CCNA – Operations 2
Here you will find answers to Operations Questions (part 2)
Question 1
On a network of one department, there are four PCs connected to a switch, as shown in the following figure:
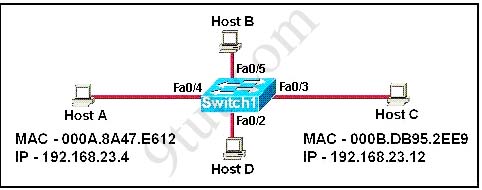
After the Switch1 restarts. Host A ( the host on the left ) sends the first frame to Host C (the host on the right). What the first thing should the switch do?
A. Switch1 will add 192.168.23.12 to the switching table.
B. Switch1 will add 192.168.23.4 to the switching table.
C. Switch1 will add 000A.8A47.E612 to the switching table.
D. None of the above
Answer: C
Explanation
When Switch1 receives the first frame from Host A, it will write Host A’s MAC address into its MAC address table (including the corresponding port Fa0/4) and flood the frame to all other ports.
Question 2
The user of Host1 wants to ping the DSL modem/router at 192.168.1.254. Based on the Host1 ARP table that is shown in the exhibit, what will Host1 do?
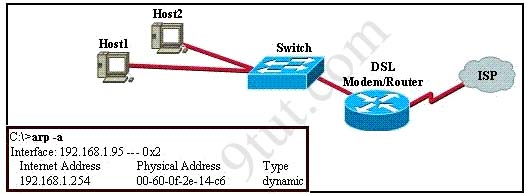
A. send a unicast ARP packet to the DSL modem/router
B. send unicast ICMP packets to the DSL modem/router
C. send Layer 3 broadcast packets to which the DSL modem/router responds
D. send a Layer 2 broadcast that is received by Host2, the switch, and the DSL modem/router
Answer: B
Explanation
Because Host1 has already had information about DSL modem so it doesn’t need to broadcast an ARP Request to find out the MAC address of DSL modem. It just needs to send unicast ICMP packets directly to that modem.
Question 3
Which two values are used by Spanning Tree Protocol to elect a root bridge? (Choose two)
A. amount of RAM
B. bridge priority
C. IOS version
D. IP address
E. MAC address
F. speed of the links
Answer: B E
Question 4
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two.)
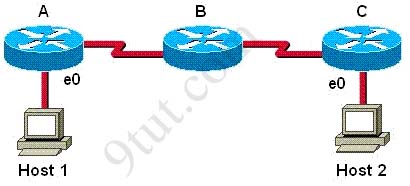
A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
Explanation
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. Its packets travel from routerA to routerB and router C. Router C (the last router) then broadcast an ARP frame onto the network looking for the MAC address of Host 2. If Host 2 can answer then router C can forward the frame. But e0 interface is down so no answer from Host 2 will be received so router C will send a Destination Unreachable message back to the originator. This message also informs that the middle network is still working correctly.
Also notice that the Destination Unreachable message is an ICMP message.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. The network shown in the exhibit is running the RIPv2 routing protocol. The network has converged, and the routers in this network are functioning properly. The FastEthernet0/0 interface on R1 goes down. In which two ways will the routers in this network respond to this change? (Choose two)

A. All routers will reference their topology database to determine if any backup routes to the 192.168.1.0 network are known.
B. Routers R2 and R3 mark the route as inaccessible and will not accept any further routing updates from R1 until their hold-down timers expire.
C. Because of the split-horizon rule, router R2 will be prevented from sending erroneous information to R1 about connectivity to the 192.168.1.0 network.
D. When router R2 learns from R1 that the link to the 192.168.1.0 network has been lost, R2 will respond by sending a route back to R1 with an infinite metric to the 192.168.1.0 network.
E. R1 will send LSAs to R2 and R3 informing them of this change, and then all routers will send periodic updates at an increased rate until the network again converges.
Answer: C D
Explanation
When Fa0/0 on R1 goes down, R1 will try to inform with R2 that its Fa0/0 interface is currently down. R2 in turn will inform to R3 that Fa0/0 of R1 is down. The split-horizon rule states that “a router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came”. It means when R1 sends information about its downed network 192.168.1.0, R2 is not allowed to send back that information to R1 -> C is correct.
