CCNA – EIGRP Questions
Here you will find answers to EIGRP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about EIGRP, please read my EIGRP tutorial
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit, when running EIGRP what is required for R1 to exchange routing updates with R3?
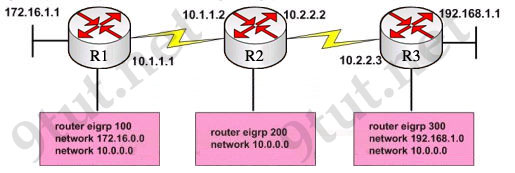
A – AS numbers must be changed to match on all the routers
B – Loopback interfaces must be configured so a DR is elected
C – The no auto-summary command is needed on R1 and R3
D – R2 needs to have two network statements, one for each connected network
Answer: A
Question 2:
As a Cisco technician, you need to know EIGRP protocol very well. Which of the following is true about EIGRP successor routes? (Choose two)
A – A successor route is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to a destination
B – Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process
C – Successor routes are flagged as “active” in the routing table
D – A successor route may be backed up by a feasible successor route
E – Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process.
Answer: A D
Explanation:
B is not correct because neighbor table only contains a list of directly connected EIGRP routers that have an adjacency with this router, it doesn’t contain successor routes.
C is not correct because successor routes are not flagged as “active”, they are always the best route to reach remote networks and are always used to send packets.
A and D are correct because successor route is the best and primary route to a remote network. It is stored in the routing table and topology table. If this route fails, a backup route (called feasible successor route) in the topology table will be used to route traffic to a destination.
Question 3:
Which two statements are true regarding EIGRP? (Choose two)
A – Passive routes are in the process of being calculated by DUAL
B – EIGRP supports VLSM, route summarization, and routing update authentication
C – EIGRP exchanges full routing table information with neighboring routers with every update
D – If the feasible successor has a higher advertised distance than the successor route, it becomes the primary route
E – A query process is used to discover a replacement for a failed route if a feasible successor is not identified from the current routing information
Answer: B E
Explanation:
Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) is the algorithm for selecting and maintaining the best path to each remote network. DUAL tracks all the routes advertised by neighbors and selects routes based on feasible successors. It inserts lowest cost paths into the routing table (these routes are known as primary routes or successor routes) -> A is not correct.
EIGRP is still a distance-vector protocol, but has certain features that belong to link-state algorithms (like OSPF) than distance-vector algorithms. For example, EIGRP sends a partial routing table update, which includes just routes that have been changed, not the full routing table like distance-vector algorithms -> C is not correct.
The feasible successor route will become the primary route when its advertised distance is lower than the feasible distance of the successor route. The feasible successor route can be used in the event that the successor route goes down. Notice that the feasible successor route does not get installed in the routing table but is kept in the topology table as a backup route -> D is not correct.
“Support VLSM, route summarization, and routing update authentication” are the features of EIGRP -> B is correct.
When a route fails and has no feasible successor, EIGRP uses a distributed algorithm called Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to discover a replacement for a failed route. When a new route is found, DUAL adds it to the routing table -> E is correct.
Question 4
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
A. a primary route,stored in the routing table
B. a backup route,stored in the routing table
C. a backup route,stored in the topology table
D. a primary route,stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance is less than the Feasible Distance of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but stored in the topology table.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output from the show ip eigrp topology command, which router is the feasible successor?
| router# show ip eigrp topology 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.255 IP-EIGRP topology entry for 10.0.0.5/32 State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 41152000 |
A.
| 10.1.0.1 (Serial0), from 10.1.0.1, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (46152000/41640000), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is 64 Kbit Total delay is 45000 Microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 |
B.
| 10.0.0.2 (Serial0.1), from 10.0.0.2, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (53973248/128256), Route is Internal Vector Metric: Minimum bandwidth is 48 Kbit Total delay is 25000 Microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 1 |
C.
| 10.1.0.3 (Serial0), from 10.1.0.3, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (46866176/46354176), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is 56 Kbit Total delay is 45000 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 |
D.
| 10.1.1.1 (Serial0.1), from 10.1.1.1, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (46763776/46251776), Route is External Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is 56 Kbit Total delay is 41000 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 |
Answer: B
Explanation
To be the feasible successor, the Advertised Distance (AD) of that route must be less than the Feasible Distance (FD) of the successor. From the output of the “show ip eigrp topology 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.255″ we learn that the FD of the successor is 41152000.
