CCNA – Subnetting Questions 3
Here you will find answers to Subnetting Questions – Part 3
Note: If you are not sure about Subnetting, please read my Subnetting tutorial.
Question 1
Workstation A has been assigned an IP address of 192.0.2.24/28. Workstation B has been assigned an IP address of 192.0.2.100/28. The two workstations are connected with a straight-through cable. Attempts to ping between the hosts are unsuccessful. What two things can be done to allow communications between the hosts? (Choose two)
A. Replace the straight-through cable with a crossover cable.
B. Change the subnet mask of the hosts to /25.
C. Change the subnet mask of the hosts to /26.
D. Change the address of Workstation A to 192.0.2.15.
E. Change the address of Workstation B to 192.0.2.111.
Answer: A B
Explanation
To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
-> To connect two hosts we must use crossover cable -> A is correct.
With the subnet mask of /28, 192.0.2.24 & 192.0.2.100 will be in different subnets (192.0.2.24 belongs to subnet 192.0.2.16/28; 192.0.2.100 belongs to subnet 192.0.2.96). To make them in the same subnet we need more space for host. Because 100 < 128 so we the suitable subnet should be /25.
Question 2
Your ISP has given you the address 223.5.14.6/29 to assign to your router’s interface. They have also given you the default gateway address of 223.5.14.7. After you have configured the address, the router is unable to ping any remote devices. What is preventing the router from pinging remote devices?
A. The default gateway is not an address on this subnet.
B. The default gateway is the broadcast address for this subnet.
C. The IP address is the broadcast address for this subnet.
D. The IP address is an invalid class D multicast address.
Answer: B
Explanation
For the network 223.5.14.6/29:
Increment: 8
Network address: 223.5.14.0
Broadcast address: 223.5.14.7
-> The default gateway IP address is the broadcast address of this subnet -> B is correct.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
| Network | Interface | Next-hop |
| 10.1.1.0/24 | e0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.2.0/24 | e1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.3.0/25 | s0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.4.0/24 | s1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.5.0/24 | e0 | 10.1.1.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/28 | e1 | 10.1.2.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/29 | s0 | 10.1.3.3 |
| 10.1.5.64/27 | s1 | 10.1.4.4 |
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.1.2.2
C. 10.1.3.3
D. 10.1.4.4
Answer: C
Explanation
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 subnets but the “longest prefix match” algorithm will choose the most specific subnet mask -> the prefix “/29″ will be chosen to route the packet. Therefore the next-hop should be 10.1.3.3 -> C is correct.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. The user at Workstation B reports that Server A cannot be reached. What is preventing Workstation B from reaching Server A?
