CCNA – TCP/IP Model & Operation
Here you will find answers to TCP/IP Model & Operation Questions
Question 1
An inbound access list has been configured on a serial interface to deny packet entry for TCP and UDP ports 21, 23 and 25. What types of packets will be permitted by this ACL? (Choose three)
A. FTP
B. Telnet
C. SMTP
D. DNS
E. HTTP
F. POP3
Answer: D E F
Explanation
The access list denies packet entry for TCP & UDP -> all the services on ports 21, 23 and 25 are disabled. Services on these ports are FTP (port 21), Telnet (port 23), SMTP (port 25). Other services are allowed so D E F are the correct answers.
Question 2
What are two characteristics of Telnet? (Choose two)
A. It sends data in clear text format.
B. It is no longer supported on Cisco network devices.
C. It is more secure than SSH.
D. It requires an enterprise license in order to be implemented.
E. It requires that the destination device be configured to support Telnet connections.
Answer: A E
Explanation
Telnet, part of the TCP/IP protocol suite, is a virtual terminal protocol that allows you to make connections to remote devices, gather information, and run programs. Telnet is considered insecure because it transfers all data in clear text -> A is correct.
The destination device needs to support Telnet connection. For example, if a device doesn’t support TCP/IP protocol suit then maybe we can’t telnet to it.
Question 3
An administrator issues the command ping 127.0.0.1 from the command line prompt on a PC. If a reply is received, what does this confirm?
A. The PC has connectivity with a local host.
B. The PC has connectivity with a Layer 3 device.
C. The PC has a default gateway correctly configured
D. The PC has connectivity up to Layer 5 of the OSI model
E. The PC has the TCP/IP protocol stack correctly installed.
Answer: E
Explanation
The address 127.0.0.1 is called loopback address. When we ping 127.0.0.1, in fact we are testing if the TCP/IP protocol suite is installed on our device.
Note: The address 127.0.0.1 does not have anything related with the NIC card. We still ping 127.0.0.1 even if we don’t have the NIC card.
Question 4
Where does routing occur within the DoD TCP/IP reference model?
A. application
B. internet
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B
Explanation
The picture below shows the comparison between TCP/IP model & OSI model. Notice that the Internet Layer of TCP/IP is equivalent to the Network Layer which is responsible for routing decision.

Question 5
A host is attempting to send data to another host on a different network. What is the first action that the sending host will take?
A. Drop the data.
B. Send the data frames to the default gateway.
C. Create an ARP request to get a MAC address for the receiving host.
D. Send a TCP SYN and wait for the SYN ACK with the IP address of the receiving host.
Answer: B
Explanation
Before sending data, the sending host checks if the destination host is inside or outside the local network. If it is outside the local network, the data will be sent to the default gateway.
Question 6
A TCP/IP Transfer is diagrammed in the exhibit.
A window size of three has been negotiated for this transfer. Which message will be returned from the receiver to the sender as part of this TCP/IP transfer?
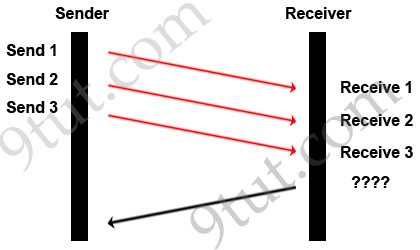
A. Send ACK 1-3
B. Send ACK 3
C. Send ACK 4
D. Send ACK 4-6
E. Send ACK 6
F. Send ACK 7
Answer: C
Explanation
In response, the receiver replies with an ACK. The acknowledgment number is set to one more than the received sequence number. The ACK means “I have got all messages up to sequence number n-1 so please send me the message for sequence number n”.
Question 7
What is the purpose using the traceroute command?
A. to map all the devices on a network.
B. to display the current TCP/IP configuration values.
C. to see how a device MAC address is mapped to its IP address.
D. to see the path a packet will take when traveling to a specified destination.
E. to display the MTU values for each router in a specified network path from source to a destination.
Answer: D
Question 8
A network admin wants to know every hop the packets take when he accesses cisco.com. Which command is the most appropriate to use?
