ?
a-udp
b-scp
c-tftp
d-tcp
e-ftp
answer is both a & b
but collitio dumps asks only one and chooses UDP why ??? and i should choose one should i choose UDP instead TCP ???
@killer4ever
DNS uses both UDP and TCP
as per wikipedia:
“DNS primarily uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port number 53 to serve requests. DNS queries consist of a single UDP request from the client followed by a single UDP reply from the server. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is used when the response data size exceeds 512 bytes, or for tasks such as zone transfers. Some resolver implementations use TCP for all queries.”
correct answers here would be A and D
@thanks xallax !!!
hi,
can anyone send me the latest dumps? I’ll take my CCNA exam next friday…
thanks,
andrew.letcon@gmail.com
Q10 was in my exam
i am telling you i have passed my exam with score of 925. please make sure you master every multiple choise and drag and drop question first and the last thing you need to know is with out knowing acl and nat u will never pass. they r always there!!!!!
hi guys…the coming week ill be taking my exam can any one plz send me the latest dump…
nikhil2488@gmail.com
thanx in advance…
Why is Q10 not C and D? For ICMP to get the unreachable message to Host 1, doesn’t it have to get processed by the hop routers A and B also ?
q11
just make no sense to me can you guys help me understand that
now hosts route packets!!!
ccnaguy@att.net
@ccnaguy
A. the MAC of a host will never be all Fs. False
B. i doubt it as there are almost no chances at all that the source and destination arent in the same subnet.
this one is false too
C. destination all Fs means “this is a broadcast”. what do swiches do with broadcasts? they send them our all ports, except the port they came on. False
D. all others are false, this must be Correct.
yes, all other devices (3 PCs and 1 Router) will receive the bits over the cable (Layer 1), will assemble the frame (Layer 2) and will check to see if the destination IP address is their own (Layer 3). True.
Hi, 9tut, Great job U”ve done here! All I wanted to mention is that in the Q9 U said that “the source and destination IP addresses are never changed” but IIRC they can be changed in the case of NAT. So I would either change this statement or add remark like “NAT is exception”.
Cheers!
thank you Xallax
I’m taking an exam on this Saturday May 5th 2012. Could you guys please send me the latest dump to ultimatearmy@gmail.com
Thank you!!
what u requid to consider is the “different network” and not mac-address so host must send to its default-gareway
Dear all,
you may also want to check below site for some useful resources. Good luck to all of us!
careercert.info
Hi all, I am taking CCNA 640-802 exam first time on 30/05/2012. Could anyone please send me latest dumps which are valid for UK? My e-mail address is puneet_gill84@yahoo.co.uk. Many thanks.
i real working hard to sit for CCNA 640-802 exam in august,2012,plse i need support in most critical areas in exams am in tanzania, raysimon@yahoo.com
I PASSED CCNA EXAM TODAY THANKS TO ALL MIGHTY ALLAH
960/1000
q6 needs more explanation please…
hi 9tut and xallax.
Please help me on this question.
http://i50.tinypic.com/64ld21.gif
i think the answer is A but the dump says it is option D.
thank in advance.
@jay
HostA pings to HostB.
there are L3 devices in-between (Router1 and Router2)
the ARP request will have the MAC address of the next L3 device on the path. this is Router1. the IP address will be the one of the destination device.
note that there is a switch between HostA and Router1. judging by the icon it is a normal L2 switch. it will just forward the frames from or to HostA.
but… why? think of it sending a letter to a friend that lives in another country.
you send the envelope with the contact information your friend has (the IP), but you send it from the post office that is closer to you (this is the MAC).
this of the switch in the exhibit as the mailman. he takes the envelope from your house but he still has to give it to the post office. he does not change any info on the envelope.
Thanks xallax.. but im bit confused about the interface address. is it referring to Destination IP address? Please advise. thanks.
