CCNA – NAT & PAT Questions
Here you will find answers to NAT & PAT Questions
Note: If you are not sure about NAT & PAT, please read my NAT tutorial.
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What does the (*) represent in the output?
| 02:16:29: NAT: s=10.10.0.2->1.2.4.2, d=1.2.4.1 [51607] 02:16:29: NAT: s=1.2.4.1, d=1.2.4.2->10.10.0.2 [55227] 62:16:29: NAT*: s=10.10.0.2->1.2.4.2, d=1.2.4.1 [51608] 02:16:29: NAT*: s=10.10.0.2->1.2.4.2, d=1.2.4.1 [51609] |
A. Packet is destined for a local interface to the router.
B. Packet was translated, but no response was received from the distant device.
C. Packet was not translated, because no additional ports are available.
D. Packet was translated and fast switched to the destination.
Answer: D
Explanation
The above output is from the “debug ip nat” command. In this output, the first two lines show the Domain Name System (DNS) request and reply debugging output.
In the first line (DNS request):
s=10.10.0.2->1.2.4.2: source of the IP address (10.10.0.2) and how it is being translated (to 1.2.4.2)
d=1.2.4.1: destination address of the packet
[51607]: the IP identification number of the packet
In the second line (DNS reply):
s=1.2.4.1: source of the reply
d=1.2.4.2->10.10.0.2: how the destination is being translated
The remaining lines show debugging output from a Telnet connection from a host on the inside of the network to a host on the outside of the network. All Telnet packets, except for the first packet, were translated in the fast path, as indicated by the asterisk (*).
Note: If the connection is already established, the security appliance does not need to re-check packets and the packets are sent to the Fast Path.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_3t/debug/command/reference/dbg_i2gt.html)
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. What command sequence will enable PAT from the inside to outside network?
| ip nat pool isp-net 1.2.4.10 1.2.4.240 netmask 255.255.255.0 ! interface ethernet 1 description ISP Connection ip address 1.2.4.2 255.255.255.0 ip nat outside ! interface ethernet 0 description Ethernet to Firewall eth0 ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 |
A. (config)# ip nat pool isp-net 1.2.4.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 overload
B. (config-if)# ip nat outside overload
C. (config)# ip nat inside source list 1 interface ethernet1 overload
D. (config-if)# ip nat inside overload
Answer: C
Explanation
The command “ip nat inside source list 1 interface ethernet1 overload” means:
+ “ip nat”: use NAT
+ “inside”: NAT from inside to outside
+ “source list 1″: the source addresses can be found in access list 1
+ “interface ethernet1″: NAT out of this interface
+ “overload”: use NAT overload (PAT)
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. A junior network engineer has prepared the exhibited configuration file. What two statements are true of the planned configuration for interface fa0/1? (Choose two)

A. The two FastEthernet interfaces will require NAT configured on two outside serial interfaces.
B. Address translation on fa0/1 is not required for DMZ Devices to access the Internet.
C. The fa0/1 IP address overlaps with the space used by s0/0.
D. The fa0/1 IP address is invalid for the IP subnet on which it resides.
E. Internet hosts may not initiate connections to DMZ Devices through the configuration that is shown.
Answer: B E
Explanation
Both inside FastEthernet interfaces can use only one outside interface to go to the Internet -> A is not correct.
DMZ devices use IP addresses in the range of 128.107.1.128/25 which are public IP addresses so they don’t need address translation to access the Internet -> B is correct.
The fa0/1 interface’s IP address is 128.107.1.254 255.255.255.128 (range from 128.107.1.128 to 128.107.1.255) while the IP address of s0/0 is 128.107.1.1 255.255.255.252 (ranges from 128.107.1.0 to 128.107.1.4) so they are not overlapped with each other -> C is not correct.
DMZ devices are in the range of 128.107.1.128/25 (from 128.107.1.128 to 128.107.1.255) and fa0/1 IP address (128.107.1.254) is a valid IP address on this subnet -> D is not correct.
DMZ devices (and other internal hosts) are using dynamic PAT, which is a type of dynamic NAT. With dynamic NAT, translations do not exist in the NAT table until the router receives traffic that requires translation. In other words, if DMZ devices communicate with outside hosts first, dynamic translation works fine. But if outside hosts communicate with DMZ devices first, no translation is created in NAT table and the packets will be dropped. This is the reason why “Internet hosts may not initiate connections to DMZ Devices through the configuration that is shown” -> E is correct.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. What statement is true of the configuration for this network?

A. The configuration that is shown provides inadequate outside address space for translation of the number of inside addresses that are supported.
