New CCNA – IP Routing 2
Question 1
Users on the 172.17.22.0 network cannot reach the server located on the 172.31.5.0 network. The network administrator connected to router Coffee via the console port, issued the show ip route command. Based on the output of the show ip route command and the topology shown in the graphic, what is the cause of the failure?

A. The network has not fully converged.
B. IP routing is not enabled.
C. A static route is configured incorrectly.
D. The FastEthernet interface on Coffee is disabled.
E. The neighbor relationship table is not correctly updated.
F. The routing table on Coffee has not updated.
Answer: C
Explanation
There are no dynamic routing protocols running on Coffee router, only a default route is configured to route all traffic to 172.19.22.2 but we don’t know about this network. The correct IP address should be the IP address on the interface of Tea router which is connected to Coffee router (maybe 172.18.22.2).
Question 2
The speed of all serial links is E1 and the speed of the all other links is 100Mb/s. A static route will be established on the Manchester router to direct traffic toward to the internet over the most direct path available. What configuration of the Manchester router will establish a route toward to the internet for traffic from workstation on the Manchester LAN?
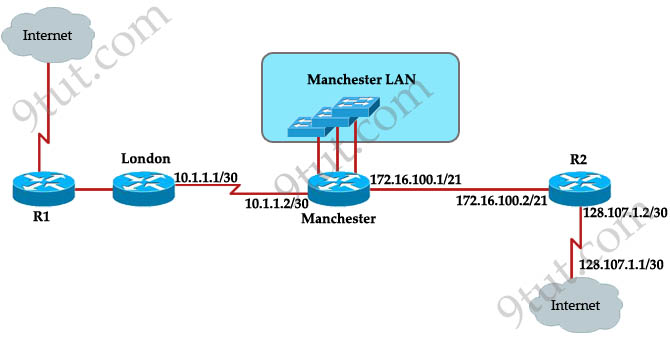
A. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.2
B. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 128.107.1.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 128.107.1.1
D. ip route 0.0.0.00.0:0:0 172.16.100.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 172.16.100.2
F. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2
Answer: F
Explanation
Maybe “the most direct path available” here means via R2 because it is directly connected with the Internet while the London path needs to go through R1. So we need a command to send traffic to R2 and the correct command is “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2″.
Question 3
Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (choose two)
A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
| Network | Interface | Next-hop |
| 10.1.1.0/24 | e0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.2.0/24 | e1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.3.0/25 | s0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.4.0/24 | s1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.5.0/24 | e0 | 10.1.1.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/28 | e1 | 10.1.2.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/29 | s0 | 10.1.3.3 |
| 10.1.5.64/27 | s1 | 10.1.4.4 |
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.1.2.2
C. 10.1.3.3
D. 10.1.4.4
Answer: C
Explanation
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 subnets but the “longest prefix match” algorithm will choose the most specific subnet mask -> the prefix “/29″ will be chosen to route the packet. Therefore the next-hop should be 10.1.3.3 -> C is correct.
Question 5
Which destination addresses will be used by Host A to send data to Host C? (Choose two)
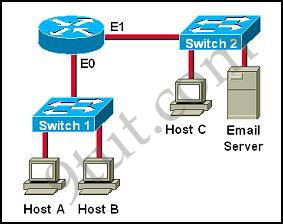
A. the IP address of Switch 1
B. the MAC address of Switch 1
C. the IP address of Host C
D. the MAC address of Host C
E. the IP address of the router’s E0 interface
F. the MAC address of the router’s E0 interface
Answer: C F
Explanation
While transferring data through many different networks, the source and destination IP addresses are not changed. Only the source and destination MAC addresses are changed. So in this case Host A will use the IP address of Host C and the MAC address of E0 interface to send data. When the router receives this data, it replaces the source MAC address with it own E1 interface’s MAC address and replaces the destination MAC address with Host C’s MAC address before sending to Host C -> C and F are correct.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator must establish a route by which London workstations can forward traffic to the Manchester workstations. What is the simplest way to accomplish this?
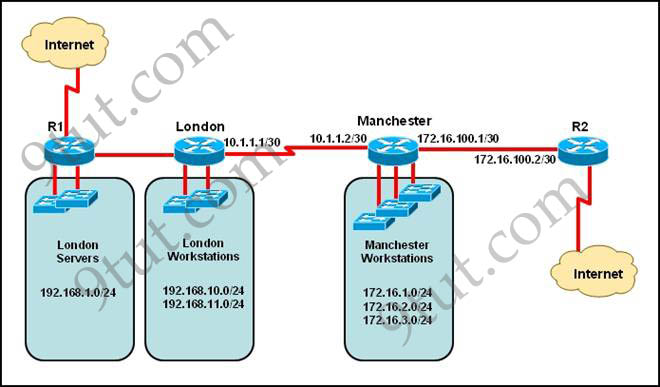
A. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise all routes to Manchester.
B. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on London to advertise summarized routes to Manchester.
C. Configure a dynamic routing protocol on Manchester to advertise a default route to the London router.
D. Configure a static default route on London with a next hop of 10.1.1.1.
E. Configure a static route on London to direct all traffic destined for 172.16.0.0/22 to 10.1.1.2.
F. Configure Manchester to advertise a static default route to London.
Answer: E
Question 7
Which parameter can be tuned to affect the selection of a static route as a backup when a dynamic protocol is also being used?
A. link bandwidth
B. hop count
C. link cost
D. administrative distance
E. link delay
Answer: D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit:
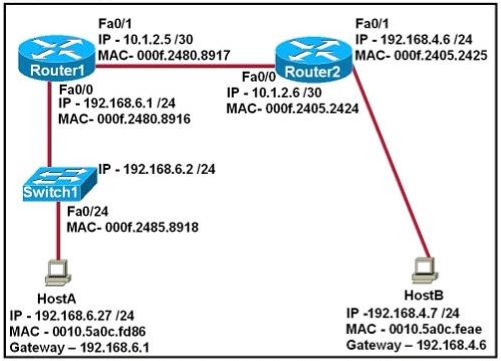
After HostA pings HostB, which entry will be in the ARP cache of HostA to support this transmission?
A.
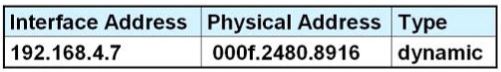
B.
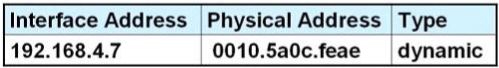
C.
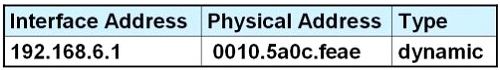
D.
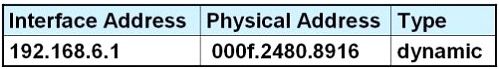
E.
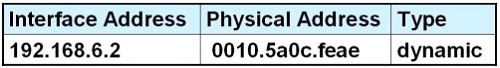
F.

Answer: D
Explanation
Host A knows host B is in another network so it will send the pings to its default gateway 192.168.6.1. Host A sends a broadcast frame asking the MAC address of 192.168.6.1. These information (IP and MAC address of the default gateway) is saved in its ARP cache for later use.



Answer to question 8 is A….
@Anonymous Actually, non of them is correct. PCs do not add ARP entries for destinations outside their subnet. Which makes sense, you don’t need their MAC.
The closest to being correct, is the one that used the local Router’s interface IP, since that MAC is where packets meant for Host B will be sent.
What would be the point of writing down an IP address you get from the application layer, or a MAC you won’t even be using? D is more correct then A.
Also, of course, if this is the first interaction with the default gateway, then the host doesn’t have it’s MAC yet, in a first communication scenario like that, Host A would add the default gateway to its ARP table.
I believe that question 8 is number A
question 8: after reading all these comments I got totally got confused.
decided to build the topology in packet tracer.
arp -a command showed that ANSWER “D” IS THE RIGHT CHOISE
thanks you Mahmoud
My proof
http://i57.tinypic.com/2s0lm9t.png
Q5 answer should be MAC address of the router E0 interface or E1 interface
thank u mr Mahmoud
can any clarify Q6 please
explain Q6 please
@OBIEKAY The question ask for the “simplest way to route London Workstations to Manchester Workstations”. The simplest way is obviously a Static Route because yopu have to enter just one command, in the dynamic routes you need to enter multiple commands in multiples routers (RIP, EIGR or OSPF in all routers) —> A, B, C are not correct.
The simplest way is also a Static Default Route but this will be a mess if the London Workstations need to acces to the internet —> F, D are not correct.
