New CCNA – STP
Note: If you are not sure about Spanning Tree Protocol, please read our Spanning Tree Protocol STP Tutorial (Premium Tutorial).
Question 1
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
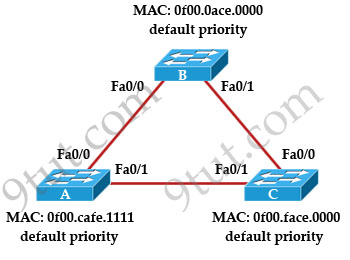
A. Switch A – Fa0/0
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.
On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.
Question 2
What value is primarily used to determine which port becomes the root port on each non-root switch in a spanning-tree topology?
A. lowest port MAC address
B. port priority number and MAC address.
C. VTP revision number
D. highest port priority number.
E. path cost
Answer: E
Explanation
The path cost to the root bridge is the most important value to determine which port will become the root port on each non-root switch. In particular, the port with lowest cost to the root bridge will become root port (on non-root switch).
Question 3
What is one benefit of PVST+?
A. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches in the network.
B. PVST+ automatically selects the root bridge location, to provide optimization.
C. PVST+ allows the root switch location to be optimized per vlan.
D. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops.
Answer: C
Explanation
Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) maintains a spanning tree instance for each VLAN configured in the network. It means a switch can be the root bridge of a VLAN while another switch can be the root bridge of other VLANs in a common topology. For example, Switch 1 can be the root bridge for Voice data while Switch 2 can be the root bridge for Video data. If designed correctly, it can optimize the network traffic.
Question 4
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 5
In which circumstance are multiple copies of the same unicast frame likely to be transmitted in a switched LAN?
A. after broken links are re-established
B. in an improperly implemented redundant topology
C. when upper-layer protocols require high reliability
D. during high traffic periods
E. when a dual ring topology is in use
Answer: B
Explanation
If we connect two switches via 2 or more links and do not enable STP on these switches then a loop (which creates multiple copies of the same unicast frame) will occur. It is an example of an improperly implemented redundant topology.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.
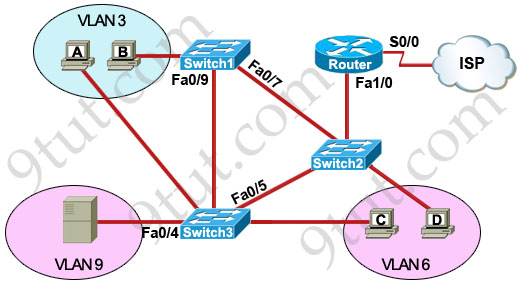
A problem with network connectivity has been observed. It is suspected that the cable connected to switch port Fa0/9 on Switch1 is disconnected. What would be an effect of this cable being disconnected?
A. Host B would not be able to access the server in VLAN9 until the cable is reconnected.
B. Communication between VLAN3 and the other VLANs would be disabled.
C. The transfer of files from Host B to the server in VLAN9 would be significantly slower.
D. For less than a minute, Host B would not be able to access the server in VLAN9. Then normal network function would resume.
Answer: D
Question 7
Which port state is introduced by Rapid-PVST?
A. learning
B. listening
C. discarding
D. forwarding
Answer: C
Explanation
PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). But PVST+ has only 3 port states (discarding, learning and forwarding) while STP has 5 port states (blocking, listening, learning, forwarding and disabled). So discarding is a new port state in PVST+.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the information given, which switch will be elected root bridge and why?
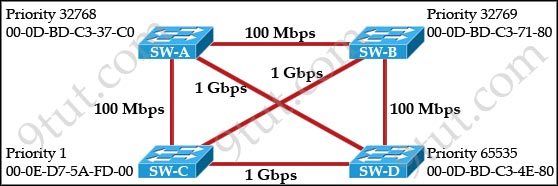
A. Switch A, because it has the lowest MAC address
B. Switch A, because it is the most centrally located switch
C. Switch B, because it has the highest MAC address
D. Switch C, because it is the most centrally located switch
E. Switch C, because it has the lowest priority
F. Switch D, because it has the highest priority
Answer: E
Question 9
Which term describes a spanning-tree network that has all switch ports in either the blocking or forwarding state?
A. redundant
B. spanned
C. provisioned
D. converged
Answer: D
Explanation
Spanning Tree Protocol convergence (Layer 2 convergence) happens when bridges and switches have transitioned to either the forwarding or blocking state. When layer 2 is converged, root bridge is elected and all port roles (Root, Designated and Non-Designated) in all switches are selected.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
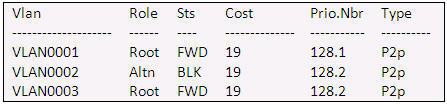
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C



Question number 1 ,,,,MAC address of switch A & switch C ,, why Switch A F0/1 be the designated port it has higher MAC address than Switch C ?
The election for the root port is the Lowest MAC Dilan.
Dear All
Regarding all CISCO exams CCNA CCNA Security CCNP (Route Switch Tshoot) updated valid dumps & Exam discount vouchers available globally.
1. CCNA 200-120 60 % discounted vouchers
2. CCNP (Route Switch TShoot) 25 % discounted Vouchers
3. CCNA Security 640-554 60 % discounted Vouchers
Ask any kind of technical and exam related questions from our CCIE experts.
