CCNA – RIP Questions
Here you will find answers to RIP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about RIP, please read my RIP tutorial.
Question 1
Which statement about RIPng is true?
A. RIPng allows for routes with up to 30 hops.
B. RIPng is enabled on each interface separately.
C. RIPng uses broadcasts to exchange routes.
D. There can be only one RIPng process per router.
Answer: B
Explanation
RIPng is similar to RIPv2 but is used for IPv6. But unlike RIPv1 and RIPv2, RIPng is enabled on each interface separately. For example:
Router(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing (Enables the forwarding of IPv6 unicast datagrams globally on the router)
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ipv6 rip 9tut enable (9tut is the process name of this RIPng)
Question 2
What are two characteristics of RIPv2? (Choose two)
A. classful routing protocol
B. variable-length subnet masks
C. broadcast addressing
D. manual route summarization
E. uses SPF algorithm to compute path
Answer: B D
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Which (config-router) command will allow the network represented on the interface to be advertised by RIP?
| router rip version 2 no auto summary ! interface ethernet0 ip address 10.12.6.1 255.255.0.0 |
A. redistribute ethernet0
B. network ethernet0
C. redistribute 10.12.0.0
D. network 10.12.0.0
Answer: D
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. What information can be gathered from the output?
| RouterA#debug ip rip RIP protocol debugging is on00:34:32: RIP: sending v2 flash update to 224.0.0.9 via FastEthernet8/0 (172.16.1.1) 00:34:32: RIP: build flash update entries 00:34:32: 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.6, metric 1, tag 0 00:34:32: RIP: sending v2 flash update to 224.0.0.9 via Loopback (10.10.1.1) 00:34:32: RIP: build flash update entries 00:34:32: 10.0.0.0/8 via 0.6.0.0, metric 2, tag 0 00:34:32: 172.16.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 00:34:32: RIP: ignored v2 packet from 16.10.1.1 (sourced from one of our addresses) 06:34:33: RIP: received v2 update from 172.16.1.2 on FastEthernet0/6 66:34:33: 16.6.0.0/8 via 6.0.6.6 in 1 hops 66:34:44: RIP: sending v2 update to 224.6.6.9 via FastEthernet0/0 (172.16.1.1) 66:34:44: RIP: build update entries 66:34:44: 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 |
A. One router is running RIPv1.
B. RIP neighbor is 224.0.0.9.
C. The network contains a loop.
D. Network 10.10.1.0 is reachable.
Answer: D
Question 5
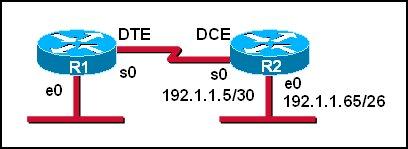
Which series of commands will configure router R1 for LAN-to-LAN communication with router R2? The enterprise network address is 192.1.1.0/24 and the routing protocol in use is RIP. (Choose three)
A.
R1 (config)# interface ethernet 0
R1 (config-if)# ip address 192.1.1.129 255.255.255.192
R1 (config-if)# no shutdown
B.
R1 (config)# interface ethernet 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.1.1.97 255.255.255.192
R1 (config-if)# no shutdown
C.
R1 (config)# interface serial 0
R1 (config-if)# ip address 192.1.1.4 255.255.255.252
R1 (config-if)# clock rate 56000
D.
R1 (config)# interface serial 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.1.1.6 255.255.255.252
R1 (config-it)# no shutdown
E.
R1 (config)# router rip
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.4
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.128
F.
R1 (config)# router rip
R1 (config-router)# version 2
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.0
Answer: A D F
Explanation
First we notice that the ip address of the E0 interface of R2 is 192.1.1.65/26, which has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.1.1.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.1.1.127
Therefore, the ip address of the E0 interface of R1 cannot belong to this range or the network cannot operate correctly.
In answer A, the ip address of E0 interface of R1 is 192.1.1.129, which does not belong in this range -> A is correct.
In answer B, E0 interface of R1 has the ip address of 192.1.1.97, which belongs in this range -> B is not correct.
