CCNA – EIGRP Questions
Here you will find answers to EIGRP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about EIGRP, please read my EIGRP tutorial
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit, when running EIGRP what is required for R1 to exchange routing updates with R3?
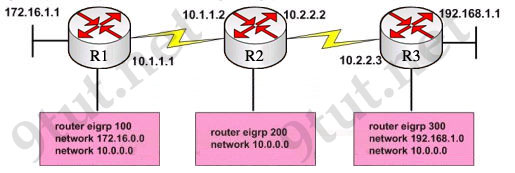
A – AS numbers must be changed to match on all the routers
B – Loopback interfaces must be configured so a DR is elected
C – The no auto-summary command is needed on R1 and R3
D – R2 needs to have two network statements, one for each connected network
Answer: A
Question 2:
As a Cisco technician, you need to know EIGRP protocol very well. Which of the following is true about EIGRP successor routes? (Choose two)
A – A successor route is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to a destination
B – Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process
C – Successor routes are flagged as “active” in the routing table
D – A successor route may be backed up by a feasible successor route
E – Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process.
Answer: A D
Explanation:
B is not correct because neighbor table only contains a list of directly connected EIGRP routers that have an adjacency with this router, it doesn’t contain successor routes.
C is not correct because successor routes are not flagged as “active”, they are always the best route to reach remote networks and are always used to send packets.
A and D are correct because successor route is the best and primary route to a remote network. It is stored in the routing table and topology table. If this route fails, a backup route (called feasible successor route) in the topology table will be used to route traffic to a destination.
Question 3:
Which two statements are true regarding EIGRP? (Choose two)
A – Passive routes are in the process of being calculated by DUAL
B – EIGRP supports VLSM, route summarization, and routing update authentication
C – EIGRP exchanges full routing table information with neighboring routers with every update
D – If the feasible successor has a higher advertised distance than the successor route, it becomes the primary route
E – A query process is used to discover a replacement for a failed route if a feasible successor is not identified from the current routing information
Answer: B E
Explanation:
Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) is the algorithm for selecting and maintaining the best path to each remote network. DUAL tracks all the routes advertised by neighbors and selects routes based on feasible successors. It inserts lowest cost paths into the routing table (these routes are known as primary routes or successor routes) -> A is not correct.
EIGRP is still a distance-vector protocol, but has certain features that belong to link-state algorithms (like OSPF) than distance-vector algorithms. For example, EIGRP sends a partial routing table update, which includes just routes that have been changed, not the full routing table like distance-vector algorithms -> C is not correct.
The feasible successor route will become the primary route when its advertised distance is lower than the feasible distance of the successor route. The feasible successor route can be used in the event that the successor route goes down. Notice that the feasible successor route does not get installed in the routing table but is kept in the topology table as a backup route -> D is not correct.
“Support VLSM, route summarization, and routing update authentication” are the features of EIGRP -> B is correct.
When a route fails and has no feasible successor, EIGRP uses a distributed algorithm called Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to discover a replacement for a failed route. When a new route is found, DUAL adds it to the routing table -> E is correct.
Question 4
Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
A. a primary route,stored in the routing table
B. a backup route,stored in the routing table
C. a backup route,stored in the topology table
D. a primary route,stored in the topology table
Answer: C
Explanation
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance is less than the Feasible Distance of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but stored in the topology table.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output from the show ip eigrp topology command, which router is the feasible successor?
| router# show ip eigrp topology 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.255 IP-EIGRP topology entry for 10.0.0.5/32 State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 41152000 |
A.
| 10.1.0.1 (Serial0), from 10.1.0.1, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (46152000/41640000), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is 64 Kbit Total delay is 45000 Microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 |
B.
| 10.0.0.2 (Serial0.1), from 10.0.0.2, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (53973248/128256), Route is Internal Vector Metric: Minimum bandwidth is 48 Kbit Total delay is 25000 Microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 1 |
C.
| 10.1.0.3 (Serial0), from 10.1.0.3, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (46866176/46354176), Route is Internal Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is 56 Kbit Total delay is 45000 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 |
D.
| 10.1.1.1 (Serial0.1), from 10.1.1.1, Send flag is 0×0 Composite metric is (46763776/46251776), Route is External Vector metric: Minimum bandwidth is 56 Kbit Total delay is 41000 microseconds Reliability is 255/255 Load is 1/255 Minimum MTU is 1500 Hop count is 2 |
Answer: B
Explanation
To be the feasible successor, the Advertised Distance (AD) of that route must be less than the Feasible Distance (FD) of the successor. From the output of the “show ip eigrp topology 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.255″ we learn that the FD of the successor is 41152000.