But maybe you will ask “Why answer D is also correct when it seems contradictory to answer C?” Yes, it is really contradictory! This is called the “Poison Reverse” rule:
The poison reverse rule overwrites split horizon rule. For example, if router R2 receives a route poisoning of network 192.168.1.0 from router R1 then router R2 will send an update back to router R1 (which breaks the split horizon rule) with the same poisoned hop count of 16. This ensures all the routers in the domain receive the poisoned route update.
Notice that the “Poison Reverse” doesn’t send erroneous information to R1 but just only one message to make sure R1 is working correctly.
For your information, answer B is not correct because if R2 and R3 get an update with a better metric than the originally recorded metric (1 for R2 and 2 for R3) within the hold-down timer period, the hold-down timer is removed and data can be sent to that network. It means that now R2 and R3 have a better way to reach R1.
For more information about RIP, please read my RIP tutorial.
Question 6
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two.)
A. It is locally significant.
B. It is globally significant.
C. It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database.
D. It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router.
E. All routers in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information.
Answer: A C
Explanation
The process identifier used in OSPF is locally significant, which means it does not need to be the same on other OSPF routers and is not passed between routers -> A is correct.
Each process identifier is a unique instance of an OSPF database. We can create many process identifiers as we want (but ranges from 1 to 65,535) but it is not recommended because the router needs many resources to maintain these OSPF databases -> C is correct.
Process identifier is a “must” parameter even if we only run only one OSPF process -> D is not correct.
Routers in the same OSPF area can have different process identifier (process ID) because it is only locally significant -> E is not correct.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. The FMJ manufacturing company is concerned about unauthorized access to the Payroll Server. The Accounting1, CEO, Mgr1, and Mgr2 workstations should be the only computers with access to the Payroll Server. What two technologies should be implemented to help prevent unauthorized access to the server? (Choose two)
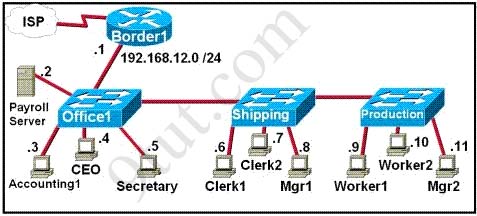
A. access lists
B. encrypted router passwords
C. STP
D. VLANs
E. VTP
F. wireless LANs
Answer: A D
Explanation
Access lists and VLANs can be used to prevent unauthorized to the Payroll Server. By assigning the server to a secure VLAN and using access list to permit only Accounting1, CEO, Mgr1, and Mgr2 workstations to access that VLAN, we can dramatically enhance the security of the whole network.
We don’t need to encrypt router password because it only helps prevent unauthorized access to the router, not Payroll server -> B is not “totally” correct ^^.
Question 8
Which two statements are true about the command ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4? (Choose two.)
A. It establishes a static route to the 172.16.3.0 network.
B. It establishes a static route to the 192.168.2.0 network.
C. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination to the 172.16.3.0 network.
D. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination out the interface with the address 192.168.2.4.
E. It uses the default administrative distance.
F. It is a route that would be used last if other routes to the same destination exist.
Answer: A E
Explanation
The command “ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4″ means that “if there is a packet to the network 172.16.3.0/24 then route it to 192.168.2.4 first.
The syntax of static route is:
ip route <subnet-mask> <next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface> [metric]
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network
+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network
+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router
+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
+ metric: the distance metric for this route. If not specified, it uses the default administrative distance of 1
Question 9
Which three statements are correct about RIP version 2? (Choose three)
A. It has the same maximum hop count as version 1.
B. It uses broadcasts for its routing updates.
C. It is a classless routing protocol.
D. It has a lower default administrative distance than RIP version 1.
E. It supports authentication.
F. It does not send the subnet mask in updates.
Answer: A C E
Explanation
A and E are correct according to the theory of RIP.
RIP version 1 updates are broadcasts, and RIP version 2 updates are multicast to 224.0.0.9 -> B is not correct.
RIP v1 is a classful routing protocol but RIP v2 is a classless routing protocol -> C is correct.
RIPv1 and RIPv2 have the same default administrative distance of 120 -> D is not correct.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol so it does send the subnet mask in updates -> F is not correct.
Question 10
How should a router that is being used in a Frame Relay network be configured to avoid split horizon issues from preventing routing updates?