The s0 interface of R1 must belong to the same network of s0 interface of R2, which has:
+ Increment: 4 (/30 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1100)
+ Network address: 192.1.1.4
+ Broadcast address: 192.1.1.7
The ip 192.1.1.5 has been used by s0 of R2 so the only suitable ip address of s0 of R1 is 192.1.1.6 -> C is wrong but D is correct.
Now the last thing we must do is enabling RIP. Because e0 interface of R1 and e0 interface of R2 have the same major network (192.1.1.0/24) so we must use RIP version 2 to support discontiguous network -> F is correct.
For answer E, if we configure 2 networks
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.4
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.128
then these networks will be automatically summarized as 192.1.1.0 network.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. Two routers have just been configured by a new technician. All interfaces are up. However, the routers are not sharing their routing tables. What is the problem?
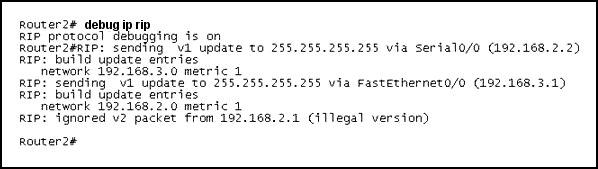
A. Split horizon is preventing Router2 from receiving routing information from Router1.
B. Router1 is configured for RIP version 2, and Router2 is configured for RIP version 1.
C. Router1 has an ACL that is blocking RIP version 2.
D. There is a physical connectivity problem between Router1 and Router2.
E. Router1 is using authentication and Router2 is not.
Answer: B
Explanation
As we can see from the output, Router2 is sending v1 update and ignoring v2 update from neighbor so we can conclude Router2 is running RIPv1. Its neighbor, Router1 (ip address of 192.168.2.1), is running RIPv2.
Notice that router running RIPv2 can “understand” RIPv1 update but router running RIPv1 cannot understand RIPv2 update.
Question 7
What is the default routing update period for RIPv2?
A. 15 seconds
B. 30 Seconds
C. 180 Seconds
D. 240 Seconds
Answer: B
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. The network manager is evaluating the efficiency of the current network design. RIPv2 is enabled on all Layer 3 devices in the network. What network devices participate in passing traffic from the PC at 10.10.1.7 to File Server at 10.20.1.6 in the order that they will forward traffic from source to destination?
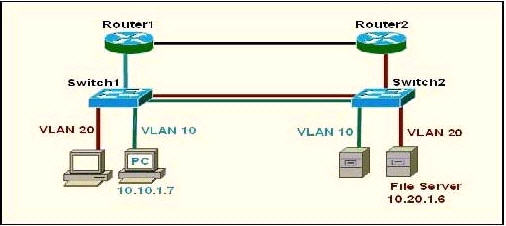
A. Switch, Switch2
B. Switch, Switch2, Router2, Switch2
C. Switch1, Router1, Switch1, Switch2
D. Switch1, Router1, Router2, Switch2
Answer: D
Explanation
The PC and File Server are in different VLANs so surely traffic from PC to File Server must go through Router1 but which path will the packet go next, through Router 2 or Switch1? Well, it is a hard question to answer.
As many comments said “the connection between R1 and Switch is Blue, so that means its under Vlan 10, and R2 to Switch 2 is red. The two routers do not have subinterfaces and are not running router on a stick basing on the color of the links” so D should be the correct answer.
Just for your information, I keep this explanation (which supports answer C) but in the exam you should choose D as your answer!
I haven’t had tested it yet but I guess that because there is a VLAN 20 on Switch 1 so Router1 will try to send that packet back to Switch1. If the link between Switch1 and Switch2 is a trunk link then the returned packet will also be sent to this link. Switch 2 receives that packet and it sends to the File Server at VLAN20. So the path will be Switch1 -> Router1 -> Switch1 -> Switch2.
There are some debates about this question but if the routers are properly configured then the packets can go from Switch1 -> Router1 -> Router2 -> Switch2 (D answer) so D can be a correct answer.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Router A has interfaces with addresses 192.168.1.1 and 172.16.1.1. Router B, which is connected to router A over a serial link, has interfaces with address 172.16.1.2 and 10.1.1.2.