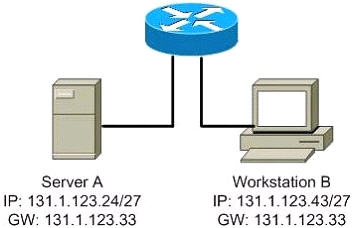
A. The IP address for Server A is a broadcast address.
B. The IP address for Workstation B is a subnet address.
C. The gateway for Workstation B is not on the same subnet.
D. The gateway for Server A is not on the same subnet.
Answer: D
Question 5
Given the address 192.168.20.19/28, which of the following are valid host addresses on this subnet? (Choose two)
A. 192.168.20.29
B. 192.168.20.16
C. 192.168.20.17
D. 192.168.20.31
E. 192.168.20.0
Answer: A C
Question 6
Which of the following IP addresses fall into the CIDR block of 115.64.4.0/22? (Choose three)
A. 115.64.8.32
B. 115.64.7.64
C. 115.64.6.255
D. 115.64.3.255
E. 115.64.5.128
F. 115.64.12.128
Answer: B C E
Question 7
The Ethernet networks connected to router R1 in the graphic have been summarized for router R2 as 192.1.144.0/20. Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
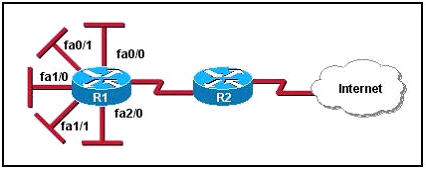
A. 192.1.159.2
B. 192.1.160.11
C. 192.1.138.41
D. 192.1.151.254
E. 192.1.143.145
F. 192.1.1.144
Answer: A D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. All of the routers in the network are configured with the ip subnet-zero command. Which network addresses should be used for Link A and Network A? (Choose two)
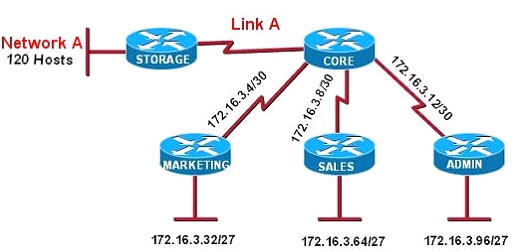
A. Network A – 172.16.3.48/26
B. Network A – 172.16.3.128/25
C. Network A – 172.16.3.192/26
D. Link A – 172.16.3.0/30
E. Link A – 172.16.3.40/30
F. Link A – 172.16.3.112/30
Answer: B D
Explanation
Network A needs 120 hosts < 128 = 27 -> Need a subnet mask of 7 bit 0s -> “/25″.
Because the ip subnet-zero command is used, network 172.16.3.0/30 can be used.
Answer E “Link A – 172.16.3.40/30″ is not correct because this subnet belongs to MARKETING subnet (172.16.3.32/27).
Answer F “Link A – 172.16.3.112/30″ is not correct because this subnet belongs to ADMIN subnet (172.16.3.96/27).
Question 9
Which two subnetworks would be included in the summarized address of 172.31.80.0/20? (Choose two)
A. 172.31.17.4/30
B. 172.31.51.16 /30
C. 172.31.64.0/18
D. 172.31.80.0/22
E. 172.31.92.0/22
F. 172.31.192.0/18
Answer: D E
Explanation
From the summarized address of 172.31.80.0/20, we find the range of this summarized network:
Increment: 16
Network address: 172.31.80.0
Broadcast address: 172.31.95.255
-> Answer D & E belong to this range so they are the correct answers.
Question 10
Which three IP addresses can be assigned to hosts if the subnet mask is /27 and subnet zero is usable? (Choose three)
A. 10.15.32.17
B. 17.15.66.128
C. 66.55.128.1
D. 135.1.64.34
E. 129.33.192.192
F. 192.168.5.63
Answer: A C D
Explanation
First we need to find out the forms of network addresses and broadcast addresses when the subnet mask of /27 is used:
Increment: 32
Network address: In the form of x.x.x.(0,32,64,96,128,160,192,224)
Broadcast address: In the form of x.x.x.(31,63,95,127,159,191,223)
So we only need to check the fourth octets of the IP addresses above. If they are not in the form of network addresses or broadcast addresses then they can be assigned to hosts.
Notice that the IP 66.55.128.1 belongs to the subnet zero and the question says subnet zero is usable so it is valid.
Question 11
Which of the following IP addresses can be assigned to the host devices? (Choose two)
A. 205.7.8.32/27
B. 191.168.10.2/23
C. 127.0.0.1
D. 224.0.0.10
E. 203.123.45.47/28
F. 10.10.0.0/13
Answer: B F
Explanation
This is a time-consuming question (but not hard ^^) because we have to calculate the range of each sub-network separately (excepting answer C is the local loopback address & answer D is a multicast address) so make sure you can do subnet quickly. After solving above questions I believe you can find out the result so I don’t explain this question in detail.
Question 12
How many subnets can be gained by subnetting 172.17.32.0/23 into a /27 mask, and how many usable host addresses will there be per subnet?