A. Configure a separate sub-interface for each PVC with a unique DLCI and subnet assigned to the sub-interface.
B. Configure each Frame Relay circuit as a point-to-point line to support multicast and broadcast traffic.
C. Configure many sub-interfaces on the same subnet.
D. Configure a single sub-interface to establish multiple PVC connections to multiple remote router interfaces.
Answer: A
Explanation
In Frame Relay, one router’s interface is often connected to many other routers. According to the split horizon rule, it is not allowed to send and receive routing updates on the same interfaces so we need to configure sub-interface to overcome this problem.
Question 11
A network administrator is configuring the routers in the graphic for OSPF. The OSPF process has been started and the networks have been configured for Area 0 as shown in the diagram. The network administrator has several options for configuring RouterB to ensure that it will be preferred as the designated router (DR) for the 172.16.1.0 /24 LAN segment. What configuration tasks could be used to establish this preference? (Choose three)
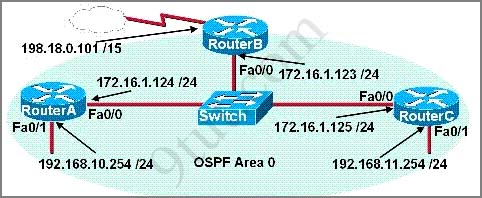
A. Configure the priority value of the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB to a higher value than any other interface on the Ethernet network.
B. Change the router id of Router B by assigning the IP address 172.16.1.130/24 to the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB.
C. Configure a loopback interface on RouterB with an IP address higher than any IP address on the other routers.
D. Change the priority value of the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB to zero.
E. Change the priority values of the Fa0/0 interfaces of RouterA and RouterC to zero.
F. No further configuration is necessary.
Answer: A C E
Explanation
DR and BDR election is done via the Hello protocol. The router with the highest OSPF priority on a segment will become the DR for that segment -> A is correct.
In case of a tie, the router with the highest Router ID will win. The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router and is chosen using the following sequence:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
+ The router ID can be manually assigned
In this case, the router ID of RouterB is 198.18.0.101 (regardless that interface does not run OSPF). So if we assign the IP address 172.16.1.130/24 to the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB, the router ID of RouterB is not changed and we can not guarantee RouterB will take DR role -> B is not correct.
C is correct as mentioned above.
A priority value of zero indicates an interface will not be elected as DR or BDR. So:
+ If we “change the priority value of the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB to zero”, RouterB will never be elected as DR -> D is not correct.
+ If we “change the priority values of the Fa0/0 interfaces of RouterA and RouterC to zero”, router A and RouterC will not be elected as DR for that segment -> E is correct.
For answer F, if there is no loopback interface configured on RouterA or RouterC then F is correct (as RouterB has the highest IP address on active physical interface 198.18.0.101) but we are not sure about that.



is the answer to Q5 correct???I think correct answers are B and D because the Q is how wil the router respond to this change??split horizon wil never allow an interface to send an update if it received info thru tht interface….but the Q is wat happens after the link fails….so first the R1 wil send a route poisoning message to R2 and R2 sends poison reverse message as a ACk..
correct me if i’m wrong
C and D are correct answers! Routers R2 and R3 can not mark the route as inaccessible but with a hop count of 16
Question 11
Router B has one of its serial int with ip 198.18.0.101
which is the highest number and the question did not mention any thing about loopback , so it should be the root without any configuration
please correct me 9tut
Because they don’t mention anything about loopback so we can not confirm there are no loopback interfaces and we can not guarantee router B will be the designated router
I didnt understand questions 5,6,8,10 and 11 could someone please help me. I would really appreciate it
Adam: May this ll help you.
anyone if i am wrong anywhere please let me know…ll be thankful
for 5th : You need to have a knowledge of STP and how it work.
1)according to STP if a link goes down the split-horizon algorithm will
which ll prevent R2 to send the enormous information.
2) As the routing table of router keep on updating so when the link on R1 goes down
the routing table ll be updated by the matric 2 as it will not found the existing path
it will assume the path which is not there. in this manner every time when the routing
table ll be updated the matric ll be increased.. So it will reach to infinite matric.
Please go through the STP working procedure u ll understand.
For 6th : it is somthing related to the features og OSPF and an identifier has local
use only and which is used to identify the unique instance of the OSPF data base.
