New CCNA – Switch Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
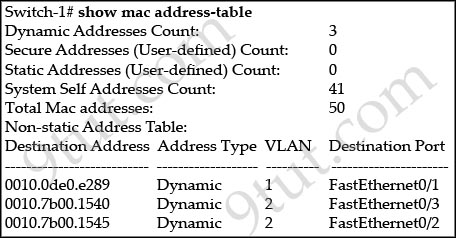
Switch-1 needs to send data to a host with a MAC address of 00b0.d056.efa4. What will Switch-1 do with this data?
A. Switch-1 will drop the data because it does not have an entry for that MAC address.
B. Switch-1 will forward the data to its default gateway.
C. Switch-1 will flood the data out all of its ports except the port from which the data originated.
D. Switch-1 will send an ARP request out all its ports except the port from which the data originated.
Answer: C
Explanation
The MAC address of 00b0.d056.efa4 has not been learned in its MAC address table so Switch-1 will broadcast the frame out all of its ports except the port from which the data originated.
Question 2
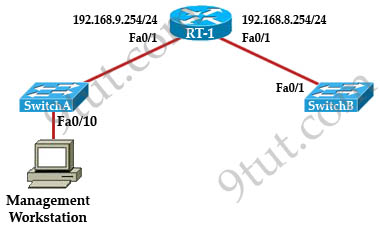
A technician has installed SwitchB and needs to configure it for remote access from the management workstation connected SwitchA. Which set of commands is required to accomplish this task?
A.
SwitchB(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
B.
SwitchB(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
C.
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
D.
SwitchB(config)#ip default-network 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
Answer: B
Explanation
To remote access to SwitchB, it must have a management IP address on a VLAN on that switch. Traditionally, we often use VLAN 1 as the management VLAN (but in fact it is not secure).
In the exhibit, we can recognize that the Management Workstation is in a different subnet from the SwitchB. For intersubnetwork communication to occur, you must configure at least one default gateway. This default gateway is used to forward traffic originating from the switch only, not to forward traffic sent by devices connected to the switch.
Question 3
A switch is configured with all ports assigned to vlan 2 with full duplex FastEthernet to segment existing departmental traffic. What is the effect of adding switch ports to a new VLAN on the switch?
A. More collision domains will be created.
B. IP address utilization will be more efficient.
C. More bandwidth will be required than was needed previously.
D. An additional broadcast domain will be created.
Answer: D
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. The two connected ports on the switch are not turning orange or green. What would be the most effective steps to troubleshoot this physical layer problem? (Choose three)
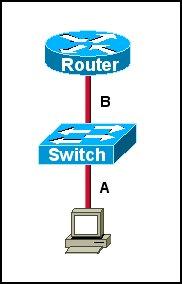
A. Ensure that the Ethernet encapsulations match on the interconnected router and switch ports.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reseat all cables.
Answer: B D F
Explanation
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.
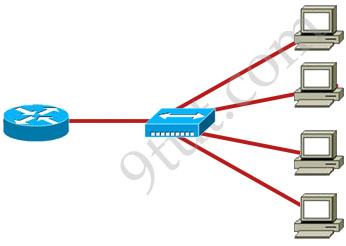
What two results would occur if the hub were to be replaced with a switch that is configured with one Ethernet VLAN? (Choose two)
A. The number of collision domains would remain the same.
B. The number of collision domains would decrease.
C. The number of collision domains would increase.
D. The number of broadcast domains would remain the same.
E. The number of broadcast domains would decrease.
F. The number of broadcast domains would increase.
Answer: C D
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. Give this output for SwitchC, what should the network administrator’s next action be?
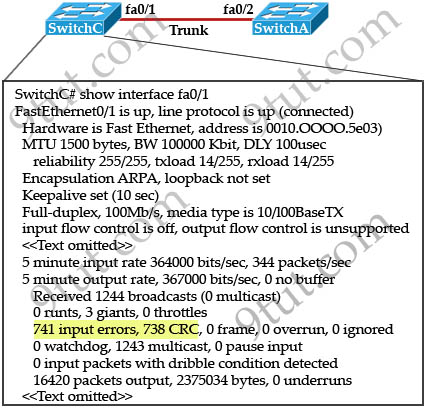
A. Check the trunk encapsulation mode for SwitchC’s fa0/1 port.
B. Check the duplex mode for SwitchC’s fa0/1 port.
C. Check the duplex mode for SwitchA’s fa0/2 port.
D. Check the trunk encapsulation mode for SwitchA’s fa0/2 port.
Answer: C
Question 7
Which three statements accurately describe layer 2 Ethernet switches? (choose three)
A. Microsegmentation decreases the number of collisions on the network.
B. If a switch receives a frame for an unknown destination.it uses ARP to resolve the address.
C. Spanning Tree Protocol allows switches to automatically share vlan information.
D. In a properly functioning network with redundant switched paths, each switched segment will contain one root bridge with all its ports in the forwarding state. All other switches in that broadcast domain will have only one root port.