Now we will mention about the answers, in the “Composite metric is (…/…)” statement the first parameter is the FD while the second parameter is the AD of that route. So we need to find out which route has the second parameter (AD) less than 41152000 -> only answer B satisfies this requirement with an AD of 128256.
Question 6
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
A. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
B. Router# show ip eigrp topology
C. Router#show ip eigrp interfaces
D. Router#show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D
Explanation
Below is an example of the show ip eigrp neighbors command. The retransmit interval (Smooth Round Trip Timer – SRTT) and the queue counts (Q count, which shows the number of queued EIGRP packets) for the adjacent routers are listed:

Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. How many paths can the EIGRP routing process use to forward packets from HQ_Router to a neighbor router?
| HQ_Router# show ip protocols Routing Protocol is “eigrp 109″ Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Default networks flagged in outgoing updates Default networks accepted from incoming updates EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0 EIGRP maximum hopcount 100 EIGRP maximum metric variance 3 Redistributing: eigrp 109 EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s Automatic network summarization is not in effect Maximum path: 4 Routing for Networks: 20.10.10.0/24 172.30.10.0/24 192.168.1.0 Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 20.10.10.2 90 00:13:12 172.30.10.2 90 01:13:06 Distance: internal 90 external 170 HQ_Router# |
A. two equal-cost paths
B. two unequal-cost paths
C. three equal-cost paths
D. three unequal-cost paths
E. four equal-cost paths
F. four unequal-cost paths
Answer: F
Explanation
The “Maximum path: 4″ means EIGRP can use up to 4 equal-cost paths to forward packets from HQ_Router to a neighbor router. But here the variance is set to 3 which allows unequal-cost paths. Therefore in this case EIGRP can use up to four unequal-cost paths.
Question 8
IP address and routing for the network are configured as shown in the exhibit. The network administrator issues the show ip eigrp neighbors command from Router1 and receives the output shown below the topology. Which statement is true?
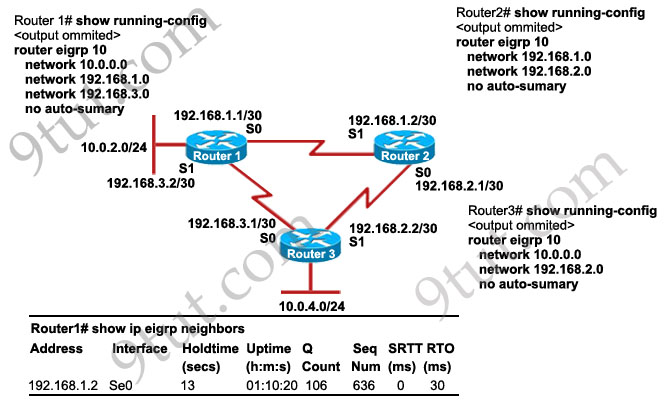
A. It is normal for Router1 to show one active neighbor at a time to prevent routing loops.
B. Routing is not completely configured on Router3.
C. The IP addresses are not configured properly on the Router1 and Router3 interfaces.
D. The no auto-summary command configured on the routers prevents Router1 and Router2 from forming a neighbor relationship.
Answer: B
Explanation
From the output of Router1, we learn that Router1 has not established neighborship with R3 yet. Also from the “show running-config” on Router3 we notice that the “network 192.168.3.0″ statement is missing -> the configuration on Router3 is not complete.



Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps.vidya.r.pai@gmail.com
Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps.
vidya.r.pai@gmail.com
Could someone please send me the latest dump on, lalo0227@gmail.com. Thank you….
needing to recert.. does anyone know of a free (unlimited) reader for the dumps??
these VCE files are wanting a reader but all I can find cost bucks..
and the “free” readers limit to the same 5 questions each time I launch..
the answer of Question No.7 should be F. four unequal-cost paths
Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps. waynezliu@gmail.com
Q. no. 7
The variance is not 1. Here it is 3.
In this case, can you explain the ans. E.
more elaborately, Please.
Thank-you 9tut.
Hi Jink,
Q. no 7.
Please Can you explain, why you think the correct ans is ‘F’ . Thank-you.
hello everyone, i can’t access ccna training lab. do you have another link like that?
thanks :)
I think the Answer to the question 7 is incorrect. The answer should be 4 unequal cost paths.
Here is another similar question from the same website ICND2 though:
http://www.9tut.net/icnd2/eigrp-questions
Question 2
HQ_Router# show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “eigrp 109″
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing: eigrp 109
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Automatic address summarization: 20.0.0.0/0 for FastEthernet0/1
Summarizing with metric 28160 172.30.0.0/16 for FastEthernet0/0
Summarizing with metric 28160
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
20.0.0.0
172.30.0.0
192.160.1.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
20.10.10.2 90 260796
172.30.10.2 90 454765
Distance: internal 90 external 170
How many paths can the EIGRP routing process use to forward packets from HQ_Router to a neighbor router?