A. path cisco.com
B. debugcisco.com
C. trace cisco.com
D. traceroute cisco.com
Answer: D
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Host A pings Host B. What source MAC address and source IP address are contained in the frame as the frame leaves R2 destined for host B?
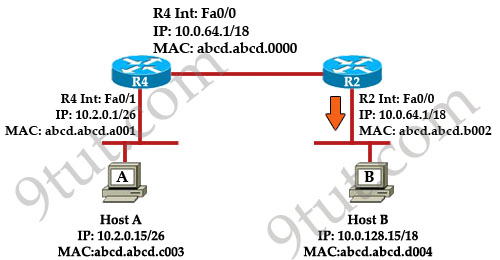
A. abcd.abcd.a001
B. abcd.abcd.b002
C. abcd.abcd.c003
D. 10.2.0.15
E. 10.0.64.1
F. 10.0.128.15
Answer: B D
Explanation
When packets are sent from Host A to Host B, the source and destination IP addresses are never changed and they are the IP addresses of Host A & Host B. Only the MAC addresses will be changed to reflect the device of the current network. In this case, when the frame leaves R2 destined for host B. It will have:
+ Source IP: IP of Host A - 10.2.0.15 (never changed)
+ Destination IP: IP of Host B – 10.0.128.15 (never changed)
+ Source MAC: MAC of Fa0/0 of R2 – abcd.abcd.b002
+ Destination MAC: MAC of Host B – abcd.abcd.d004
Question 10
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two)
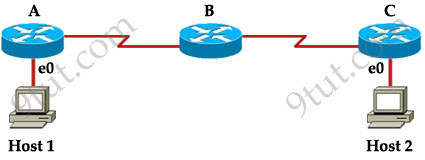
A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The last known good router will try to inform you that the destination cannot be reached (with a Destination Unreachable message type) so from that information you can learn how far your packets can travel to and where the problem is.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. The switch in the graphic has a default configuration and the MAC table is fully populated. In addition, this network is operating properly. The graphic represents selected header information in a frame leaving host A. What can be concluded from this information?
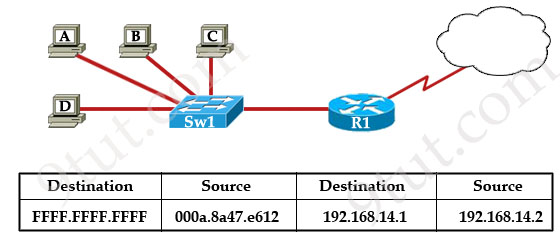
A. The MAC address of host A is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
B. The router will forward the packet in this frame to the Internet.
C. The switch will only forward this frame to the attached router interface.
D. All devices in this LAN except host A will pass the packet to Layer 3.
Answer: D
Explanation
This frame is leaving host A so host A is the source of this frame. In this frame, the MAC destination is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF which is a broadcast address so Sw1 will flood this frame out all its ports except the port it received the frame -> Hosts B, C, D and the interface connected to Sw1 on R1 will receive this frame. When receiving this frame, they will pass the packet to Layer 3 (because they consider broadcast address “everyone, including me”). At Layer 3, the Destination IP will be checked and only the host (or the interface on the router) with correct IP will respond to Host A while others keep silence -> D is correct.
Just for your information, maybe you can ask “this is a broadcast message so why router R1 doesn’t drop it?”. Suppose this is an ARP Request message. In fact, R1 drops that packet but it also learns that it is an ARP Request so R1 looks up its routing table to find a route to that destination. If it can find one, it will send an ARP Reply back for host A”.



Thanks 9tut.com
i Passed today with 920 marks…Thank you very much :)
can someone please email me the latest dumps to btymes2@yahoo.com
thanks so much!!
Q, 9 and 10 were in exam today
Can someone mail me the latest dumps? billybob9187@hotmail.com Thank You!
Please please please guys i am preparing for the exam next month, can someone be kind enough to send me the latest dumps on my e-mail: kalonji73@yahoo.co.uk
I l cleared my exam and i got t examsdump.gmail.com he pass4sure dump from this link study material also avaiable
Please Can you send me the latest dump of ccna 640-802 to dh.burgos199@gmail.com Thank you so much
Hello Guys I hope you will be fine there. I have CCNA (640-802) and CCNA security (640-554) Vouchers on special discount of 58% for World wide, with six months expiry date till you purchase. Each voucher cost 70USD.