For 8th: for configuring static route u have a command
ip route or
ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4
here the static route is for 172.16.3.0 N/W and through gateway 192.168.2.4
For 10: need to study frame rely in brief and again need to know STP
FOR 11: For electing a DR in an OSPF u need to have higher priority on that interface
Loopback inteface should have higher IP address
and oviously the rest of the router interface i.e on Ra and Rc should have lowest priorty
or zero
hi, 9tut
i would like to start by greating all members of this forum and also share this question 397 from p4s
which subnet mask would be appropriate for a network address range to be subnetted for up to 8 lans,with each lan content 5 to 26 hosts?
and the possible answer are
A-0.0.0.240
B- 255.255.255.252
c-255.255.255.224
WHEN I DID MY CALCULATION I FUND THIS 8 LANS N 32 HOSTS
I CHOSE (C) AS ANSWER BUT THE ANSWER IN THE PS4SURE WAS GIVING ME NO CORRECT ANSWER.FROM WHERE I GOT CONFUSE
can someone help?
regards,
desire
The question didn’t mention about which class the network belongs to. So if the network belongs to class C, it is true with C choice. But if the network belongs to class B, the 255.255.255.224 subnet mask will create 2^11 subnets. Same with class A…
Read comments on the “Share your experience” area, you will find useful information there
hi…. :)
can any one give answer for ?
21. A network administrator is explaining VTP configuration to a new technician. What should the network administrator tell the new technician about VTP configuration? (Choose three.)
A. A switch in the VTP client mode cannot update its local VLAN database.
B. A trunk link must be configured between the switches to forward VTP updates.
C. A switch in the VTP server mode can update a switch in the VTP transparent mode.
D. A switch in the VTP transparent mode will forward updates that it receives to other switches.
E. A switch in the VTP server mode only updates switches in the VTP client mode that have a higher VTP revision number.
F. A switch in the VTP server mode will update switches in the VTP client mode regardless of the configured VTP domain membership.
Hi Sainath,
I think A, B and D are the correct answers.
VTP Transparent mode can update its local VTP database
VTP tranparent mode receives and sends updates to other swithes in the VTP domain.
All switches must be in the same VTP domain for sharing the VTP configuration.
9TUT, FIRST OF ALL, GREAT WORKS YOU ARE DOING!
PLEASE CAN YOU EXPLAIN THIS RIDDLE?
WHICH THREE IP ADDRESSES CAN BE ASSIGNED TO HOSTS IF THE SUBNET MASK IS /27 AND SUBNET ZERO IS USABLE? (CHOOSE THREE)
A. 10.15.32.17
B. 17.15.66.128
C. 66.55.128.1
D. 135.1.64.34
E. 129.33.192.192
F. 192.168.5.63
I THINK THE ANSWER SHOULD A,B AND D.
WHAT DO YOU THINK?
The subnet mask is /27 -> increment is 32 (for the last octet) so B and E are not correct because they are network addresses (128 = 32 * 4 & 192 = 32 * 6). F is not correct because it is a broadcast address. A,C and D can be assigned to hosts.
Q4: the option C looks very valid considering that the icmp message is bound to pass through both the routers before reaching host 1….
9tut wat could you explain the choice why A instead of C?
Although the packets need to go through both routers before reaching Host 1 but only Host 1 will learn that Host 2 can not be reached.
Question 8:
ANswer: B is not correct. syntax for ip route is destionation subnet mask (next hop ip address | interface of itself) so, 192.168.2.4 is ip address for neighbor router.
Which two statements are true about the command ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4? (Choose two.)
A. It establishes a static route to the 172.16.3.0 network.
B. It establishes a static route to the 192.168.2.0 network.
C. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination to the 172.16.3.0 network.
D. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination out the interface with the address 192.168.2.4.
E. It uses the default administrative distance.
F. It is a route that would be used last if other routes to the same destination exist.
@gwbaby
You are right. When I’m reading this question now, it is obvious for me:)
Thanks
Is it possible to contact administration?
Hope for no silence
You can send me a email to support@9tut.com
Hi 9tut
I don’t understand answer D being correct in case of Question 5. Shouldn’t B and C be the correct options?
B. Routers R2 and R3 mark the route as inaccessible and will not accept any further routing updates from R1 until their hold-down timers expire.
C. Because of the split-horizon rule, router R2 will be prevented from sending erroneous information to R1 about connectivity to the 192.168.1.0 network.
As soon as the network goes down, R1 will poison its route with a metric of 16 (meaning it’s unreachable now) and send it to R2 and R3.
R2 and R3 upon receiving a route with a metric of 16 will mark the network unreachable and invoke their hold-down timers for this specific route. They will not accept any further updates about this network from R1 or any other router until their hold-down timers expire.