B. Because of the addressing on interface FastEthernet0/1, the Serial0/0 interface address will not support the NAT configuration as shown.
C. The number 1 referred to in the ip nat inside source command references access-list number 1.
D. ExternalRouter must be configured with static routers to network 172.16.2.0/24
Answer: C
Explanation
The “list 1″ refers to the access-list number 1.
Question 5
What are two benefits of using NAT? (choose two)
A. NAT protects network security because private networks are not advertised.
B. NAT accelerates the routing process because no modifications are made on the packets.
C. Dynamic NAT facilitates connections from the outside of the network.
D. NAT facilitates end-to-end communication when IPsec is enable.
E. NAT eliminates the need to re-address all host that require external access.
F. NAT conserves addresses through host MAC-level multiplexing.
Answer: A E
Explanation
By not reveal the internal Ip addresses, NAT adds some security to the inside network -> A is correct.
NAT has to modify the source IP addresses in the packets -> B is not correct.
Connection from the outside of the network through a “NAT” network is more difficult than a more network because IP addresses of inside hosts are hidden -> C is not correct.
In order for IPsec to work with NAT we need to allow additional protocols, including Internet Key Exchange (IKE), Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) -> more complex -> D is not correct.
By allocating specific public IP addresses to inside hosts, NAT eliminates the need to re-address the inside hosts -> E is correct.
NAT does conserve addresses but not through host MAC-level multiplexing. It conserves addresses by allowing many private IP addresses to use the same public IP address to go to the Internet -> F is not correct.
Question 6
Which two statements about static NAT translations are true? (choose two)
A. They are always present in the NAT table.
B. They allow connection to be initiated from the outside.
C. They can be configured with access lists, to allow two or more connections to be initiated from the outside.
D. They require no inside or outside interface markings because addresses are statically defined.
Answer: A B
Explanation
With static NAT, translations exist in the NAT translation table as soon as you configure static NAT command(s), and they remain in the translation table until you delete the static NAT command(s).
With dynamic NAT, translations do not exist in the NAT table until the router receives traffic that requires translation. Dynamic translations have a timeout period after which they are purged from the translation table.
-> A is correct.
Because static NAT translations are always present in the NAT table so outside hosts can initiate the connection without being dropped -> B is correct.
Static translations can not be configured with access lists. To configure static NAT, we only need to specify source IP, NAT IP, inside interface & outside interface.
-> C is not correct.
We have to specify which is the inside and outside interface -> D is not correct.
For your information, below is an example of configuring static NAT:
R0(config)#int f0/0
R0(config-if)#ip nat inside
R0(config-if)#int f0/1
R0(config-if)#ip nat outside
R0(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.1 200.0.0.2
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk361/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f31.shtml)
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about packet addresses are true during data exchange when host A makes Web-request to WWW Server, considering that there is NAT overload scheme for data passing from Corp LAN hosts to outside networks in use?
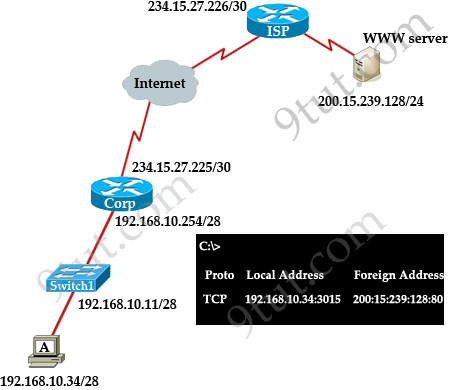
A. Source 234.15.27.226:3015 and destination 234.15.27.225:80
B. Source 200.15.239.128:3015 and destination 192.168.10.34:80
C. Destination 192.168.10.11:3015 and source 200.15.239.128:80
D. Source 192.168.10.34:80 and destination 192.168.10.254:3015
E. Destination 234.15.27.225:3015 and source 200.15.239.128:80
Answer: E
Explanation
From A to Corp router:
+ Source: 192.168.10.34: 3015 & Destination: 200.15.239.128:80
From Corp to WWW Server:
+ Source: 234.15.27.225:3015 & Destination: 200.15.239.128:80
From WWW Server to Corp:
+ Source: 200.15.239.128:80 & Destination: 234.15.27.225:3015
From Corp to Host A:
+ Source: 200.15.239.128:80 & Destination: 192.168.10.34:3015
So the only correct answer is E (from WWW server to Corp)



I PASSED CCNA EXAM TODAY THANKS TO ALL MIGHTY ALLAH
960/1000
Pls can’t sum1 explain question 7.
@sez
easy enough. remember that overload infers PAT.
