CCNA – Subnetting Questions 3
Here you will find answers to Subnetting Questions – Part 3
Note: If you are not sure about Subnetting, please read my Subnetting tutorial.
Question 1
Workstation A has been assigned an IP address of 192.0.2.24/28. Workstation B has been assigned an IP address of 192.0.2.100/28. The two workstations are connected with a straight-through cable. Attempts to ping between the hosts are unsuccessful. What two things can be done to allow communications between the hosts? (Choose two)
A. Replace the straight-through cable with a crossover cable.
B. Change the subnet mask of the hosts to /25.
C. Change the subnet mask of the hosts to /26.
D. Change the address of Workstation A to 192.0.2.15.
E. Change the address of Workstation B to 192.0.2.111.
Answer: A B
Explanation
To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
-> To connect two hosts we must use crossover cable -> A is correct.
With the subnet mask of /28, 192.0.2.24 & 192.0.2.100 will be in different subnets (192.0.2.24 belongs to subnet 192.0.2.16/28; 192.0.2.100 belongs to subnet 192.0.2.96). To make them in the same subnet we need more space for host. Because 100 < 128 so we the suitable subnet should be /25.
Question 2
Your ISP has given you the address 223.5.14.6/29 to assign to your router’s interface. They have also given you the default gateway address of 223.5.14.7. After you have configured the address, the router is unable to ping any remote devices. What is preventing the router from pinging remote devices?
A. The default gateway is not an address on this subnet.
B. The default gateway is the broadcast address for this subnet.
C. The IP address is the broadcast address for this subnet.
D. The IP address is an invalid class D multicast address.
Answer: B
Explanation
For the network 223.5.14.6/29:
Increment: 8
Network address: 223.5.14.0
Broadcast address: 223.5.14.7
-> The default gateway IP address is the broadcast address of this subnet -> B is correct.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. According to the routing table, where will the router send a packet destined for 10.1.5.65?
| Network | Interface | Next-hop |
| 10.1.1.0/24 | e0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.2.0/24 | e1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.3.0/25 | s0 | directly connected |
| 10.1.4.0/24 | s1 | directly connected |
| 10.1.5.0/24 | e0 | 10.1.1.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/28 | e1 | 10.1.2.2 |
| 10.1.5.64/29 | s0 | 10.1.3.3 |
| 10.1.5.64/27 | s1 | 10.1.4.4 |
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.1.2.2
C. 10.1.3.3
D. 10.1.4.4
Answer: C
Explanation
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 subnets but the “longest prefix match” algorithm will choose the most specific subnet mask -> the prefix “/29″ will be chosen to route the packet. Therefore the next-hop should be 10.1.3.3 -> C is correct.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. The user at Workstation B reports that Server A cannot be reached. What is preventing Workstation B from reaching Server A?