After the hold-down timer, flush timer is started. If during this period, R2 and R3 get an update about the route, they’ll add it back to the routing table, otherwise it will be removed once flush timer expires.
And yes C is correct. Because R2 will never send back the same route to the place it learned it from initially. Not even with the metric 16. It was R1 who poisoned the route with metric 16 and advertised it to R2 so there is no point in R2 telling the same story back to R1.
Please correct me if I’m wrong. I don’t wana get caught in such a simple question on the exam day.
Thanks a lot
Hi 9tut
I corrected my understanding of RIP process and figured out the answers after reading detailed RIP process from Cisco docs. Correct answers are B and D but not C. Pls update.
A. False: RIP and RIPv2 don’t calculate backup routes.
B. True: When R1 detects the network going down, it POISONS its route by increasing the metric to 16 and advertises the POISONED ROUTE to R2. This is called ROUTE POISONING.
R2 will forward this poisoned route to R3 as well and both will invoke their HOLD-DOWN TIMERS. During this period they will not accept any updates with whatever metric from R1 or any other router. After the HOLD-DOWN TIMER expires, they both will invoke a FLUSH TIMER. If during this period, they get an update about the network, they’ll add it back to the routing table otherwise route will be flushed (removed) once flush timer expires.
C. False: Normally SPLIT HORIZON works this way when all routes are good. But in this case as soon as R1 advertises a poisonous route to R2, R2 will leave SPLIT HORIZON for a while and start following POISON REVERSE instead.
D: True: Because of the POISON REVERSE, R2 will advertise the same poisonous route back to R1 and to R3 as well. R3 will also start following POISON REVERSE and advertise metric 16 route back to R2. At this point, hold-down timers on all routers are on for that specific route. They are not accepting any update about the down network and at the same time POISON REVERSING the whole network so that the bad route update may reach every where in the network if it hasn’t yet.
E: Obviously False
Guys and Girls
POISON REVERSE is of extreme importance in the sense that it will prevent R1 being incorrectly informed about some route to the down network in case split-horizon is inactive somewhere else.
Cheers
Hi everybody and 9tut
I think I am wrong on Question 5 in my above two posts about options B and D being correct. I can’t get it but 9tut’s answers C and D match with every other website on the internet.
EVERYBODY PLEASE IGNORE MY ABOVE 2 POSTS REGARDING QUESTION 5…
and sorry for all the confusion it has caused. C is mentioned correct everywhere on the web but I still don’t get it. It’s 100% against the RIP process described in books that I’ve seen and the POISON REVERSE rule as far as my understanding works. I’ll be greatly thankful if someone comes forward and explains it to me.
Regards
i got my exam yesterday and passed with 974. especial thanks for the 9tut. pass4sure & testinside dumps are still valid. sims are eigrp,vtp & access-list only the ip addresses are changed. in access-list the the pc also changed. again thanks for the 9tut and all of the contributors
if any one need help from me pls email to
hasy_001@yahoo.com
In Q9 why not b isnot RIP broadcast its updates
I am with gwbaby I have to say that question 8. is incorrect. What’s the word on this 9tut are you going to change this to the correct answer or explain to us how answer A. can be correct.
the proper syntax for a static route: (taken directly from Cisco’s website)
The following example routes packets for network 172.31.0.0 to a router at 172.31.6.6:
ip route 172.31.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.31.6.6
Please don’t get me wrong 9tut I appreciate all of your hard work here, I just thinks it is vitally important that all of these answers are correct otherwise they will cause confusion and a lot of second guessing.
The command “ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4″ tells this router that “if there is a packet to the network 172.16.3.0/24 then route it to 192.168.2.4 first
The syntax of static route is:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network
+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network
+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router
+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
We have a lab about static route here: http://www.9tut.com/configure-static-route-gns3-lab
these tutorials are so useful.. thanks 9tut :)
can sone send me the latest ccna dump?
manpueblo@lycos.com
Q11
how come that answer A is correct
isn’t it supposed for the DR router to have the lowest priority ???
please help
Hi!
Did my ccna today – 961.
9tut.com, acme – totally awesome!
five to six questions from “ip routing” sub-section in Acme
Jsut wo questions on subnetting and ip addressing.
Got sims on EIGRP, VTP, Accesslists
Few questions were out of the pool of dumps.