If you configure a Static Route like this: “ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.252.0 10.1.1.2″ you will accomplish the task (the command says: if you want to go to 172.16.0.0/22 go through 10.1.1.2 as next hop)—> E is Correct
Passed today with 958
Q7 was on test
thanx 9tut
I believe the answer to ques 8 is A, because host A would already have host B’s ip address, because it is sending a packet there, this is how it would know that host B is on another subnet, by analyzing Host B’s subnet mask, it would see that it is different from the local network. It would need a layer 2 address also, hence it sends an arp. Because it is on another network the default router would respond with its own mac address. It would save host B ip address in its ARP Cache along with its default router’s mac address. So for future communication with host B, A would simply use the default router’s mac address.
Tomorrow I have Exam. Any valid suggestion or update or tips..
It would be appreciate .
Q8 ans should be A
because
When a host needs to reach a device on another subnet, the ARP cache entry will be that of the Ethernet address of the local router (default gateway) for the physical MAC address. The destination IP address will not change, and will be that of the remote host (HostB).
Ya u r correct Taj. Destination address wont change in a “packet” But its not a packet…its an arp table
To truly determine that D is correct for question 8, all you have to do is have the following in GNS3:
PC1 ==> Router ==> PC2
Use any IP address you want, and ping from PC 1 to PC 2.
Now just do: “show arp”, and you would see that D is correct for question 8!
question 8 on exam today
@danny what was the answer you marked for question 8
Q7 answer is D, because in a local network host use mac-address to communicate, so by default proxy arp is enable in Cisco router it means that when a local host want to send data to a remote host it send a arp request (exemple I need the mac address of 192.168.x.x) or the arp request is a layer 2 broadcast address (FF.FF.FF.FF.FF.FF) as we know it the router don’t forward a broacast , the router will keep the address 192.168.x.x and answer to source host with it own IP address (like that Eeeeh it me this is my IP address xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx).
so the source host will update it arp table with the gateway IP address and Mac address, the router looks in it routing table to where the network 192.168.x.x is associeted.
I wanted to say this my mac-address
q-8 on exam today
9tut et al:
Is it possible, during the exam, to http into server to verify that the access-list works as designed?
Thanks
kam, did you get the correct answer on Q8?
Would you be so kind to share it with everyone because it is confusing everyone!
Thanks!
Please send me an email iamkane07@yahoo.com. Thanks!
q5 today
@MrYoSo, the answer for Q8 is correct. I confirm (Cedrick MEWO) read my explanation and you will understand.
Thanks IP MAN!
I know that D is the correct answer for Q8. I just want to confirm from the person who experienced answering this question during the exam..
Anyone??
Q1, Q8 on exam yesterday
Nobody questioned the answer for Q1? I think the correct answer should be D. because if the correct answer is ” A static route is configured incorrectly”, then ping from Coffee should be failure also.
hi Erika, what’s your answers for Q1 and have you gotten your mark?
Hello Everyone,
I am preparing myself for CCNA 200-120 vendor exam.
It would be grateful to me if any one can send the latest dumps & questions to my mail ID: arunachalam1987@gmail.com
Thanks in advance
Q8 the answer is A
passed the exam today.
good thing i answer D. for Q8 :)
got a score of 1000/1000!
thanks 9tut!
@haru. let me first congratulate you. Please, could u let guys know how many questions from 9tut or similar that was in the exam? Tanx
q1….Dec 18
q5 n 8 on 11 dec
Guys what will be the correct answer for Q8 im confused.
thanks guyz!
is it D or A?
Hosts A and B are on different subnets and are separated by routers, so the MAC address of HostB will
never get back to HostA: Router2 will decapsulate the frames that HostB sends. Router1 will reencapsulate
the ping packet sent by HostB and put its own MAC address in the frame. Therefore, HostA
will put 192.168.6.1 and 000f.2480.8916 into its ARP table as a dynamic entry.
is D
HAPPY NEW YEAR TO ALL THE PARTICIPANT OF 9TUT
is D correct for 8th ?
Q4, Today, 1/12/14
Q4 & Q5 in my exam today.
Hello there :) taking my exam in 2 days.. Lorenzo regarding question 4, are they changing the ip addresses in the test? or its exactly the same?
Q4. what if I have in the routing table a 10.1.5.64/32 address
Refer to the exhibit. According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
1. what if I have in the routing table a 10.1.5.64/32 separately
2. what if I also have in the routing table a 10.1.5.65/24 separately
3. what if I also have in the routing table a 10.1.5.65/32 separately also
Hi Tolution,
It is impossible to have a subnet mask of /32 = 255.255.255.255
Hi Tolution,
the /32 is only for the 10.1.5.64 host. So for the .65 it’ll choose the most specific route to it, which is still 10.1.5.64/29.