A. two equal-cost paths
B. two unequal-cost paths
C. three equal-cost paths
D. three unequal-cost paths
E. four equal-cost paths
F. four unequal-cost paths
Answer: E
Explanation
Because the “EIGRP maximum metric variance” is 1 so only equal-cost paths are used.
The “Maximum path” is 4 so EIGRP can use up to 4 paths to forward packets.
Therefore EIGRP can only use four equal-cost paths -> E is correct.
Notice: This question has another version with “EIGRP maximum metric variance” is set to a value greater than 1 than the answer should be “four unequal-cost paths” can be used.
Q7
please go to this link “https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/docs/DOC-7436″ and download the attachment “Comparison DataSheet of Routing Protocols RIP EIGRP OSPF.xls”
from this comparison I learned that there are 4 Unequal cost paths in EIGRP by default.So which one is the correct? E? or F?
hi friends,
can anyone send dumps for my ccna exam and writing the exam very soon thanks.
ccna.krishna86@gmail.com
@Udana *@Q7
I m confused a bit too, but i believe it asked “How many paths ” so that is 4 paths (E) correct
If it would have asked how many equal-unequal paths the answer would have been 3 (F).
( 3 unequal as variance is 3 but 4 total as max-path is 4 )
@Q7
if metric variance is 1, then the answer is four-equal-paths
if metric variance is greater than 1, then the answer is four-unequal-paths
Q2.
Hi All
Is this true or only typo..?
D – A successor route may be backed up by a feasible successor route
Thnx
Hi All,
Can You explain how difference of four equal-cost paths and four unequal-cost paths?
Thnx
Q7
THE ANSWER SHOULD BE F , FOUR UNEQUAL COST PATHS BECAUSE VARIANCE >1.
IF VARIANCE EQUALS 1 ANSWER WOULD BE E.
REFERENCE:http://www.networkworld.com/community/node/19743
Surely the answer E is wrong.
Answer F is correct bcoz variance = 3 means we are using unequal load balancing and maximum paths are four so the answer is four unequal paths
Hi all,
is anybody from UK (Derbysh or Leicestershire area) ?
going to write exam on 28th march… can anyone send the dumps to prabhucs45@gmail.com..
Thanks in advance……
@9tut
Could you please confirm the answer for Q7?
@Saranya: My mistake. The answer for Q7 should be F – four unequal-cost paths. Thanks for your detection!
Yes, the correct answer to #7 is F, the variance command allows for unequal paths to be used in the routing table. The variance of 3 mean 3 times as bad as the successor and EIGRP in this question allows for 4 maximum paths. The variable n can take a value between 1 and 128. The default is 1, which means equal cost load balancing.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a008009437d.shtml
Hi All,
Can you explain. How to determine about successor route and feasible successor route in EIGRP?
Thnx
@nazty
the AD of the feasible successor must be less than the FD of the current successor. logic…
anyways, read more here: http://www.9tut.com/eigrp-routing-protocol-tutorial
you could start on the second page of the tutorial
q5:: i saw a question like this on the test
@xallax:
About Q3, I understand that AD of the feasible successor must be less than the FD of the current successor, in order to be in topology table and be a backup route if primary (successor) fails.
But, I don’t understand explanation of 9tut, that in that case: “The feasible successor route will become the PRIMARY route”?
@jelenna82
“primary route” means “successor” :)
:) They wrote in Expl.3: “The feasible successor route will become the primary route when its advertised distance is lower than the feasible distance of the successor route”. Isn’t it just a condition for becoming feasible route, not a successor, or I’m wrong?
@9tut
Q3, I think you could expand upon your explanation about why “A” is incorrect, especially what Passive and Active routes are as this (at least to me) is counter intuitive.
A Passive route is one whose metric has been calculated. As long as a feasible successor is alive ans in the topology table, a route should remain in the Passive state.
An Active route is one whose metric is currently under calculation by the DUAL algorithm due to there being no feasible successor available.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f07.shtml#rout_states
@Anonymous: Passive routes are stable routes and their metrics have been calculated, which means the DUAL algorithm is not running on these routes. For answer A, the correct statement should be:
“Active routes are in the process of being calculated by DUAL”.
HI. M GOING TO TAKE EXAM IN FIRST WEEK OF MAY. ANYBODY HAVING FRESH DUMPS. PLZ I NEED IT URGENT
MY EMAIL ID: nahidrauf@yahoo.com
Hi EVERYONE – I WOULD LOVE TO GET THE LATEST DUMP FROM ANYONE WHO CAN GIVE IT TO ME> Please!!! I am taking the exam on May 15th and really would appreciate it.