Feel Free to Contact
Email Contact:dheprofessionals@gmail.com
Skype Id:net.rideplay
Thanks
Best Regard
Admin
Passed today with 958
Q10 was on test
thanx 9tut
PASS MY EXAM TODAY SEPT 17 with 1000/1000
Q2, Q4, Q8 in exam today
Great Work.. Questions are same in the exam
Hello. I think there is a mistake in the Q8. How will SW-C the Root whether he has a “invalid” lowest priority? When you configure a priority, for a vlan for instance, you CAN NOT introduce a priority of “1″ because IOS won’t let you.
in theory, the priorities has to be by multiples of 4096!!!!!
JoseLuis it is true… it should be in this order
0 4096 8192 …. and on!
JoseLuis,
This has been answered by Jason on page 1. Setting the priority for a switch in vlan 1 to 0 effectively gives a switch a priority of 1.
This can be verified:
Switch#sho spanning-tree vlan 1
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 1
Address 0001.C9EB.C004
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 se
JoseLuis
Yes you are right, you cant configure 1.
but if you configure a multiples of 4096 the IOS add a value called system-id extension which is
a number chosen according to the vlan number(this a pvst feature)
ex: if configure “spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 4096″ for vlan 10, the priority for the this switch’s vlan 10 will be show up in the output of the show spanning-tree vlan 10 command as 4106.
based on this if you configure spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 0 command for vlan 1, the priority for the vlan 1 will be 1. I repeat this is a pvst concept so you better find out the different format between the bridge-ids of STP and PVSTP which will answer the question of why the IOS only allow multiples of 4096.
In Q6 could C be a right answer aswell? Because when the network is running normally the cost to get to the server on VLAN 9 is 38. Now that f0/9 is down, the cost to get to vlaN 9 is now 57, wouldn’t that make frames going to vlan 9 slower?
Question #5, #6 on my exam last Sunday, 2014/10/5.
Thanks a lot 9tut. Almost all questions were from here except for two.
Had the EIGRP and ACL 1 sims.
jevdawg,
perhaps. slower…a little…but not SIGNIFICANTLY SLOWER…
thanks to you logan,,you make me understd that concept system-id extension clearly.i av bn struggling to understd for a long time.
can anyone explain to me the concept of root bridge and bridge ID. This is still not clear for me….
Thanks
Righ if you configure a priority of 0, by typing sh span it will display priority 1.
Q-3,5,6,7 on exam today!
6,8 and 9 today
Q 5,7 and 10
g
Can someone send me the latest dumbs for CCNA to albertomch13@gmail.com,
Thanks,
can someone explain Q6… please please. thank you
whats the difference between 802.1d and 802.1q?
Q1, Q2 on exam yesterday
802.1d: is a Cisco protocol for bridge and switch loops avoidence, it has same function as STP (Spanning-tree Protocol).
802.1q: trunking protocol able to carry multiple vlan between Switches (help to carry untagged frame, frame which belong to default vlan), is a open standard and for is ISL (InterSwitch Link) use between Cisco devices. but the use is 802.1q.
Please can someone explain the question 10? I didn’t understand.
Thanks!
Question 10:
Sometimes a good process of elimination help you to get the correct ans.
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.>>Not correct because from the given exhibit Vlan 2 has one connected interface
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree. >> Not correct because no where on the given exhibit we can tell if it is RSTP or not.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch. >> Not correct because no where in the given exhibit we have any info about VLAN 2 bridge ID
The only one ans left is C and that the correct ans.
can someone send me the latest dumps for CCNA to metamorphic9@gmail.com
Q7 Must be: Which port state is introduced by Rapid PVST+?
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+, or sometimes PVSTP), is a Cisco-proprietary improvement of 802.1D STP. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP).
Over time, the IEEE improved STP beyond the 802.1D standard with the Rapid STP (802.1W) protocol. Then Cisco took that standard and made another proprietary improvement, creating another mode in Cisco switches: Rapid PVST+, or simply RPVST+.
Explanation must be: “Rapid PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D (specification as IEEE802.1D-2004) Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). But Rapid PVST+ has only 3 port states..”
The answer will not change, but maybe there is some misunderstanding.
Could someone please explain Q7?
why the PVST+ has 3 states?
and what is the discarding state?
q2,q4,q6,q8…Dec 18
q2 on 11 dec
Q3, 5 & 6
Today in my exam
q4 today
Q10 today
hi
which one is easier ICND1 or CCNA
In Q10:
How come A is not correct?
The port for this VLAN is in blocking state – it wouldn’t be that way if there would be only one interface connected to that VLAN, right? And it’s not root because the other one has lower interface number.
Pls send me the latest dumps for 200-120 CCNA Exam.
maidulkuet@yahoo.com
Q5, 8 Today, 1/12/14
Can anyone explain Q6?
Please send me latest dumps for 200-120 CCNA Exam to
manikandangm2005@gmail.com
Can anyone explain Q6?
I’m planning to take up exam in next week. Please share latest dumps @ zameer.ise@gmail.com
Hi,
For Q6 answer: we need to assume that the root port for vlan 3 in sw1 is f0/9. If it gets disconnected, STP will need less than 1 minute to reconverge the network and assign fa 0/7 as root port for vlan 3. Once it’s done, the traffic from host B to the server will be forwarded through the network.
@Tara: ICND1 is half of composite ccna exam. I am taking the test tomorrow… Please tell me would be enough to read 9tut and go for the exam?
Please send me latest dumps for 200-120 CCNA Exam to sonfele@gmail.com
Q8 today. Passed
please send me the latest Dumps for the CCNA Exam 200-120 wzulfiqar@hotmail.com
Q8 in today exam of mine passed with 1000 marks…i think paper was so easy due to studied allot 9tut… thanks 9tut