Now we will mention about the answers, in the “Composite metric is (…/…)” statement the first parameter is the FD while the second parameter is the AD of that route. So we need to find out which route has the second parameter (AD) less than 41152000 -> only answer B satisfies this requirement with an AD of 128256.
Question 6
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
A. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
B. Router# show ip eigrp topology
C. Router#show ip eigrp interfaces
D. Router#show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D
Explanation
Below is an example of the show ip eigrp neighbors command. The retransmit interval (Smooth Round Trip Timer – SRTT) and the queue counts (Q count, which shows the number of queued EIGRP packets) for the adjacent routers are listed:

Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. How many paths can the EIGRP routing process use to forward packets from HQ_Router to a neighbor router?
| HQ_Router# show ip protocols Routing Protocol is “eigrp 109″ Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Default networks flagged in outgoing updates Default networks accepted from incoming updates EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 EIGRP maximum hopcount 100 EIGRP maximum metric variance 3 Redistributing: eigrp 109 EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s Automatic network summarization is not in effect Maximum path: 4 Routing for Networks: 20.10.10.0/24 172.30.10.0/24 192.168.1.0 Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 20.10.10.2 90 00:13:12 172.30.10.2 90 01:13:06 Distance: internal 90 external 170 HQ_Router# |
A. two equal-cost paths
B. two unequal-cost paths
C. three equal-cost paths
D. three unequal-cost paths
E. four equal-cost paths
F. four unequal-cost paths
Answer: F
Explanation
The “Maximum path: 4″ means EIGRP can use up to 4 equal-cost paths to forward packets from HQ_Router to a neighbor router. But here the variance is set to 3 which allows unequal-cost paths. Therefore in this case EIGRP can use up to four unequal-cost paths.
Question 8
IP address and routing for the network are configured as shown in the exhibit. The network administrator issues the show ip eigrp neighbors command from Router1 and receives the output shown below the topology. Which statement is true?
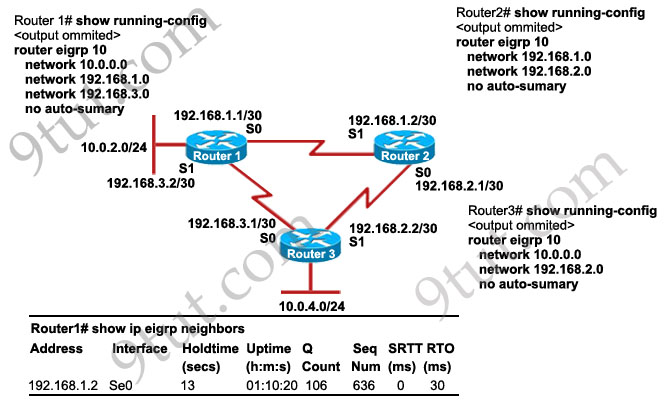
A. It is normal for Router1 to show one active neighbor at a time to prevent routing loops.
B. Routing is not completely configured on Router3.
C. The IP addresses are not configured properly on the Router1 and Router3 interfaces.
D. The no auto-summary command configured on the routers prevents Router1 and Router2 from forming a neighbor relationship.
Answer: B
Explanation
From the output of Router1, we learn that Router1 has not established neighborship with R3 yet. Also from the “show running-config” on Router3 we notice that the “network 192.168.3.0″ statement is missing -> the configuration on Router3 is not complete.



@tohritz: Yes, it is what I mean!
@9tut:
Thanks for the clarification mate. I’m taking the exam by the 3rd week of January. Your site really helps a lot.
hey guys – i found a free eigrp configuration video:
http://www.bosscbt.tv/icnd2/eigrp-required-configurations-verification/
enjoy!
Can someone please provide me the latest dumps, email – patel_divyesh13@hotmail.com.
Thanks in advance.
i want to inquire about the 1st question that AS number should b same in order to communicate but in question 1 the answer is to change the AS number. how?
@tariq: For example, EIGRP AS number should be 300:
R1>en
R1#conf t
R1(config)#router eigrp 300
R1(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#exit
R1#copy run start
R2>en
R2#conf t
R2(config)#router eigrp 300
R2(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#exit
R2#copy run start
After that EIGRP AS number will be the same and routers will able to communicate.
thnx alot DimS
Hi, I’m taking the test in 2 weeks. Can someone plz send me the latest dumps sonnynh@yahoo.com
Thanks so much =)
plz send me the latest dumps
My Id s.mohanmca86@gmail.com
Any news about A defector’s unexplainable disappearance?