A. 8 subnets, 31 hosts
B. 8 subnets, 32 hosts
C. 16 subnets, 30 hosts
D. 16 subnets, 32 hosts
E. A Class B address cant be subnetted into the fourth octet.
Answer: C
Explanation
Subnetting from /23 to /27 gives us 27 – 23 = 4 bits -> 24 = 16 subnets.
/27 has 5 bit 0s so it gives 25 – 2 = 30 hosts-per-subnet.



Which three IP addresses can be assigned to hosts if the subnet mask is /27 and subnet zero is usable? (Choose three)
A. 10.15.32.17
B. 17.15.66.128
C. 66.55.128.1
D. 135.1.64.34
E. 129.33.192.192
F. 192.168.5.63
CAN U EXPLAIN
@balaji
the ip has to be valid on a subnet that has the mask of 255.255.255.224
subnet zero is enabled (by default) so we can use the very first subnet too
A is valid
B is a subnet ID (multiple of 32), invalid
C is valid
D is valid
E same as B, invalid
F is the broadcast IP (N*32-1), invalid
@balaji: I added explanation to that question, please check again.
Thanks for posting all these! :)
we can use ….
A.10.15.32.17
C.66.55.128.1
D.135.1.64.34
after that
B. 17.15.66.128 is Subnet
E. 129.33.192.192 is Subnet
F. 192.168.5.63 is broadcast address
where is the explanation for question no. 7?
question 12: /23 has 2^7 =128 subnets and /27 has 2^11=2048 subnets. It gains 2048-128=1920, how could it be just 16 subnets?
Please help!!!
@johncc42
let’s take this network: 150.150.0.0 /16
this is a random public class B full network.
if we had it subnetted with a /23 mask then we had: 2^23 : 2^16 = 2^7 subnets = 128 subnets
if we had it subnetted with a /27 mask then we had: 2^27 : 2^16 = 2^11 subnets = 2048 subnets.
so far so good
now…
if i take a subnetwork like… 150.150.150.128 /23 and apply it a mask of /27…
i get 2^27 : 2^23 = 2^4 = 16 subnets
easy! :)
@mike
Q.7:
The summarized address is 192.1.144.0/20
Solution:
Network bits Host bits
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
144 = 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
159= 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
151= 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
160= 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 160 is too high value.
138= 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 less than 144
143= 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 less than 144
Forget the right handside (host bits) bits, you don’t even need to accomplish that…just fill left side (network side) with binary numbers
Since in 192.1.144.0/20 1st octet and second octet’s whole bits are in network(16 bits) we don’t touch that. Third octet’s 4 bits gone to network and 4 bits remained in hosts so we would open this octet as elucidated above by opening up the third octet value i.e. 144. 1 0 0 1 came as the actual binary value of 144. From options, select third octet value and open them as I showed you above. if they match 1 0 0 1 then Router B will forward those packets to Router A coz they are encompassed in this summary =>> 192.1.144.0/20
Note: To save time remember to deduct those of those 3rd octet values from the options which are less than the summarized one’s third octet value which is 144. Because 144 cannot encompass those which are less than 144.
@mike sorry mates….previous one just got smashed….Posted again…
Q.7:
The summarized address is 192.1.144.0/20
Solution:
Network bits | Host bits
128 64 32 16 | 8 4 2 1
144 = 1 0 0 1 | 0 0 0 0
159= 1 0 0 1 | 1 1 1 1
151= 1 0 0 1 | 0 1 1 1
160= 1 0 1 0 | 0 0 0 0 === 160 is too high value.
