IPv6 Tutorial
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is responsible for the assignment of IPv6 addresses. ICANN assigns a range of IP addresses to Regional Internet Registry (RIR) organizations. The size of address range assigned to the RIR may vary but with a minimum prefix of /12 and belong to the following range: 2000::/12 to 200F:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF::/64.
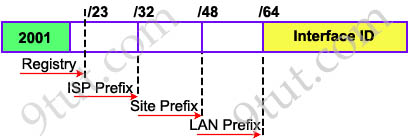
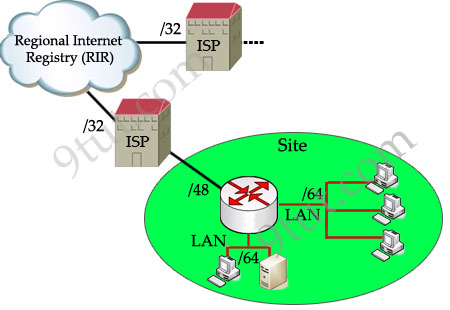
Each ISP receives a /32 and provides a /48 for each site-> every ISP can provide 2(48-32) = 65,536 site addresses (note: each network organized by a single entity is often called a site).
Each site provides /64 for each LAN -> each site can provide 2(64-48) = 65,536 LAN addresses for use in their private networks.
So each LAN can provide 264 interface addresses for hosts.
-> Global routing information is identified within the first 64-bit prefix.
Note: The number that represents the range of addresses is called a prefix
Now let’s see an example of IPv6 prefix: 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64:

In this example, the RIR has been assigned a 12-bit prefix. The ISP has been assigned a 32-bit prefix and the site is assigned a 48-bit site ID. The next 16-bit is the subnet field and it can allow 216, or 65536 subnets. This number is redundant for largest corporations on the world!
The 64-bit left (which is not shown the above example) is the Interface ID or host part and it is much more bigger: 64 bits or 264 hosts per subnet! For example, from the prefix 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD::/64 an administrator can assign an IPv6 address 2001:0A3C:5437:ABCD:218:34EF:AD34:98D to a host.
IPv6 Address Scopes
Address types have well-defined destination scopes:
| IPv6 Address Scopes |
Description |
| Link-local address | + only used for communications within the local subnetwork (automatic address configuration, neighbor discovery, router discovery, and by many routing protocols). It is only valid on the current subnet. + routers do not forward packets with link-local addresses. + are allocated with the FE80::/64 prefix -> can be easily recognized by the prefix FE80. Some books indicate the range of link-local address is FE80::/10, meaning the first 10 bits are fixed and link-local address can begin with FE80, FE90,FEA0 and FEB0 but in fact the next 54 bits are all 0s so you will only see the prefix FE80 for link-local address. + same as 169.254.x.x in IPv4, it is assigned when a DHCP server is unavailable and no static addresses have been assigned + is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address). |
| Global unicast address | + unicast packets sent through the public Internet + globally unique throughout the Internet + starts with a 2000::/3 prefix (this means any address beginning with 2 or 3). But in the future global unicast address might not have this limitation |
| Site-local address | + allows devices in the same organization, or site, to exchange data. + starts with the prefix FEC0::/10. They are analogous to IPv4′s private address classes. + Maybe you will be surprised because Site-local addresses are no longer supported (deprecated) by RFC 3879 so maybe you will not see it in the future. |
All nodes must have at least one link-local address, although each interface can have multiple addresses.
However, using them would also mean that NAT would be required and addresses would again not be end-to-end.
Site-local addresses are no longer supported (deprecated) by RFC 3879.
Special IPv6 Addresses
| Reserved Multicast Address | Description |
| FF02::1 | + All nodes on a link (link-local scope). |
| FF02::2 | + All routers on a link |
| FF02::5 | + OSPFv3 All SPF routers |
| FF02::6 | + OSPFv3 All DR routers |
| FF02::9 | + All routing information protocol (RIP) routers on a link |
| FF02::A | + EIGRP routers |
| FF02::1:FFxx:xxxx | + All solicited-node multicast addresses used for host auto-configuration and neighbor discovery (similar to ARP in IPv4) + The xx:xxxx is the far right 24 bits of the corresponding unicast or anycast address of the node |
| FF05::101 | + All Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers |
Reserved IPv6 Multicast Addresses
| Reserved Multicast Address | Description |
| FF02::1 | + All nodes on a link (link-local scope). |
| FF02::2 | + All routers on a link |
| FF02::9 | + All routing information protocol (RIP) routers on a link |
| FF02::1:FFxx:xxxx | + All solicited-node multicast addresses used for host auto-configuration and neighbor discovery (similar to ARP in IPv4) + The xx:xxxx is the far right 24 bits of the corresponding unicast or anycast address of the node |
| FF05::101 | + All Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers |



Thank you. It really helped me alot
hi team!
please send dumps on ICND1 to my email sami.dsami@gmail.com
am sitting for my exam next Tuesday the 11th
thank you!
Good summary of IPv6 !!
Thanks. Good tutorial on IPv6.
Very Nice, to understand about IPv4
Thank you
nice one and cool.God bless you.
really helpful …thanx
Thanks……..really helpful..!!!!!!
great tutorial…easy to understand
Than you it is veru usefull tuturial
Thanks you so much . it clear my doubt about ipv6
Excelente, muy acertado el tutorial
chakerim
Hello everyone here,
I was wondering if any one has the CCNA CBT Nuggets.
Especially IPv6 part.
Feel free to send them to my email address:arwa.alansary@yahoo.com
Also, I am going to have my exam on August 14. If you have any useful resources, please let me know.
Arwa
thank you for the explanation. am ok now.
this website is gold! thanks alot
v
Are any of these ipv6 questions on the test
I want to ask something that if a person gets prepared for CCNA and CCNP but have n’t give the Industry paper,Can he appear for CCIE?
nice one…
please send CCNA latest dumps on my mail ID is
sanjeevyaliballi@gmail.com
nice .exp…
Please share the latest dump on my mail :
parthi.win.dce@gmail.com
very good concept
Dear all
Please anyone send a recently dump because the next week I Have the exam CCNA , my mail is aribi_walid@yahoo.fr
Helped me a lot to kill more People
your obama
Please send me the latest dumps for CCNA 200-120 to ukiran7779@gmail.com I’m having my exam on 9/2/2015.
Please can some one send me the latest dumps for CCNA 200-120 to michsawyer2000@yahoo.com. I am having my Exam at the end of this month.
Hi,
Please kindly send me the lastest dumps for CCAN 200-120 to samathsot@gmail.com. i will having my Exam soon.
does this mean that when we are assigning static IPv6 to our computer/host for example, we can cause IP address conflict to possibly another host that is located on another place or organization?
Could you please send me the lastest dumps for CCAN 200-120 to marcelo.parreira@gmail.com, that´s cause I´m taking the exam very very soon !
comprehensible examples!
Hello all ..
can Some one please help me and send me the latent dumps to praxtice for my exam …
Appieroots@hotmail.com thank you and keep up the awsone site…
can you any one send me the latest dumps as i have my exam on 11th of may. wathessatya@gmail.com
Thanks
I would be most greatful if someone can me me the lastest dump to nscoburgh@yahoo.ca because I have my ccna exam at the end of May 2015. thanks.