So examine which port it will be leaving on 192.168.10.34:3015
Port is 3015. Because it is PAT the ip is stripped and replaced by the outside 234.15.27.255 and the port number is added. 234.15.27.255:3015
plz can sumone send me the latest dumps for ccna at shaikhhayee@yahoo.com? as i have my test in next week. thankz
@abdul hayee
Lun te charrh !! Dumps mangda rehnda ae har wele… Phuddi da… !!
Q-7 :
whenever you see a word ‘overloading’ it means PAT is used and public IP of router interface is used in translations. Here, Corp router is translating addresses from private to single public IP.
Q 7
keyword is ‘data exchange’, either direction, they want to know whats a possible destination and source address. the ‘overload’ is just there to confuse you, has nothing to do with source and destination, ‘overload’ has to do with port numbers.
sorry, with the overload, it does remind you you will need the translated address.
Could you send me the dump to booksonoffer@yahoo.com? Thanks!
could someone send me latest dump to tatendamacha@yahoo.com,for CCNA,Thanks…
I passed my ccna exam today Praise be to God! Thank you Jesus! and thanks to 9TUT for the tutorials and explanations, great site and thanks to xallax for your explanations to questions and thanks to http://www.examcollection.com for the dumps. Pls guys lets donate and help to keep this site up!
48 ques for exams including 3 simulation, I had EIGRP, Acesslist2 and VTP . Make sure you practice the simulation, use packet tracer or gns3. Best wishes to all!
http://www.freeimagehosting.net/tjl6i
could someone tell me why it’s C?
@moomoo
look at the interface at the bottom, it is configured as sub-interface.
Regard Q1. Base on what criteria to determined the communication ( option c and d) are telnet
@pheryl , nice observation !!
please mail me the 64 bit crack file for Virtual CertExam Manager guys…………i need the 64 bit file…….
mail it to vipin.heat@gmail.com
Thanks
Muham, please explain. I’ve seen mentioned a couple of times that you got a very high score on the CCNA exam thanks to “ALL MIGHTY ALLAH”? What does mighty allah have to do with it??
I need to do exam ccna 640-802
could someone help
Não percebo nada disto
please mail me the 64 bit crack file for Virtual CertExam Manager guys @ smsmutubuki409@gmail.com
Touchdown! That’s a really cool way of pttiung it!
TO GIBA What kind of help do you need?
Q5 -
Actually the reason why D is not correct is that, in fact, unless we use NAT-Traversal, NAT BREAKS IPsec. So actually NAT DIFFICULTS end-to-end communication when IPsec is used.
In sim questions if get and address rage (eg: IP address: 192.168.0.193 –
192.168.0.206 )and without giving any subnetmask , how can we create the accesslist to this range?what will be the network address of this range?
============================================
Original Question:
You are the network administrator at Ranet, and have to
config the Ranet-GW router via Console Terminal to let
hosts in our LAN that have IP address: 192.168.0.193 –
192.168.0.206 can connect to the internet.
Your ISP has given global IP for 6 IP as 25.5.5.65 –
25.5.5.70.
Remark: 1. Use ACL no.1 for Local IP list.
2. Use pool name “Ranet” for Global IP list.
I want to know how they are calculating the network address. Because we only have a address range, and any one can assign any network address … plz help me
193=11000001
206=11001110
So 1100 common from left. 1(128)+1(64)+0+0=192
So network address is 192.168.0.192/28
thanks Bhupendra ,
But someone can use the subnet mask as /27,because the given address range is also includes within this mask, how can we say that /28 is the mask for that?
Hi Muditha! My understanding is that if one less bit is used for the network mask->more hosts are selected. For the case of ACL, the goal is to control the range of IP addresses permitted/denied. So in this case /28 is chosen over /27.
In this case it’s to allowed the private IP range to use the 6 public IP->the ACL goal is to control the IP range permitted.
147. Refer to the exhibit. Which command would allow the translations to be created on the router?
Q: 147 http://certcollection.org/forum/topic/23269-some-questions/
Can someone help me by explaining the question and answer ? And what is “prefix-length” here please ??
@Alboma: thanks friend I got it now …. !!!!!!
please Help above my question…
Hi Jamshed! I saw the post from there explaining prefix-length 19 means /19
And the question looks similar to the Q from Muditha
In the 3rd octet, the range is 128-135
128 = 10000000
135 = 10000111
So /19 is chosen over /18 as /18 will allow 8 more host IPs, i.e. 128-143, which is beyond the range as given.