@jay
yes, it should’ve been “Internet Address”…
check for yourself by doing this on a windows machine: winkey+r (or Start->Run), type in “cmd” (no quotes) and press Enter, type “arp -a” (no quotes) and press Enter.
it should display a list of all known ARP entries.
now try this in the same command prompt window: ping http://www.google.com
after it is done pinging try “arp -a” again.
it doesn’t show an entry for the IP address that corresponds to the google server. my question is: why?
answer: they are not on the same network. ARP is only used locally.
this question is a bit stupid to say the least as it does not reflect the reality. the 2 hosts are on different networks…
still, go with the task at hand and correctly identify the destinations at L2 and L3.
destination at L2 is the MAC of the default gateway. it always is when leaving the network
destination at L3 is the IP of the destination device (be it PC, router, switch, printer, LAN coffee machine, etc.)
@jay
regarding the above… it added on its own “h t t p : / /” before the google ping command above. please use “ping google.com” instead
thanks xallax.
Hi, Im Priya from Kerala(India).Im taking ccna exam on 30th June.Really im fed up.Can any one plz send me latest dumps to my email priya.ccna@yahoo.in Love you all .God Bless ..Thanks
priya
Q5:
I tried to ping from 192.168.0.10 to 192.168.1.10 across a router in the middle (all devices with default settings)
This is script from Packet Tracer simulation.
First goes Layer3. Situation is:
1. The Ping process starts the next ping request.
2. The Ping process creates an ICMP Echo Request message and sends it to the lower process.
3. The source IP address is not specified. The device sets it to the port’s IP address.
4. The device sets TTL in the packet header.
5. The destination IP address is not in the same subnet and is not the broadcast address.
6. The default gateway is set. The device sets the next-hop to default gateway.
Than comes Layer2. Situation is:
1. The next-hop IP address is a unicast. The ARP process looks it up in the ARP table.
2. The next-hop IP address is not in the ARP table. The ARP process tries to send an ARP request for that IP address and buffers this packet.
Mine answer will be “B”.
Please check question 1
An inbound access list has been configured on a serial interface to deny packet entry for TCP and UDP ports 21, 23 and 25. What types of packets will be permitted by this ACL? (Choose three)
A. FTP
B. Telnet
C. SMTP
D. DNS
E. HTTP
F. POP3
Answer: D E F
Explanation
The access list denies packet entry for TCP & UDP -> all the services on ports 21, 23 and 25 are disabled. Services on these ports are FTP (port 21), Telnet (port 23), SMTP (port 25). Other services are allowed so D E F are the correct answers.
*****
Answers should be A B and C
@jpmarinm
I can’t see how FTP, Telnet and SMTP is permited. In question, ACL is configured to deny packets for that ports?
Hi all, I am having my CCNA (640-802) exams this week. Can anyone please send me latest dumps: allient@post.sk
Thank you ;)
check this out guys. Hope it helps!
Cisco ActualTests 640-802 v2012-06-08 by Anonymous 641q.vce
Cisco Acme 640-802 v2012-05-31 by suresh 521.vce
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.ActualTests.640-802.v2012-06-08.by.Anonymous.641q.vce.file.html
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2012-05-31.by.suresh.521.vce.file.html
I passed my ccna exam today Praise be to God! Thank you Jesus! and thanks to 9TUT for the tutorials and explanations, great site and thanks to xallax for your explanations to questions and thanks to http://www.examcollection.com for the dumps. Pls guys lets donate and help to keep this site up!
48 ques for exams including 3 simulation, I had EIGRP, Acesslist2 and VTP . Make sure you practice the simulation, use packet tracer or gns3. Best wishes to all!
Passed CCNA exam.. thank u 9tut & exam collection!
Got 947/1000..
anyone want help, can contact me on my email id: prakhar.gour@aol.com
@ amar
Had ACL, NAT and EIGRP sims
there were 8 question on frame relay in my exam which are not in colliso and Jericoo dump
but if u read frame relay from todd lammle and from cisco site you can answer all
i read frame relay a day before the exam so was able to judge correct ans