Thank you!!!!
erica3025@gmail.com
Erica
Hi, i am not able to access the link you idovpred, here is what i am getting when i try to use the link idovpred by you********All sharing functionality on FileSonic is now disabled. Our service can only be used to upload and retrieve files that you have uploaded personally.If this file belongs to you, please login to download it directly from your file manager.*********Can you help please. Thanks
Yes EIGRP is a distance covter, in the sense each router only knows about the routes held by the directly neighbouring routers, and it still learns routes via the routing by rumour method.Link State routing each router has a full map of the entire network, even what routers are behind otehr routers. and it uses this map to work out its routing table. I think of it as link state is like looking at a map, lets say you know you are standing in New York. Then say you want to get to Boston, you work out you route, and that determins what road you take out of new york. On the other hand distance covter is like standing in new at a cross roads with a hug sign post, which tells you what road to go down to start your journey to any city, and how far/long/hops it will take. (in the case of EIGRP, the sign post might point down several roads for the same destination, hence the redundancy) EIGRP by this definition is clearly a distance covter protocol. it is defiantly an enhanced version, and has many of the strenths of link state (fast convergence and resplendence) but is still is based on the distance covter model in how it learns its routes,
I used to be good in mathematics, so I ottured some neighbors. just like that I doubled my allowance and money. it wasn’t long before I found out that the more I taught the subject I could now absorb new lessons right away even the difficult one’s.
Hi everyone !! I need THE LATEST DUMP can u help please. Thanks
I will take the ICND2 again next Wednesday afternoon. I don’t care what the score is as long as I pass. I pasesd the CCNA 10 years ago but didn’t renew. It is a lot harder now.
If anyone taken exam please update the status and conform whether the dumps are valied….
Thanks in advance….
@Nazty
Diffrence between equal cost & unequal cost load balancing
if you have 2 links to the same network of 2 Mbps each, routing protocols will bundle them and work as 4 Mbps in total, sending 1 packet on one link and one packet to other. this is equal cost load balancing.
But what if you have one link of 2 Mbps and another 4 Mbps?
EIGRP comes to the rescue;It will detect one link is half of other, then will bundle them and send 2 packet on 4 Mbps while 1 packet on 2 Mbps link. this is unequal cost load balancing.
>>EIGRP comes to the rescue;It will detect one link is half of other, then will bundle them and send 2 packet on 4 Mbps while 1 packet on 2 Mbps link. this is unequal cost load balancing.
It was my main misunderstanding – I thought that EIGRP cares about every link bandwidth; but it doesn’t! It calculates metric according to minimum bandwidth of all th links on the path! So, if you are going to load-balance unequally, bandwidth is not a good choice – it’s worth to use delay!
And one more point about EIGRP:
In simulations VUE whats to get it’s answer (not the correct one). For example, in the routing CCNP exam there is EIGRP sim and it thinks that defining network by the exact IP (network 10.15.1.1 0.0.0.0) is incorrect, but whats to see classless net (network 10.15.1.0 0.0.0.255).
One more my misunderstanding was about network statement; remember:
1. If it’s written as “network 192.168.0.0″ – it’s equal to “network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255″ – so classful mask is applied; “network 10.0.0.0″ the same as “network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255″.
2. If you have two interfaces 10.0.1.1/24 & 10.0.2.1/24, then you can use either of declarations:
“network 10.0.0.0″
or “network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255″ + “network 10.0.2.0 0.0.0.255″
or “network 10.0.0.0 0.0.3.255″
or “network 10.0.1.1 0.0.0.0″ + “network 10.0.2.1 0.0.0.0″
Best regards!!!
PS: do not forget passive-interface in EIGRP… “passive-int default” rules! :)
do i have to configurations during ccna exam
q7 what i understand when variance >1 it has unequal-route equal to maximum path
but when variance is 1 it has equal-route equal to max path i am right
Hi all, I am taking CCNA 640-802 exam first time on 30/05/2012. Could anyone please send me latest dumps which are valid for UK? My e-mail address is puneet_gill84@yahoo.co.uk. Many thanks.
Mbwana — I agree with you — variance 1 then possible for equal cost paths is 4??
q7
@jelenna82
i think you’re right about Q3, ” feasible successor ” will become a back-up route and be put in the topology table if it satisfies the condition, which is – it must have a lower AD… :-)
Hi Can anybody send me latest dumps valid for usa to my mail id, basavarajpardi@gmail.com.
thank you