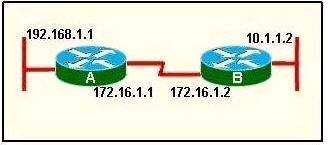
Which sequence of commands will configure RIPv2 on router B?
A.
B( config)# router rip
B(config-router)#version 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
B(config-router)# end
B.
B(config)# router rip 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
B(config-router)# end
C.
B(config)# router rip
B(config-router)#version 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
B(config-router)#end
D.
B(config)# router rip version 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
B(config-router)#end
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. S0/0 on R1 is configured as a multipoint interface to communicate with R2 and R3 in this hub-and-spoke Frame Relay topology.
While testing this configuration, a technician notes that pings are successful from hosts on the 172.16.1.0/24 network to hosts on both the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks. However, pings between hosts on the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are not successful. What could explain this connectivity problem?
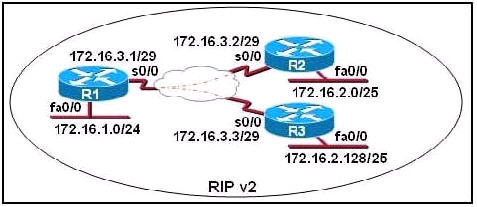
A. The ip subnet-zero command has been issued on the R1 router.
B. The RIP v2 dynamic routing protocol cannot be used across a Frame Relay network.
C. Split horizon is preventing R2 from learning about the R3 networks and R3 from learning about the R2 networks.
D. The 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are overlapping networks that can be seen by R1, but not between R2 and R3.
E. The 172.16.3.0/29 network used on the Frame Relay links is creating a discontiguous network between the R2 and R3 router subnetworks.
Answer: C
Explanation
The “ip subnet-zero” allows the use of the first subnet but it doesn’t cause this problem and we don’t have that first subnet (like 172.16.0.0/24) so we can’t confirm if the “ip subnet-zero” was used or not -> A is not correct.
Frame-Relay can use RIPv2 with no problem if we configure it correctly -> B is not correct.
In the exhibit above we notice that the s0/0 interface of R1 has not been divided into sub-interfaces so the split horizon will prevent updates from R2 to R3 and vice versa. The split horizon rule states “A router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came”. In this case R2 send an update to S0/0 of R1 so R1 cannot send that update back on S0/0 -> R3 will not learn about networks of R2 (and vice versa) -> C is correct.
172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are not overlapping networks. They are two different sub-networks -> D is not correct.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol so it supports VLSM and discontiguous networks -> E is not correct.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. After a RIP route is marked invalid on Router_1, how much time will elapse before that route is removed from the routing table?
| Router_1# show ip protocols Routing Protocol is “rip” Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 8 seconds Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240 Outgoing update filter list foe all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Router 1# |
A. 30 seconds
B. 60 seconds
C. 90 seconds
D. 180 seconds
E. 240 seconds
Answer: B
Explanation
The question reads: After a RIP route marked invalid on Router_1, how much time will elasped before that route is removed from the routing table.
The word “REMOVED” in the question means “FLUSHED”
Carefully look at the Router_1 show ip protocol output:
Invalid is 180 secs.
Flushed is 240secs.
RIP route marked invalid (180secs.)
Time elasped before route is removed (Flushed 240secs.)
The difference is 60secs……..240-180=60. Actually is 180+60=240.
Please notice that the invalid timer, hold down timer and flush timer start counting at the same time.
Question 12
Refer to the graphic. Host 1 cannot receive packets from Host 2. Assuming that RIP v1 is the routing protocol in use, what is wrong with the IP configuration information shown? (Choose two)
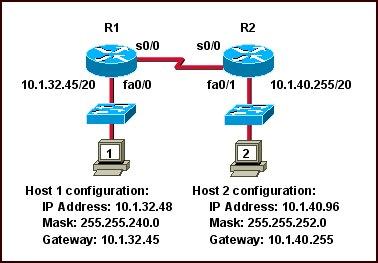
A. The fa0/1 interface of router R2 has been assigned a broadcast address.
B. The fa0/1 network on router R2 overlaps with the LAN attached to R1.
C. Host 2 has been assigned the incorrect subnet mask.
D. Host 1 has been configured with the 255.255.248.0 subnet mask.
E. Host 2 on router R2 is on a different subnet than its gateway.
Answer: B C
Explanation
The fa0/1 interface of R2 is assigned an IP address of 10.1.40.255/20. It seems to be a broadcast address but it is not. If we calculate the range of this network we will understand why:
Network 10.1.40.255/20
Increment: 16 (/20 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 0000.0000 0000)
Network address: 10.1.32.0
Broadcast address: 10.1.47.255
-> 10.1.40.255/20 is an usable host address -> A is not correct.