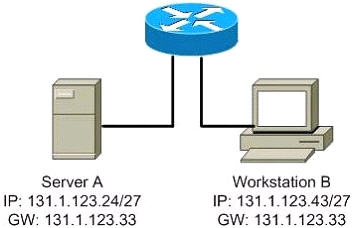
A. The IP address for Server A is a broadcast address.
B. The IP address for Workstation B is a subnet address.
C. The gateway for Workstation B is not on the same subnet.
D. The gateway for Server A is not on the same subnet.
Answer: D
Question 5
Given the address 192.168.20.19/28, which of the following are valid host addresses on this subnet? (Choose two)
A. 192.168.20.29
B. 192.168.20.16
C. 192.168.20.17
D. 192.168.20.31
E. 192.168.20.0
Answer: A C
Question 6
Which of the following IP addresses fall into the CIDR block of 115.64.4.0/22? (Choose three)
A. 115.64.8.32
B. 115.64.7.64
C. 115.64.6.255
D. 115.64.3.255
E. 115.64.5.128
F. 115.64.12.128
Answer: B C E
Question 7
The Ethernet networks connected to router R1 in the graphic have been summarized for router R2 as 192.1.144.0/20. Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
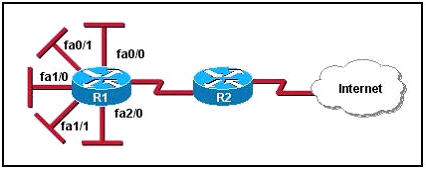
A. 192.1.159.2
B. 192.1.160.11
C. 192.1.138.41
D. 192.1.151.254
E. 192.1.143.145
F. 192.1.1.144
Answer: A D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. All of the routers in the network are configured with the ip subnet-zero command. Which network addresses should be used for Link A and Network A? (Choose two)
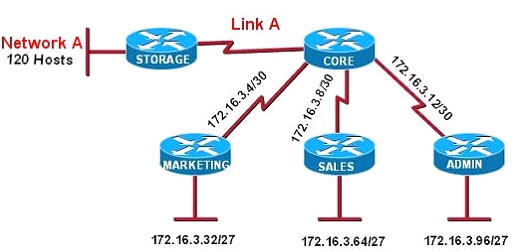
A. Network A – 172.16.3.48/26
B. Network A – 172.16.3.128/25
C. Network A – 172.16.3.192/26
D. Link A – 172.16.3.0/30
E. Link A – 172.16.3.40/30
F. Link A – 172.16.3.112/30
Answer: B D
Explanation
Network A needs 120 hosts < 128 = 27 -> Need a subnet mask of 7 bit 0s -> “/25″.
Because the ip subnet-zero command is used, network 172.16.3.0/30 can be used.
Answer E “Link A – 172.16.3.40/30″ is not correct because this subnet belongs to MARKETING subnet (172.16.3.32/27).
Answer F “Link A – 172.16.3.112/30″ is not correct because this subnet belongs to ADMIN subnet (172.16.3.96/27).
Question 9
Which two subnetworks would be included in the summarized address of 172.31.80.0/20? (Choose two)
A. 172.31.17.4/30
B. 172.31.51.16 /30
C. 172.31.64.0/18
D. 172.31.80.0/22
E. 172.31.92.0/22
F. 172.31.192.0/18
Answer: D E
Explanation
From the summarized address of 172.31.80.0/20, we find the range of this summarized network:
Increment: 16
Network address: 172.31.80.0
Broadcast address: 172.31.95.255
-> Answer D & E belong to this range so they are the correct answers.
Question 10
Which three IP addresses can be assigned to hosts if the subnet mask is /27 and subnet zero is usable? (Choose three)
A. 10.15.32.17
B. 17.15.66.128
C. 66.55.128.1
D. 135.1.64.34
E. 129.33.192.192
F. 192.168.5.63
Answer: A C D
Explanation
First we need to find out the forms of network addresses and broadcast addresses when the subnet mask of /27 is used:
Increment: 32
Network address: In the form of x.x.x.(0,32,64,96,128,160,192,224)
Broadcast address: In the form of x.x.x.(31,63,95,127,159,191,223)
So we only need to check the fourth octets of the IP addresses above. If they are not in the form of network addresses or broadcast addresses then they can be assigned to hosts.
Notice that the IP 66.55.128.1 belongs to the subnet zero and the question says subnet zero is usable so it is valid.
Question 11
Which of the following IP addresses can be assigned to the host devices? (Choose two)
A. 205.7.8.32/27
B. 191.168.10.2/23
C. 127.0.0.1
D. 224.0.0.10
E. 203.123.45.47/28
F. 10.10.0.0/13
Answer: B F
Explanation
This is a time-consuming question (but not hard ^^) because we have to calculate the range of each sub-network separately (excepting answer C is the local loopback address & answer D is a multicast address) so make sure you can do subnet quickly. After solving above questions I believe you can find out the result so I don’t explain this question in detail.
Question 12
How many subnets can be gained by subnetting 172.17.32.0/23 into a /27 mask, and how many usable host addresses will there be per subnet?
A. 8 subnets, 31 hosts
B. 8 subnets, 32 hosts
C. 16 subnets, 30 hosts
D. 16 subnets, 32 hosts
E. A Class B address cant be subnetted into the fourth octet.
Answer: C
Explanation
Subnetting from /23 to /27 gives us 27 – 23 = 4 bits -> 24 = 16 subnets.
/27 has 5 bit 0s so it gives 25 – 2 = 30 hosts-per-subnet.