E. Establishing vlans increases the number of broadcast domains.
F. Switches that are configured with vlans make forwarding decisions based on both layer 2 and layer 3 address information.
Answer: A D E
Question 8
Why will a switch never learn a broadcast address?
A. Broadcast frames are never sent to switches.
B. Broadcast addresses use an incorrect format for the switching table.
C. A broadcast address will never be the source address of a frame.
D. Broadcasts only use network layer addressing.
E. A broadcast frame is never forwarded by a switch.
Answer: C
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit:
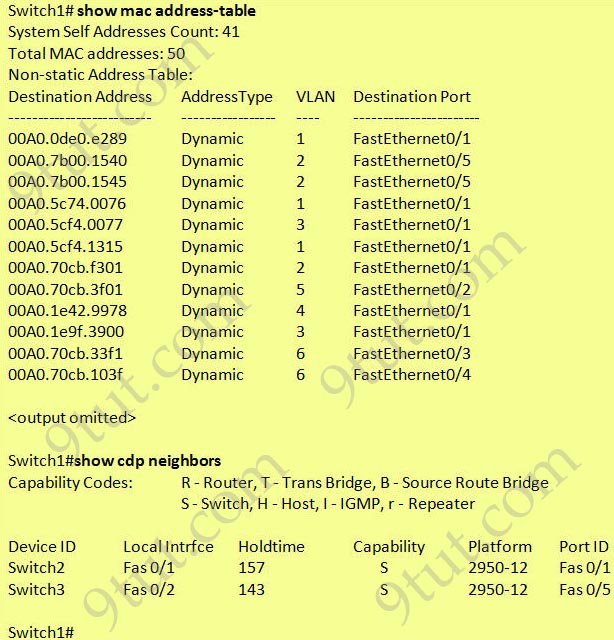
Which two statements are true of the interfaces on Switch1? (Choose two)
A. Interface FastEthernet0/2 has been disabled.
B. Multiple devices are connected directly to FastEthernet0/1.
C. FastEthernet0/1 is configured as a trunk link.
D. FastEthernet0/1 is connected to a host with multiple network interface cards
E. FastEthernet0/5 has statically assigned MAC addresses.
F. A hub is connected directly to FastEthernet0/5
Answer: C F
Explanation
FastEthernet0/1 can receive traffic from multiple VLANs -> it is configured as a trunk.
There are two MAC addresses learned from FastEthernet0/5 -> a hub is used on this port.
Question 10
The network administrator normally establishes a Telnet session with the switch from host A. The administrator’s attempt to establish a connect via Telnet to the switch from host B fails, but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful. What is the issue for this problem?
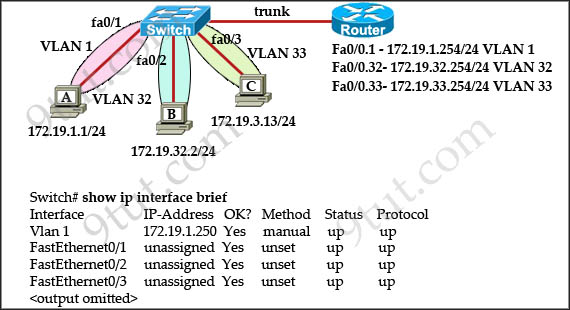
A. Host B and the switch need to be in the same subnet.
B. The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.
C. The switch interface connected to the router is down.
D. Host B need to be assigned an IP address in vlan 1.
Answer: B
Explanation
Host A (172.19.1.1) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are in the same subnet so telnet from host A to the switch can be successful even if a default gateway is not set on host A.
But host B (172.19.32.2) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are not in the same subnet so host B needs a default gateway to telnet to the switch. The default gateway on host B should be 172.19.32.254.



The problem was to the gateway, no matter for subnet or vlan because the router care about that.
q3,q5,q7 on exam today
Q2) whats the different between B and D its the same answer
abdulrauf, it’s different. B is ip default-gateway while D is ip default-network
3,4 on today ex
Q 1,2 ,7 and 10 exam on 10th Nov’14
Q2, Q8 on exam yesterday
Q)6 isn’t clear
show con
Q1, Q3, Q5, Q10 on exam today! thanks 9tut. exam pass successful
please send me the latests dumps please my e-mail sandeepagarwal57@gmail.com
Questions 1 2 4 10 Ipassed all thanks to 9 tut
i passed yesterday .
my advice just read 9.tut you will pass with fox on sim of ACL1&2 and EIGRP.
Q8, Q9 and Q10 today
plz tell me which simulation is “acl 1″ (everybody is talking about). Plz tell me i’ve exam after 2 days
Q3 , Q7 in Today Exam
FIX 10!! :)
gtz
q1 …. Dec 18
q5 on 11th dec
Q3, 5 & 10 today
Q2 today
Can someone please explain Q6.
What is the meaning of Fa0/0/.1,Fa0/0/.32,Fa0/0/.33 in Q10?
I don’t understand question itself.
Show ip interface brief command doesn’t show IP assigned to other VLANS.
Q2 is clear to understand but not Q10.