Oops I think I screw up with the mask, the last part I’m referring to is using /20 mask. But the idea is same, one less network bit used->more hosts
hello. m writting on the 15th, can someone send me the latest dumps on nontobekog@yahoo.com
http://www.freeimagehosting.net/fx4l1
can someone explain to me why the answer is letter C?
Hi Thenjlos,
The best one..
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.ActualTests.640-802.v2012-07-15.by.Sekhar.697q.vce.file.html
hello associates,,can someone send me the latest dumps guys my e-mail kipbenard@yahoo.com..thank you in advance…
hellow send me this week’s ccna dumps to my mail john.karago@yahoo.com
can u help me this my email address kev_jovellanos92@yahoo.com
please send me the latest dump
for the q1
1. how can we identify dat first 2 lines show the dns request & reply?
2. how can we identify dat last 2 lines show the dat its a telnet connection?
3.in the explaination, i want to knw y does the first telnet packet not translated in fast path?
plz help me guys i hv my xm in few days………..tnx in advance
in q4 :
1. according to me since both fa0/1 & serial0/0 are on same network 128.107.1.0 y it is said that they dnt overlap?
2. if DMZ IPs dnt require NAT while going from inside to outside, as said in explanation, then y do the outside IPs (outside hosts) require the NAT to go from outside to inside(to go to DMZ) ?
plz help me …….tnx in advance……
@ AnkushK
For question 4.
1. answer. —-> No, F0/1 ( its in 128.107.1.0 subnet, 1st ip address of that particular subnet is assigned) and S0/0 ( last IP address will be assigned 128.107.1.128 subnet) are on the different subnet ( Check subbnetting).
2. As it is said, occurs only at time of initialization. Ex. If you ping from your end first, then the packet from outside N/w will not be dropped.
@ 9tut. Q7 is not well defined. the question is that the request is made from LAN to the web server. and we know that there is nat to convert the private address to the public. so for that reason i think + (Source: 192.168.10.34: 3015 & Destination: 200.15.239.128:80) was suppose to be part of the solution. because what we have as the ans is the response from the web server. think about this and update me
@ Sniffer
Q7 is right.
As you know NAT ing is the used for conversing IP address, in which the local LAN IP (Private IP) convert to PUBLIC IP (or IP from pool). Once the packet will forward to remote network the Private IP address will not be visible and through NAT and PAT process the Source IP will be changed, which is also secure.
This is the Main purpose of NAT ing
@AnkushK
For Ques 4
For 2nd Answer – First ping will not work because of the time that ARP takes to resolve IP address to its corresponding hardware MAC address.
I FEEL SO SOORY COAZ I COULD NOT UNDERSTAND ANY THING IN CCNA , SO DIFFNATLY I WILL FAIL THE EXAM NEXT WEEK
ALL THE BEST FOR ALL
Q5
D must be correct (does using NAT mean you cannot use IPSec?)
A is a consequental benefit (would one deploy NAT just to gain this as a benefit?).
This is my honest opinion, any other opinions on this?
Q3
Answer: B E
B. Address translation on fa0/1 is not required for DMZ Devices to access the Internet.
E. Internet hosts may not initiate connections to DMZ Devices through the configuration that is shown.
Explanation
DMZ devices (and other internal hosts) are using dynamic PAT, which is a type of dynamic NAT. With dynamic NAT, translations do not exist in the NAT table until the router receives traffic that requires translation. In other words, if DMZ devices communicate with outside hosts first, dynamic translation works fine. But if outside hosts communicate with DMZ devices first, no translation is created in NAT table and the packets will be dropped. This is the reason why “Internet hosts may not initiate connections to DMZ Devices through the configuration that is shown” -> E is correct.
How comes if B is also correct?
B. Address translation on fa0/1 is not required for DMZ Devices to access the Internet.
Is it because it Externat Router would not have a route, thus NAT would fix that only outbound and not on inbound?
One of questions from dump that is confusing my ans, can anyone explain the answer to me, pls?
interface serial1
ip address 200.2.2.18 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface fastethernet0
ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
speed auto
!
ip nat pool test 199.99.9.40 199.99.9.62 netmask 255.255.255.224
ip nat inside source list 1 pool test
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 200.2.2.17
!
access-list 1 permit 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.255
A host on the LAN is accessing FTP server across the Internet. Which of the following addresses could appear as a source address for the packets forwarded by the router to the destination server?
A. 10.10.0.1
B. 10.10.0.2
C. 199.99.9.3
D. 199.99.9.5
E. 200.2.2.17
F. 200.2.2.18
The dump said it was D. I don’t know why??? The pool assigned IP range was not covered 199.99.9.5. Is there any mistake?