I passed my ccna exam today Praise be to God! Thank you Jesus! and thanks to 9TUT for the tutorials and explanations, great site and thanks to xallax for your explanations to questions and thanks to http://www.examcollection.com for the dumps. Pls guys lets donate and help to keep this site up!
48 ques for exams including 3 simulation, I had EIGRP, Acesslist2 and VTP. Make sure the practice the simulation, use packet tracer or gns3. Best wishes to all!
Can someone explain the last question #12, I understand the Hosts (32-2=30) but I don’t understand the 16 Subnets?
Q12-How many subnets can be gained by subnetting 172.17.32.0/23 into a /27 mask, and how many usable host addresses will there be per subnet?
A. 8 subnets, 31 hosts
B. 8 subnets, 32 hosts
C. 16 subnets, 30 hosts
D. 16 subnets, 32 hosts
E. A Class B address cant be subnetted into the fourth octet.
Answer: C
Explanation
Subnetting from /23 to /27 gives us 27 – 23 = 4 bits -> 24 = 16 subnets.
/27 has 5 bit 0s so it gives 25 – 2 = 30 hosts-per-subnet.
@ joe m
16 subnets how many subnets GAINED 27-23=4
30 will be host 27= 32 – 2 broadcast and network = 30 yeeeeee!!!!
@Supercabron
Thanks but I’m still not getting it – I understand that a:
/27 has 8 subnets with 32 IP addresses per subnet (0,32,64,96,128,160,192,224), a
/23 has 128 subnets with 2 IP addresses per subnet (0,2,4,6,8…32…254)
but I am missing something here that must be really basic, i’m trying to teach this stuff to myself by going thru these examples :).
Does it have something to do with the /23 affects the 3rd octet and the /27 affects the 4th octet? I’m trying to back into this one, ugh! I got most of all the rest of the qutesions this one has just gotten me mixed up.
The Ethernet networks connected to router R1 in the graphic have been summarized for router R2 as 192.1.144.0/20. Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
IP_summarize.jpg
A. 192.1.159.2
B. 192.1.160.11
C. 192.1.138.41
D. 192.1.151.254
E. 192.1.143.145
F. 192.1.1.144
is that right question?as it is class c adress,1st 3 octets shud have have been reserved for network parts as it cannot subnetted. explain plz?
@JoeM,
if you check the turorial, you can see that the formula in getting the subnet is 2 to the power of ‘n’ where n is the number of bits to be borrowed. say from /23 to /27, we borrowed 4 bits. now 2 to the n is 2 to the 4, hope you can still follow. the value is 16, right? so we have 16 subnets out of the 4 bits that we borrowed. for the hosts per subnet, the formula is 2k-2 = host/subnet. notice that out of 32bits, only 5 remains after we used /27. the value of 5 is 32, right? say 2 raise to 5 is 32. now subtract 2 from 32, the remaining will be the usable hosts. therefore, we have 16 subnets and each subnet we can use 30 hosts/subnet. hope this is clear already. kindly master the concepts and you won’t be confused. :)
I don’t agree with question 7 (q7). They give you the summarized address of 192.1.144.0/20. This range for this aggregate address is 192.1.144.0 – 192.1.160.255. The /20 means the last bit borrowed in the 3rd octet is 16, so you’re increment is 16. If you start counting by 16′s, you reach 144. The next subnet after that is 160 (144+16):
192.1.144.0 – 192.1.159.255 –> this is the range we’re interested in
192.1.160.0 – 192.1.175.255
192.1.176.0 – etc.
It asks “Which of the following packet destination addresses will R2 forward to R1, according to this summary? (Choose two)
A. 192.1.159.2
B. 192.1.160.11
C. 192.1.138.41
D. 192.1.151.254
E. 192.1.143.145
F. 192.1.1.144
The only subnets that fall in this range (192.1.144.0 – 192.1.159.255) are A and D.
Correction to the above. I meant to remove my “disagreement” comment before submitting. Question 7 is correct (answers A and D).
can any one make me understand question 3 and4?