Hello,
Taking exam in 2 weeks can someone please send the latest dumps to:
yudayuda(at)yahoo(dot)com
Thanks
Hi everyone,
Would you guys please explain for me this question:
http://img103.herosh.com/2012/01/03/792457050.jpg
Thanks in advance.
In that question, I dont know what they based on to get the answer F. As we know, there are maximum 4 equal-cost paths by default in routing table.
The variance number for calculate equal-cost paths is used as following rule:
Variance number x FD = product
Any FS who metric is less than above product is considered to be equal route and may be placed in routing table.
In the output exhibit, we have 2 noticeable numbers:
-the variance number is set 3
-maximum equal-cost paths is 4.
Hm, still dont get it. ???
Question guys regarding eigrp configuration. i guess there are a lot of ways on how to advertise the network. What’s the best way and why would you think this is better than the others?
example for networks: 192.168.1.0 /24; 172.168.16.0/24; and 10.11.8.0/24
Would it be a better option to include a wild card like:
router eigrp 100
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 172.168.16.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.11.8.0 0.0.0.255
no auto-summary
a bit confused, since i read somewhere that i can also use a summary wild card.
TIA
@hai
i think “variance X” means that the router will use paths that have a cost of as low as 1/X of the best path… am i wrong?
@xallax:
Let see what is the definition of the variance.
According to Wendell Odom, page 400 of the CCNA ICND 2 book:
“variance allows routes who metrics are relatively close in value to be considered equal, allowing multiple unequal-metric routes to the same subnet to be added to the routing table”
“Variance multiplier EIGRP router subcommand defines an interger between 1 and 128. The router then multiplies the variance times a route’s FD- the best metric with which to reach that subnet. Any FS routes who metric is less than the product of variance times the FD are considered to be equal routes and may be placed in the routing table, depending on the setting of the maximum-paths command”
Example from that book: routes from R4 to a certain network through R1, R2, and R3 have metrics (50/30), (90/40), and (120/60) respectively—> the successor route is 50 (FD)-the route through R1; and the FS is 40- the route through R2.
-If variance is 1 then we have 50×1=50–> route through R1 is added to routing table because it matches exactly with the successor route (definitely equal).
-If variance is 2 then we have 50×2=100—> routes through R1 and R2 were added to routing table because their FD 50 and 90 respectively lower than 100.
-If variance is 3 then we have 50×3= 150—> all three FDs are less than 150 but the route through R3 is NOT added to routing table because its FD is not the FS.
That’s all about the variance number.
Hm, this question is fairly tricky.
All the answers mention to equal or unequal-cost path that makes me think of the variance, but the question is about the processing of forward packets to a neighbor router, NOT for a network, that makes me think of the two gateways with the default distance (90).
Anyone help me out???
All right, I might explain that answer as following:
-if the variance is not 1 (default) that means the router will load UNEQUAL-cost paths to its routing table.
-the maximum paths cost by the default is 4 (can be set up to 16)
Hi eveyone,
I just ask my master about that question, he said because the output exhibits that there are two gateways for 2 neighbors, therefore the answer should be 2 unequal-cost paths. Any comment?
@hai
so… a maximum of 4 paths if there were 4 gateways?
@xallax:
Yes, the number of gateways will tell us about actual paths to get the neighbors
@hai
so the answer is 2 unequal cost paths… brilliant :)
thank you for sharing this
Question guys regarding eigrp configuration. i guess there are a lot of ways on how to advertise the network. What’s the best way and why would you think this is better than the others?
example for networks: 192.168.1.0 /24; 172.168.16.0/24; and 10.11.8.0/24
Would it be a better option to include a wild card like:
router eigrp 100
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
network 172.168.16.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.11.8.0 0.0.0.255
no auto-summary
a bit confused, since i read somewhere that i can also use a summary wild card.