138= 1 0 0 0 | 1 0 1 0 === less than 144
143= 1 0 0 0 | 1 1 1 1 === less than 144
|
Forget the right handside (host bits) bits, you don’t even need to accomplish that…just fill left side (network side) with binary numbers
Since in 192.1.144.0/20 1st octet and second octet’s whole bits are in network(16 bits) we don’t touch that. Third octet’s 4 bits gone to network and 4 bits remained in hosts so we would open this octet as elucidated above by opening up the third octet value i.e. 144 the binary of which is 1 0 0 1. From options, select third octet value and open them as I showed you above. if they match 1 0 0 1 then Router B will forward those packets to Router A coz they are encompassed in this summary =>> 192.1.144.0/20
Note: To save time remember to deduct those of 3rd octet values from the options which are less than the summarized one’s third octet value which is 144. Because 144 cannot encompass those which are less than 144.
i am unable to post it in a format as i wanted to post it….. 128 64 32…… all values are appearing at the rightmost side and thus its corresponding binary numbers seem to be out of order…if any one has any problem with the question explained….and he cant get it due to illegibility. send me your email addresses i will send it to you in word doc.
syedkashifshahab@hotmail.co.uk
@Xallax kindly check question 3.
In binary form when we write /27, /28 and /29 then compare the left bits to 10.1.5.65 then /27 has more matching bits and should be elected as the best route. Kindly clarify
@jb
hello
/27 is 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1110 0000 <= 27 bits
/29 is 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1000 <= 29 bits
/29 has more used bits on the network side, thus it will be a more specific mask to use.
thank you for asking, have a nice weekend
please i need explananion for question number7 please!!
@Anonymous:
Network 192.1.144.0 – is a C-class network. Netmask /20 combines networks from 192.1.144.0 to 192.1.159.0 (24-20=4 2^4=16) and hosts 192.1.144.1 – 192.1.159.254
So right answers are:
A. 192.1.159.2
D. 192.1.151.254
can anyone explain for me Q3 ? plz
@MB
This is where you apply the “Longest Prefix Match”
When the router has multiple route to forward a packet. The router will run a search in its routing table and chooses the longest prefix match. (The matching right most bits)
The idea of the Longest Prefix Match will always result in the route with the smallest mask.
For instance, the bigger the number after this sign “/” the smaller the mask, and the longer the prefix match.(The matching right most bits)
For example, /24 has a bigger mask than /29, but /29 has the longest prefix match than /24 so on and so on………
Look closely at the routing table. During the search, the router realizes that network 10.1.5.64/29 has the smallest mask and therefore has the longest prefix match. The router chooses this route to forward the packet destined for 10.1.5.65……int s0…next-hop 10.1.3.3 (option C)
I hope this help. Thanks.
@Koffy
thx alot
plz explain me wat is summarizn & subnet zero?
Hi! Do you have an explanation for Question # 6? thanks
@yep yep
hey there
115.x.x.x – class A IP network
115.64.4.0 /22…
/22 means 8+8+6+0 bits
255.255.252.0
the increment is 256 – (the value of the last incomplete byte, 252) = 256 – 252 = 4.0
the subnetwork range is…
115.64.4.0 ~ 115.64.7.255
A. 115.64.8.32
nope
B. 115.64.7.64
yep
C. 115.64.6.255
yep
D. 115.64.3.255
nope.
E. 115.64.5.128
yep
F. 115.64.12.128
nope
you must be a master at subnetting if you wish to get your CCNA.
please read here: http://www.9tut.com/subnetting-tutorial
Which of the following IP addresses can be assigned to the host devices? (Choose two)
A. 205.7.8.32/27
B. 191.168.10.2/23
C. 127.0.0.1
D. 224.0.0.10
E. 203.123.45.47/28
F. 10.10.0.0/13
Answer: B F
what about option e??
@ccna
203.123.45.47/28
203.123.45.32 ~ 203.123.45.47
203.123.45.47 is the broadcast address…
please someone explain me Q3
what is the longest prefix match algorithm. i couldn’t understand ur explanation….
@bakki
This is where you apply the “Longest Prefix Match”
When the router has multiple routes to forward a packet. The router will run a search in its routing table and chooses the longest prefix match. (The matching right most bits)
The idea of the Longest Prefix Match will always result in the route with the smallest mask.