Details Required For CCNA Voucher For Discount Processing:
1-Full Name. 1st Name & Last Name (as you want to appear on certificate & documents)
2-Country.
3-City.
4-State.
5-Pin Code (or Area Code)
6-Residential Address (or where you can collect your Certificate or further correspondence
can be received)
7-Date of birth
Add me on Skype through this information which is written below:
Skype Name: rockon660
you can also email me at this email address which is written below:
madeelqaiser@gmail.com
If you have any Questions feel free to contact me.
Thanks,
Best regards,
Adeel
Nope.
Default action at the end of access-list is deny ip any any (implicit rule) so none of them are allowed.
Please email me latest Dump Please – roseller_1621@yahoo.com
no 5 THE ANS IS B OR C
Thanks 9tut. I made it. I passed my CCNA 200-120 today. The sim is Access-list 1 , Access-list 2 & EIGRP. A lot of new questions like Netflow, Syslog, SNMP, VRRP, and GLBP.
MOSE, you’re wrong. It will not ARP for the host. C would work if the statement said ‘ARP for router’. The client will not ARP for the host if it knows the host is in a different network, it would only ARP for the router in the event it did not know the routers MAC.
‘question 1′ commenter, you’re wrong. It didn’t say there was only one line in the ACL. It said the purpose is to “deny packet entry for TCP and UDP ports 21, 23 and 25″. You must deduce that the ACL is correctly written to do just that.
The answer for Ques 1 is correct – D E F allowed …. All that is being done here is blocking 21 23 25. The explicit deny comes AFTER the permit. Remember in ACL ordering is very important. So the deny ip any any will deny all other EXCEPT 21 23 25
** It’s a Rubicon**
I gotta take a dump with all these wanna-be test-takers asking for a the latest dump ;)
Please say why D i chosen as correct answer in Q8. C&D are the same commands,just first(i.e C ) short form of another one (i.e D).
can someone please send me latest dump of ccna 640-802 to ofiritay123456@walla.com ?
In the explanation, it states pinging 127.0.0.1 ping the network card. This is incorrect. Pinging 127.0.0.1 will work even if a network card is not present. It simply tests to the loop back, not the NIC. To test to the NIC, you have to ping it’s assigned address. Consider the situation with multiple NICs. If pinging 127.0.0.1 pings a NIC, which of the multiple NICs gets pinged?
Since when do routers pass ARP requests? ARP requests and replies are not IP. They’re a method to determine an IP address, but can also be used with other protocols. The only device that should respond to an ARP request is the device with the target IP or a proxy for it. Also, ARP replies return the MAC address of the destination and since MAC addresses are valid only on the local network, there’s absolutely no point in sending an ARP request through a router.
@Question 3 Explanation error: Yes, thanks you for pointing out about the loopback 127.0.0.1. We have updated the explanation!
@Question 11 Explanation error: We don’t say routers pass ARP requests. We only say the router will reply the ARP Request.
In question 11, D it says ‘In fact, R1 drops that packet but it also learns that it is an ARP Request so R1 looks up its routing table to find a route to that destination. If it can find one, it will send an ARP Reply back for host A”.’
What would be the contents of that ARP reply? If the MAC address of remote host, that address will be useless on the local LAN. If the MAC address of the router, then it would also be useless, as host A, when it determines the destination is on another network uses the router MAC address, after associating the routers IP address with it. It will never associate any MAC address for a host that is not on the local network. So, such an ARP request should never be sent and even if it is, the router shouldn’t respond to it.
Further on the above, the only exception is when the router is acting as a proxy for another host, but even then, that host’s IP address still has to be within the local LAN address range.
oyC05v Muchos Gracias for your article post.Thanks Again.
Please guys email me the Dumps for CCnA 804-602, I am writing month end JAn 2014. Pta@abakali.co.za
sorry Guys i meant 640-802