@rohit
on question 3 there are 3 reachable networks via 3 different interfaces.
you have to look for the most specific subnet mask.
on this scenario the /29 mask is the most specific one
on question 4 the IP address of the default gateway is outside the subnet range of the server.
the subnet range for the server is: 131.1.123.0 ~ 131.1.123.31
you should read 9tut’s tutorial subnetting here: http://www.9tut.com/subnetting-tutorial
JoeyM
Answer for Q12 is wrong
It supposed to be 8 n/ws not 16 nw/ks and host 30 exact right
Cidr 27/ 111000000 —>>> 2^3 = 8 n/ws and (2^5)-2 = 30 hosts
Joe M
Common sense comes up ther…
networks ranges
0,32,64,96,128,160,192,224 Total 8 nwks
Peace :)
thanx xallax
Q.11
191.168.10.2/23 is not a network address? can somebody explain please.
To pass the exam it is good enough if u only prepare dumbs from 9tut???
Hi Stefan, I am trying to insatll the DBFW in a virtual environment and have successfully completed the steps until ORACLE Database Firewall Tutorial Part4: Integration Standalone Firewall With Management Server . What befuddles me more is to how did we get from Part 1 to Part 4 without being able to configure *network settings on each of the three VMs listed below ?1. FWMS (Management Server)2. DBFW (Firewall with three network interfaces)3. Analyzer (Windows Server 2008 R2 VM)I am using VM Workstation 8 and the latest updated editions of DBFW and compatible Oracle Enterprise Linux. I created a host-only network on VMWare and I am able to connect (more specifically ping) FMWS from Analyzer. I put every single interface on DBFW on the same subnet, which I think is part of the problem. I didn’t understand the phrase in-line as described in . Please help me in getting the VMs to talk to each other so that we can proceed further to creating a DBFW demo environment on VMware. Thanks, Oracle DBFW Dummy
Please explain Q7
@WarFreak
192.1.144.0/20
/20 = 16 hosts per network
The range we’re interested in is 192.1.144.0 – 192.1.159.255
Any networks falling within this range are going to be summarized with the above statement
Therefore the correct answers are A and D
A. 192.1.159.2
B. 192.1.160.11
C. 192.1.138.41
D. 192.1.151.254
E. 192.1.143.145
F. 192.1.1.144
explanation for Q.1 option B is not clear that how they are not in the same subnet?
any 1 please help
explai q8…..9tut,xallax
@9tut@xallax@all.explain in detail q8
@razza
for Link A you should adopt an addressing scheme that conserves IPs (even if it’s using private IPs). the subnet mask should be /30
option E is invalid. that subnet is part of .32/27 (marketing LAN)
option F is also invalid. that subnet is part of the .96/27 subnet (admin LAN)
this leaves only option D as correct.
for network A you need a subnet that offers enough addresses for 120 hosts, while wasting the least amount of addresses.
the subnet mask that is perfect for such a subnet is /25. option B is the only one that has such a subnet mask.
@CCNA as of 8/3/12
Thanks for explaining Q7
Hi, I was looking at Q 11 and understand the explanation but have a question about option F (10.10.0.0) as the correct answer. Doesn’t it belong in the private IP address range which is from 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 and therefore nonassignable as a public ip? I also understand that if we work out the sub netting details of the rest of the ips, we are only left with that and the other host as the answer.
@9tut: Kindly explain me Q12 as I agree with Jaggi that 2^3=8 Subnets & 2^5-2=30 hosts. Its confusing.
@Jaggi, Niranjan: The question asks “subnetting 172.17.32.0/23 into a /27 mask”. Usually you only see subnetting a default subnet mask but this case is not so this case may confuses you.
@9tut Can you please answer my question? Thanks
@ironshiekh
it is still assignable to devices even tho it is on a private network. the question doesnt specify that the address should be public or private.
Hi
Can anybody please explain Q6 in detail .How come 6.255 is in the cidr and block and 3.255 is not .thanks
q6. jo hai na wo aise hi hai
I did it!!..907..everyone needs to know subnetting if u want to be CCNA…there were about 5-7 question on subnetting..know the concepts…good luck to all!!..9TUT kicks!!
Any explanation on question number 4 please. I was thinking the reason should be because both gateway IPs are the same but it appears I am wrong. any help???
@9tut Can you please check Q2 in Subnetting Questions 3 Quiz. ==> Checking logic marking with green check mark diferent answer
Right answer is [The default gateway is the broadcast address for this subnet.]
@Tedy_bear: I checked but saw nothing wrong in the quiz.