For instance, the bigger the number after this sign “/” the smaller the mask, and the longer the prefix match.(The matching right most bits)
For example, /24 has a bigger mask than /29, but /29 has the longest prefix match than /24 so on and so on………
Look closely at the routing table. During the search, the router realizes that network 10.1.5.64/29 has the smallest mask and therefore has the longest prefix match. The router chooses this route to forward the packet destined for 10.1.5.65……int s0…next-hop 10.1.3.3 (option C)
I hope this help. Thanks.
Hi dont want to to sound silly,
But on question 10
How do we know to look in the 4th Octect???? I know /27 gives 255.255.255.224 so is this why???? the reason i ask is if we were given the IP adress 172.10.10.5 /27 would we not look in the 2nd octect as it is class b address.
Im getting a bit confused now
@Dan
I don’t consider you silly at all. Quiet on the contrary. Is only smart people go after things they want.
The question ask which addresses can be assign to host.
Regardless of which octet you dealing in, you cannot assign a “broadcast address” or “network address” to a host.
255……………..255…………….. 255……………..224
1st octet 2nd octet 3rd octet 4th octet
For instance 172.10.32.5/27, the focus is on the 4th octet with increment of 32…64…96…128 etc etc.
Assignable address will be 32.5 .6 .7 .8 all up to .62 .63 is the broadcast address, and 64 is the beginning of a new network address.
Basically, we dealing in the 4th octet.
I hope this helps somewhat.
Ye Thanks a million, I get you, a “broadcast address” or “network address can only be in the 4th octet, therefore we deal in the 4th.
Thanks again.
@Dan
No my friend. You missing the point.
Subnetting is the core of networking. You seem to be missing the foundation. You would have to start from the bottom and work your way up slowly.
There is a subnetting link at the top of this page. Click on it, and read the tutorials. It will help your understanding. Thanks.
Hi guys!
Regarding Q10, should we not consider only private addresses since we’ll be assigning this to hosts? though the question asks for three answers…
@tohritz
if you have a single computer at home then… you have a single public IP address assigned to a host.
Which of the following IP addresses fall into the CIDR block of 115.64.4.0/22? (Choose three)
A. 115.64.8.32
B. 115.64.7.64
C. 115.64.6.255
D. 115.64.3.255
E. 115.64.5.128
F. 115.64.12.128
can anyone help me out with this que??
@vicki
115.64.4.0/22……………the focus is on 3rd octet, /22 is 2^2=4
Therefore the three IP addresses that fall into the CIDR block of 115.64.4.0/22 is 5,6,7
Answers are 115.64.7.64……115.64.6.255……….115.64.5.128
I hope this help.
@koffy
thnks for your help:):)
Q11
Which of the following IP addresses can be assigned to the host devices? (Choose two)
A. 205.7.8.32/27
B. 191.168.10.2/23
C. 127.0.0.1
D. 224.0.0.10
E. 203.123.45.47/28
F. 10.10.0.0/13
ANS: BF
why can’t B&D be the answer. and F seem’s to be a sort of network address. If any one is sure that F is the answer… please leave me a explanation……….
@uday
224.0.0.10 is a class D IP address. only IPs from classes A, B and C can be assigned to devices.
10.10.0.0/13 is…
10.10.0.0 255.248.0.0
the subnet ID for this network is: 10.8.0.0
the broadcast IP for this network is: 10.15.255.255
the range on which IPs can be assigned to hosts is: 10.8.0.1 ~ 10.15.255.255
10.10.0.0 fits well inside that range.