Q9 is Now so Clear
it Require more Explanation
Anyone can explain Q7 Q7 Q &??? please
ADMIN!!!
C
A
N
YOU
EXPLAIN QUESTION NO 7 ????? please!!! i can’t understnd
@i’m ccna
- Microsegmentation is the fact to divide a big collision domain into several smaller ones -> the smaller a collision domain is, the fewer collisions occur (considering half duplex, because there are no collisions in full duplex).
- Each STP instance contains 1 root bridge only with all its ports in forwarding state (designated); The other switches of this instance will only have 1 root port.
- Creating Vlans is the ability to create mode broadcast domain : each Vlan has its own subnet (its own broadcast domain).
Hope this helped.
please can any expert networking explain question 7&8
Q2 would be totally correct in my opinion if since line 3 on, the prompt mark would be (config-if) instead of just (config):
CORRECT:
SwitchB(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config-if)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config-if)#no shutdown
INCORRECT:
SwitchB(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.8.254
SwitchB(config)#interface vlan 1
SwitchB(config)#ip address 192.168.8.252 255.255.255.0
SwitchB(config)#no shutdown
@claudio valid point notice :)
9Tut Admin: Please do a correction in the second part of the Q.10 Explanation, if you agree. It is describing “Host B” IP Forwarding process and that is not an option in the set of Answers first. What must be noted there is SwitchB’s IP forwarding process (Using a Vlan interface working the same as a NIC) , since it has to forward traffic to another IP subnetwork than the local one, in this case in response to a ping originated from “Host B”. Note that “Host B” has already configured a Default Gateway, otherwise this part of the question text: “…but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful.” wouldn’t be possible. In Summary: Everything is correct except you are mixing “Host B” and “Switch B” roles at the second part of the explanation in my opinion. Hope this helps. BR
…and the missing default gateway at “Switch B” must be “ip default-gateway 172.19.1.254″. Doesn’t it?
Note: Some previous argumentation to the default-gateway missing post is awaiting being moderated by 9Tut Admin since it seems is a little long…. be patient please.
please send me the latests dumps please my e-mail hanifiozsoy@gmail.com
Adm: Please do a correction in the second part of the Q.10 Explanation, if you agree. It is describing “Host B” IP Forwarding process and that is not an option in the set of Answers first. What must be noted there is SwitchB’s IP forwarding process (Using a Vlan interface working the same as a NIC) , since it has to forward traffic to another IP subnetwork than the local one, in this case in response to a ping originated from “Host B”. Note that “Host B” has already configured a Default Gateway, otherwise this part of the question text: “…but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful.” wouldn’t be possible. In Summary: Everything is correct except you are mixing “Host B” and “Switch B” roles at the second part of the explanation in my opinion. Hope this helps. BR
Claudio ,,this is correct host B already have a Default
Gateway…so where is the question here?!
i think the question is good..the Default Gateway does exist but not introduced on the switch ,so you have to do it your self to make the switch sends packets to the appropriate Vlane(Vlan32)..this is the catch
Q6, Today, 1/12/14
good see you after
Q9,
Switch1 has your fas0/1 connected to Switch2 fas0/1. Trunk link here
Switch1 has your fas0/2 connected to switch3 fas0/5.
So the mac addresses ending with: 1540 and 1545 are showing that are connected on port fas0/5 of the switch1, so for two mac address be sharing the same port, its possible only using a hub as said on answer F.
It also should be possible if a pc is using a virtual machine, but it is not the case.
Send me the latest dumps please of ccna 200-120 in pdf form r_afridi420@hotmail.com
test will be in February need support.
Q1 & 6 in my exam today. Passed
Q6 in my exam today . Passed
Q10 – Explained as I understand it.
Host B can ping Host A and Host C, so Host B has a default gateway set. (The explanation is incorrect and should say “Switch”, not “Host B” needs a gateway set).
Host A can telnet to the Switch because they are both in the same VLAN (subnet).
In order for Host B to telnet to the Switch, it has to connect to the telnet on the Switch’s VLAN1 management interface. The Switch can communicate to all 3 Hosts at Layer 2 using MAC addresses, but the telnet requests needs to traverse networks. Therefore, in order for the switch to establish the Telnet connection with Host B, a default gateway needs to be set in the Switch so it knows how to respond to the Telnet request to it’s VLAN 1 interface from Host B.
I hope this helps. I do think that answer D would actually work since Host A has the same setup. Can anyone else confirm that?
Hi,
Can every one help me with question 1 please?
Based on my knowledge if switch doesn’t know a address it will send ARP to find it … But in Q1 said it will send the data to all the ports except data originated port???
Switch doesn’t use ARP
1 of 20
Routing and Switching Essentials (Version 5.0) – RSE Chapter 1 Exam
1
What information is added to the switch table from incoming frames?
source MAC address and incoming port number
destination MAC address and incoming port number
destination IP address and incoming port number
source IP address and incoming port number
Q1 & Q6 scored 958/1000. Thanks 9Tut!
I’ve passed my exam 890/1000 ICDN1