The IP address of host 1 (10.1.32.48) belongs to the range of interface fa0/1 on R2 as shown above -> B is correct.
In the topology above, all subnet masks are /20 (255.255.240.0) excepting the subnet mask of Host 2 (255.255.252.0) so C can be incorrect.
The subnet mask of Host 1 is 255.255.240.0, not 255.255.248.0 -> D is not correct.
Host 2 is not on a different subnet than its gateway even if the subnet mask 255.255.252.0 is used. Let’s analyze the range of Host 2 network:
Network 10.1.40.96/22
Increment: 4
Network address: 10.1.40.0
Broadcast address: 10.1.43.255
Its gateway (10.1.40.255) is still belongs to this range -> E is not correct.
Note: In this question, C is the best suitable answer after eliminating A, D, E answers. But in fact Host 2 can ping its gateway because they are on the same subnet.
Question 13
What two things will a router do when running a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. Send periodic updates regardless of topology changes.
B. Send entire routing table to all routers in the routing domain.
C. Use the shortest-path algorithm to the determine best path.
D. Update the routing table based on updates from their neighbors.
E. Maintain the topology of the entire network in its database.
Answer: A D
Question 14

Use the output from the router shown in the graphic above to determine which of the following are correct. (Choose two)
A. Router John uses a link-state routing protocol.
B. Router John will receive routing updates on the Serial0/0 interface.
C. Router John will receive routing updates on the Serial0/1 interface.
D. Router John will send routing updates out the Serial0/0 interface.
E. Router John will send routing updates out the FastEthernet0/0 interface.
F. Router John will send routing updates out the Serial0/1 interface.
Answer: B D
Explanation
As you can see under “Routing for networks”, network “10.0.0.0″ is advertising. The IP address of S0/0 is 10.168.11.17 which belongs to 10.0.0.0 network -> RIP is running on s0/0 interface only, not s0/1 -> S0/0 will send and receive RIP updates.
Question 15
What can be determined from the line of show ip route output shown in the exhibit? (Choose two)
R 10.10.10.8 [120/2] via 10.10.10.6,00:00:25, Serial0/1
A. The next routing update can be expected in 35 seconds.
B. The IP address 10.10.10.6 is configured on S0/1.
C. The IP address 10.10.10.8 is configured on S0/1.
D. This route is using the default administrative distance.
E. The 10.10.10.8 network is two hops away from this router.
Answer: D E
Explanation
From the output, we can see 2 parameters [120/2]. The first is the administrative distance of the routing protocol being used. In this case it is RIP (symbolized by the letter “R”). Because 120 is also the default administrative distance value of RIP -> D is correct.
In RIP, the metric is hop count so “2″ means the network 10.10.10.8 is two hops (routers) away from this router.



Hi 9tut
Q 14,11,6,4 can u pls explain Detail and highlight from the output, that we can find the answer
For Q8 the only answer is D
PC(VLAN 10) and File Server (Vlan 20)
Since we are trying to communicate Different VLAN’s, we need a router
the path goes like this PC > SWITCH1 > ROUTER1 > ROUTER2 > SWITCH2
notice the link between SWITCH1 and ROUTER1 it only supports VLAN 10 (blue/blue-green color)
it means when ROUTER1 will send a packet for VLAN 20, ROUTER1 can no longer send the packet to SWITCH1 rather it will send the packet to ROUTER2, link between ROUTER1 and ROUTER2 may support both VLAN 10 and VLAN 20. No legends specified but it’s the only possible way the packet can go.