TIA
For variance, just say you have 4 paths. and by default variance is one meaning it will not unequal-cost load balance…it will take the path with best OVERALL bandwidth/delay metric of the 4, meaning the addition of all bandwidths of all routers and connections from start to finish. Hence, eigrp shares topology tables of all routers in its autonomous system AS, and puts its best path in the routing table. but there should be many feasible paths in the topology table , too for this to work.
so path
1. 550 + 725 = 1275
2. 1250 + 1310= 2560
3. 2200 + 635 = 2835
4. 1500 + 100 + 635 = 2235
by default, path 1 wins because it has the lowest value. but now you want to unequal load 2 paths. so you would pick the second best. You must multiply the best by 2 and see if that value is less than the second best. if it is then you would use command variance 2. Hence, 2 times 1275 is 2550, and 2550 is more than 2235, the second best. if it was higher than 2550 than maybe a variance 3 command, just do the simple math.
with EIGRP you have the option to use wild card mask but not mandatory, if you do it just makes the summarization process a little different in a better way, maybe more accurate or just simply the way you want it.
If you take the no auto summary approach with no mask, then it will see the tables as classful since eigrp is hybrid. adding masks will make the CIDR process perform. i recommend no auto summary with the masks.
@eddie:
if i use the no auto-summary approach with no mask, how will i type the network statement?
network 10.0.0.0
no auto-summary
or
network 10.11.8.0
no auto-summary
with no auto summary and no mask, it sees it like RIPv1 does
both are Class a and so they have no mask, so they will be tied together in the routing process like RIPv1.
it is hard to believe, but EIGRP will work like RIPv1 if no mask is used….reguardless if there is no auto sum or not… In the exam, you dont have to worry about it…because they give you class c.
with no submasks, static routes are used down the paths of the remote routers…
@eddie
you mentioned about RIPv1, what about RIPv2? say my loopback address is: 10.0.8.1 /24, what shall i type to advertise the network?
router rip
version 2
network 10.0.0.0
no auto-summary
or
router rip
version 2
network 10.0.8.0
no auto-summary
Can Someone please send me the latest dump, i am going to take the exam next week.
hd1expectra@pelayo.com
Hi Guys.
Have a question. I read somewhere on these comments that the EIGRP supports upto a maximum of 16 unequal -cost paths. I also read from the CCNA Portable Command Guide that the maximum number of paths supported are 6. Someone please clarify this as am confused.
Thanks
there is no any difference you can any one . but thing that wild card mask is optional .if you are confuse do one thing take 2 router and in 1 router use normal and in the 2ed router use wild card .i already done this there no any difference.one’s again wildcard mast is OPTIONAL.
Have a question. I read somewhere on these comments that the EIGRP supports upto a maximum of 16 unequal -cost paths. I also read from the CCNA Portable Command Guide that the maximum number of paths supported are 6. Someone please clarify this as am confused.
see thing that by defult eigrp support 4 equal lode balance and eigrp support across up to 16 equal or unequal links…
Thank you everyone for information.
Can anyone please send me the dumbs you are talking about? berthavillamil7@hotmail.com Thank you
Thank you BfromA it was nice video
http://www.bosscbt.tv/icnd2/eigrp-required-configurations-verification
am going to take ma xam on this 2nd feb(third attempt)…if any new dumps inform me pls..thanks in advance
hello all
Can we use ” ? ” operator in exam simulator?
Yes we can use ? in exam simulator
passive-interface …” command somewhere in R1 configuration. in the above sim 9tut explained abt that(in eigrp lab qtn)…then using which command we will check that 1 is present or not….iam going to write ma xam tomorrow so pls give me a fast rply…..thanks in advance
Hi,
I have no idea how to practical question will be like in exam. can anyone tell me the how it will be. if you have any pdf which helps me to prepare for exam pls mail to harish7722@gmail.com
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
How can i advertise a default route using eigrp?
@Sofia: e.g.:
Int f0/0 – link with default route
conf t
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.10.2
int f0/0
ip add 192.168.10.1
exit
router eigrp AS_NUMBER
redist static
passive f0/0
net x.x.x.x
net y.y.y.y
^Z
@DimS
Thank you so much. Its working
Passed my CCNA exam 31-02-2012
Got Marks 881/1000
Very important LABS Eigrp.
MUST MUST MUST
Passed my CCNA exam 31-02-2012
Got Marks 881/1000
Very important LABS Eigrp.
MUST MUST MUST
faisalfcc2004@gmail.com
http://www.youtu.be/gg9jaPKFGKY
please guys am writing on friday 17th, can somebody send me the latest dumps, to revise
olivehez@yahoo.com
Latest dumps please!
aseem.chhab@gmail.com
Taking exam this friday. Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps.
alvinlim0502@yahoo.com.sg