Now gearing up for CCNP! :) :)
is http://www.9tut.com enough to pass ccna exam please? if not where else can I go to practice? Thank you
@UthmanHassan
About question 5
Answer C is correct because RIP uses split horizon that will prevent R2 from sending erroneous information back to R1. Such as a route to 192.168.1.0 network with a metric other than 16. (The poisoned route)
Answer D is correct because when R2 learns about the poisoned route from R1, the split horizon rule gets bypassed and R2 sends a poisoned update about that network back to R1 to prevent routing loops from occuring.
@UthmanHassan
btw About question 5
B is incorrect because R2 and R3 will receive updates from the original router where the network when down. Just not from other routers, to prevent routing loops.
Dow slipped 138 points yesterday. I fear by next week it will decline another 500! That is crappy.. I am already on my way to bankruptcy.. anyone know a good bankruptcy attorney?
about question 7
why is A?
plz explan the question 11,,,,,,,,,
All you can imagine about encryption. MS CSP, GOST (legal), Open PGP. That means S/MIME, Public Key Infrastructure (recipient based) encryption, AES, Blowfish 448 bit, GOST 34.10-2001, digital signatures, encrypted zip. Fully compatible with all email clients (Outlook Mozilla, The Bat!), Gung, PGP, Russian Crypto Arm. Hiding files and folders with fully new concept: no stupid folders like “My hidden files”, “My protected folder”. CyberSafe Top-secret is invisible on your PC. Not speaking about your hidden files. You won’t find any traces of it even in safe mode. Not enough? Go ahead… Skype encryption, Encrypted (on-the-fly) volumes.
Still want more? How about totally secured, encrypted on-line backup using famous Amazon S3 with auto-scheduling, data compression, encryption, access rights and many more. As you can see CyberSafe is the only ultimate encryption solution over the net… Look at it here http://tinyurl.com/3fv7akv – it surprised me,
Can Sombody please explain the seventh question … involvenent of router for the question. can access list implement on switches in this question???
5answer is incorrect. Correct answers is B and D . C and D cannot be right just if you are thinking logically.
How can C be right? ” R2 CAN’T SEND erroneous info for R1 because of split horizon” , but D is saying ” R2 WILL RESPOND by sending a route back to R1 with an infinite metric”
@Aravianda: I think it means: “You have to implement VLAN AND access lists on the router.”
Switch – L2 device but ACL will work on L3 device only (L3 device = router).
Without VLAN, ACL will restrict access to server from outside of LAN but all hosts on the LAN will be able to access to Payroll server.
I think fashion is just a state of mind . nomatter what you choose!
Q8 – I think A & D are the correct answer .
Hi 9tut.
Can you explain the Q4 to me. Thanks
Hello, can someone help me and explain what they mean with ‘subnet zero is usable’?
I have a question on Q. 11 on C which states – Configure a loopback interface on RouterB with an IP address higher than any IP address on the other routers.
If the user accidently creates a loopback address which is lower than one of the physical ip addresses then will the higher physical ip address be used instead of the int with the loopback. Anyways, a silly question but just wanted to make sure that the loopback doesn’t automatically become the DR. :)
@Steve: AFAIK, if router has any configured loopback int then Router ID is highest IP address any Loopback interface. And if this router has any physical interface with higher IP anyway Router ID = highest IP loopback interface.
Question #11 ***Please HELP***Testing for 640-802 on Nov. 5, 2011****
I understand why A,E are the answers but why not “B”-”Change the router id of Router B by assigning the IP address 172.16.1.130/24 to the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB”. Since the highest RID will win out in an election and by changing the interface to a ‘higher ip’ will make the RID on B the highest why is this not an option?
@certnow: I added the explanation to that question, please check again.
You might want to add into the explanation of the Question 11 the Router ID that is configured by the command:
R3(config-router)#router-id [ip_address]
This type of router id takes precedence over the highest loopback address or the highest IP on the active interfaces, and is the first tie breaker after the interface priority, in case it’s configured on the router.
Just so that the list of tie-breakers is complete.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/iproute/command/reference/1rfospf.html#wp1049279
Question 8
Which two statements are true about the command ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.4? (Choose two.)
A. It establishes a static route to the 172.16.3.0 network.
B. It establishes a static route to the 192.168.2.0 network.
C. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination to the 172.16.3.0 network.
D. It configures the router to send any traffic for an unknown destination out the interface with the address 192.168.2.4.
E. It uses the default administrative distance.
F. It is a route that would be used last if other routes to the same destination exist.
Answer: A E
im confused. the explanation stated the syntax..then why include E in the answer. isn’t it A & D?