Hi,
Can somebody explain the answer of question 14? Thanks.
@Niranjan
Look at the exhibit carefully and look for the lines.
Routing for Networks:
10.0.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway …..
10.168.11.14 .. .. ..
and look for an IP address assigned to an interface…… finally you can conclude what are the right answers.
@NetworkingStudent
can u draw flow chart or picture to descript
60 seconds is correct. 240-180=60
The question asks how many seconds after a route is marked as invalid before it is flushed. It is marketed invalid after 180 seconds. Then another 60 seconds pass before it is flushed.
@NET-ABC
Pls High light important information to support your answers is correct
Many thank in advance
Q.15
anyone pls why A. The next routing update can be expected in 35 seconds is not right answer?
Cisco ccna 4.3.1 page 2
“in the output from Show ip route that each route learned through RIP show the elapsed time since the last update, expressed in seconds”
so 60 – 25=35 seconds
@siv
routing updates are send in every 30 seconds. it does not depend on timer which is 00:00:25.
@siv : its 30-25 = 5 sec … since routing updates in RIP has a frequency of 30 sec not 60 sec
@9tut regd Q11 : the answer is 240 sec
EXPLANATION:
1.If no update is received by the router for invalid timer duration (180sec) -> route is marked INVALID
2.Hold down timer (180sec) AND FLUSH TIMER (240sec) starts -> route is marked possibly down and no route with higher metric is learned
3.After 180sec the route remains in ‘possibly down’ state for another 60sec (240-180) for the flush timer also to expire before the route is deleted .
Mohnish,
Read the question carefully, you will see. at 180s Invalid timer is activated. Later on (60s), the flush timer is activated and the route deleted.
hi recent test takers, how many subnetting questions were asked?
can someone explain q 13 please?
Qn.4
RouterA#debug ip rip
RIP protocol debugging is on00:34:32: RIP: sending v2 flash update to 224.0.0.9 via FastEthernet8/0 (172.16.1.1)
00:34:32: RIP: build flash update entries
00:34:32: 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.6, metric 1, tag 0
00:34:32: RIP: sending v2 flash update to 224.0.0.9 via Loopback (10.10.1.1)
00:34:32: RIP: build flash update entries
00:34:32: 10.0.0.0/8 via 0.6.0.0, metric 2, tag 0
00:34:32: 172.16.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0
00:34:32: RIP: ignored v2 packet from 16.10.1.1 (sourced from one of our addresses)
06:34:33: RIP: received v2 update from 172.16.1.2 on FastEthernet0/6
66:34:33: 16.6.0.0/8 via 6.0.6.6 in 1 hops
66:34:44: RIP: sending v2 update to 224.6.6.9 via FastEthernet0/0 (172.16.1.1)
66:34:44: RIP: build update entries
66:34:44: 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0
which part of the exhbit above indicates that network 10.10.1.0/24 is reachable?
Hi All,
Can somebody explain the Serial0 interface? Is it the interface define in 172.20.2.1? Thanks
R 172.20.1.0 [120/2] via 172.20.2.1, 00:00:04, Serial0
Hello all.
During RIPv2 configuration…do we have to use “no auto-summary” command?
Do we loose points if we don’t?
Thanks!
@9tut
Hi All,
Can somebody explain the Serial0 interface? Is it the interface define in 172.20.2.1? Thanks
R 172.20.1.0 [120/2] via 172.20.2.1, 00:00:04, Serial0
@9tut regd Q11 : the answer is 240 sec
@ Emad i fully agree wt u dude in Q11!!!
@ Emad after invalid time so 9tut Ans. is right ans..60 sec &.240 is wrong ans ….
@Emad And Mohnish,
The route is already invalid that means 180 seconds are already gone so in next 60seconds it will be 240. So the Correct Ans for Q11 is 60 secs. Thanks
@ccna, Chk my explanation above.
i need more explanation on q 10
Regarding Q-11:
http://blog.ine.com/2010/04/15/how-basic-are-rip-timers-test-your-knowledge-now/
In Q. 14 only 10.0.0.0 is advertizing broadcasts, the 192.168.x.x is not, thus the other networks don’t know about 192.168.x.x. A next hope 10.168.x.x responded with its interface address.