@xallax
explanation for Q.3
Explanation
The destination IP address 10.1.5.65 belongs to 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27
and 10.1.5.0/24 ?
range for this network : 10.1.5.1 — 10.1.5.254.
thanks
@max
yes, it does belong to that subnet too, but the point was to figure out which path gets chosen
thanks!
I’m confused.
Why explanation includes 10.1.5.64/28, 10.1.5.64/29 & 10.1.5.64/27 and not 10.1.5.0/24 ?
I totally agree with answer C.
@9tut Please check for typo – Right Menu URLs showing the same Questions content
http://www.9tut.com/ccna-subnetting-questions-3
http://www.9tut.com/ccna-subnetting-questions-4
pls explain Q4
@guest
About Question 4
Note that the gateway is the same in both Server and workstation, so one of them has to be wrong:
The subnet range of the workstation is:
131.1.123.32 to 131.1.123.63
So both the IP address and the gateway are correct.
The subnet range of the server is:
131.1.123.0 to 131.1.123.31
So the gateway is not in the same subnet.
I hope you can understand my explanation, my english is not that good ^.^
See for the last question below is the answer for subnet:
For /23 you will be having totally 512 addresses and for /27 = 32 addresses,
When you convert from 512(/23) to 32(27) you need to consider only how many number of multiple of 32 is available so 512/32 = 16. therefore the number of subnet would be 16.
Always make it simple to understand.
plz some1 help me, am wringting my exams next week and i feel like i know nothing atleast on subnetting i will be there,whyat materials can i used and plz some one send me the latest dump.
Can I split a hair for the benefit of better understanding on Q9? It asks “Which two subnetworks ” but the answer E. 172.31.92.0/22 doesn’t seem right- isn’t that just an IP address within a subnetwork, not a subnetwork in itself ? the subnetworks would be .80, .96, .112 , .128, .144, etc. every 16 addresses?
@dkx230 i hope this helps:
Which two subnetworks would be included in the summarized address of 172.31.80.0/20? (Choose two)
A. 172.31.17.4/30
B. 172.31.51.16 /30
C. 172.31.64.0/18
D. 172.31.80.0/22
E. 172.31.92.0/22
F. 172.31.192.0/18
E is a subnetwork because /22, SM is 255.255.252.0 interval is 4 on the 3rd octet.
so the subnetworks, including subnet zero are 172.31.0.0, .4.0, .8.0, … .80.0, … .92.0 until .252.0
@anon-
Thanks. Makes much more sense now.
9tut, could you please break down Q11 as I am still puzzled as to why “A” or “E” would not be good addresses? Thx
@Jamerican: First you have to find out the increment of the IP address of each choice, then find the network & broadcast addresses. If the IP address is not a network or broadcast address then it can be assigned to host.
Can somebody plz explain this question…
The network administrator is asked to configure 113 point-to-point links. Which IP addressing scheme best defines the address range and subnet mask that meet the requirement and waste the fewest subnet and host addresses?
A. 10.10.0.0/18 subnetted with mask 255.255.255.252
B. 10.10.0.0/25 subnetted with mask 255.255.255.252
C. 10.10.0.0/24 subnetted with mask 255.255.255.252
D. 10.10.0.0/23 subnetted with mask 255.255.255.252
E. 10.10.0.0/16 subnetted with mask 255.255.255.252
i dont get why B is correct, E makes more sense to me since you are subnetting from a Class A address.
@sally
first, the right topic is here : http://www.9tut.com/ccna-subnetting-questions-4
it’s the question 8 of subnetting question 4.
And 9tut explained it :
“Explanation
We need 113 point-to-point links which equal to 113 sub-networks < 128 so we need to borrow 7 bits (because 2^7 = 128).
The network used for point-to-point connection should be /30.
So our initial network should be 30 – 7 = 23.
So 10.10.0.0/23 is the correct answer.
You can understand it more clearly when writing it in binary form:
/23 = 1111 1111.1111 1110.0000 0000
/30 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1100 (borrow 7 bits)"
TY 9tut.
Today I have passed the CCNA. (860/825)
50 questions 3 labs (VTP, EIGRP, ACL). 35 from 9tut.
Also thanks a lot Brar and Sekhar (still valid from examcollection)
Ty again 9tut
from here Q 5