@xallax
dud can u please help me in Q10 UNDER
email: contact@psdolt.ro
pass: p4rola$$de##eMail__1
plesk: https://linux-hosting2.rcs-rds.ro:8443
admin: 3238493
pass: fdGH226N*&&2##64jksBBZsaa^^1231
admin: admin
pass: p4rola$$de##aDmin__1
ftp — 82.76.253.83
user: psdolt63
pass: ParoLa##!@!Pentru^^$Ftp
@uday
Which three IP addresses can be assigned to hosts if the subnet mask is /27 and subnet zero is usable? (Choose three)
what does /27 mean?
it means x.x.x.x /27
or
x.x.x.x 255.255.255.224
all we care about is the subnet mask
the subnets created with this mask are:
x.x.x.0 ~ x.x.x.31
x.x.x.32 ~ x.x.x.63
……
x.x.x.192 ~ x.x.x.223
x.x.x.224 ~ x.x.x.255
the increment is
255.255.255.256 –
255.255.255.224
—————
000.000.000.032
the increment is 32
all the subnets start at a multiple of 32 (.0, .32, .64, .96, .128, .160, .192, .224)
all the subnets end at (multiple of 32)-1 (.31, .63, .95, .127, .159, .191, .223, .255)
what does “subnet zero is usable”? it means that you assign IPs from the first and last subnets on a subnetted network. in our case: x.x.x.0 ~ x.x.x.31 and x.x.x.224 ~ x.x.x.255
A. 10.15.32.17
this is on the x.x.x.0 ~ x.x.x.31 subnet, valid.
B. 17.15.66.128
x.x.x.128
this is a multiple of 32. invalid IP address for a device
C. 66.55.128.1
this is on the x.x.x.0 ~ x.x.x.31 subnet, valid.
D. 135.1.64.34
this is on the x.x.x.32 ~ x.x.x.63 subnet, valid.
E. 129.33.192.192
x.x.x.192
this is a multiple of 32. invalid IP address for a device
F. 192.168.5.63
x.x.x.63
(multiple of 32)-1. this is a broadcast IP, it can not be assigned to hosts.
lol, i just posted those passwords above… genius… changing them fast :)
Question 1
Workstation A has been assigned an IP address of 192.0.2.24/28. Workstation B has been assigned an IP address of 192.0.2.100/28. The two workstations are connected with a straight-through cable. Attempts to ping between the hosts are unsuccessful. What two things can be done to allow communications between the hosts? (Choose two)
A. Replace the straight-through cable with a crossover cable.
B. Change the subnet mask of the hosts to /25.
C. Change the subnet mask of the hosts to /26.
D. Change the address of Workstation A to 192.0.2.15.
E. Change the address of Workstation B to 192.0.2.111.
Any help please. Why is B the correct choice instead of C?
@aonlie
because a /26 (255.255.255.192) subnet could not accept both the .24 and the .100 IP inside it
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
The Ethernet networks connected to router R1 in the graphic have been summarized for router R2 as 192.1.144.0/20. Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
IP_summarize.jpg
A. 192.1.159.2
B. 192.1.160.11
C. 192.1.138.41
D. 192.1.151.254
E. 192.1.143.145
F. 192.1.1.144
why A D
@noor
144+16=160…………/20 increment of 16……….159.255 is a broadcast address, which we don’t care about, and 160.11 is a different network.
Therefore 159.2 and 151.254 are the only option available to fit scenario.
I hope this help.
Hi Can someone explain Q4… Thanks.. :)
@jayz
just look at server A’s IP address. it is on the 131.1.123.0/27 subnet
the default gateway configured for the server is 131.1.123.33, which is on the 131.1.123.32/27 subnet
please read 9tut’s subnetting tutorial
http://www.9tut.com/subnetting-tutorial
have a nice week
The Ethernet networks connected to router R1 in the graphic have been summarized for router R2 as 192.1.144.0/20. Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
Question 7
The Ethernet networks connected to router R1 in the graphic have been summarized for router R2 as 192.1.144.0/20. Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
CAN ANYBODY HELP?
@tdenen
Q7 has to do with summarizing.
192.1.144.0/20 is increment of 16…..therefore 144+16=160(in the third octet)
The summarized addresses are 192.1.159.2 and 192.1.151.254
Focus on the third octet.
Q8 was there in today’s exam.