Q4 —- last line of debug output — 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 —is this the line that shows us that this address is reachable — via 0.0.0.0???? —- I am not sure how to read debug
Q14 — I take it to mean that — S0/0 is up and routing is for network 10 as seen in routing for networks section and s0/0 has a 10 address
Can aynone pls explain for q14 why S0 is the interface?
Hi , can any body send me new dumps am planning to take exam on 20th of this month. my mail id is pnp_patil@yahoo.co.in. Is 9 tut quetion are more enough to pass CCNA
in Q11 setup, routing entry that become invalid will be deleted before the hold down timer expired. im i right 9tut?
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. After a RIP route is marked invalid on Router_1, how much time will elapse before that route is removed from the routing table?
Router_1# show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “rip”
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 8 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
Outgoing update filter list foe all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router 1#
A. 30 seconds
B. 60 seconds
C. 90 seconds
D. 180 seconds
E. 240 seconds
Answer: B
as per dumps. bruce and jerico, the answer is 240. ? what is the right answer?
http://blog.ine.com/2010/04/15/how-basic-are-rip-timers-test-your-knowledge-now/
answer is 240. is explain it here…. am i right 9tut? thanks
@Mukesh but the question is refering on the exibit given…
now i understand.. the answer is 60. on the example given, ( http://blog.ine.com/2010/04/15/how-basic-are-rip-timers-test-your-knowledge-now/ ). its explains that is subtract the last valid time.
Based on the last valid update of 1:24:23, and now that it is 1:25:53, 90 seconds are up (flush timer) and the routes are deleted.
1:24:23 – Valid
flush after 90seconds…
no sorry.. i think its 240.. the total time to elapsed/removed the route based on the exibit is 240. negate the given hold time and invalid, what is important is the given time to elapsed/removed the route. and the answer is 240. final..
PLEASE help me on this.. Thanks…
@9tut – Please help.
@Please Explain: This question was discussed many times in this topic, please read the previous comments and you will find out. The answer is 60 (240 – 180).
rip v2 is unicast in nature or multicast ?
@ Question 13.
Distance Vector Protocols sends periodic updates regardless of topology changes. “A” is Correct. My understanding of the cisco material is that they also send entire routing table to all routers in the routing domain. Which means “B” should be correct. I have my doubts on answer “D”.
@9tut
I think I get it now. Answer D should be correct. Im still not too sure why answer “B” is not correct.
Q11 : Response is 240.
A lot of people who says “it’s 60s” forget about the hold down timer…
Once the route is marked as invalid, both holddown and flush timer start.
So the reponse is 240 (which corresponds to flush timer :> )
If the question was “after the hold down timer expires”, the response would be 60. (240-180)
@Koop
Wrong, all of the timers initiate from the same time.
“Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240″
1. When the actual route goes into a hold-down status, the counter starts for the hold-down AND the flushed timers.
2. The route is marked INVALID At the end of the 180sec hold down timer.
3. The route is still marked INVALID for an additional 60 seconds until it is flushed (at a total time of 240 seconds)
Kill bodies.
@Koop
Dammit, I misread your response, you’re good.
DID IT!!…907…thx 9tut!!!!..CCNA certified….tons of questions from this site…read from top to bottom every question, because you will not know what pops up…q12, 14 on exam…read and study….good luck to all!!!
Can pls any one answer my question
i done configuration practice in packet tracer
is it same pattren in exam also r it will change
if it then what all changes available to see…
pls
Explanation of answers to Question 5 is wrong. It is not a discontiguous network. So it will work with just RIP v.1.
And if it was a discontiguous network, just enabling RIP v.2 would not be enough since it does auto-summary by default. Option (E) is correct only in a sense that it will work with RIP v.2 without “no auto-summary” command, but only because it is not a discontiguous network.
Question 10. How can we configure 2 frame relay connections to a single interface without creating logical subinterfaces?
any 1 plz explain me Q.14
@all question 11 answer is 60sec or 240sec?
Pls, can somebody send me the latest dumps, i have exam this month,
my email is asholet98@hotmail.com
Thanks