CCNA – Access List Questions
Here you will find answers to CCNA Access list questions
Note: If you are not sure about how to use Access list, please read my Access list tutorial
Question 1
Your boss is learning a CCNA training course, refer to the exhibit. The access list has been configured on the S0/0 interface of router RTB in the outbound direction. Which two packets, if routed to the interface, will be denied? (Choose two)
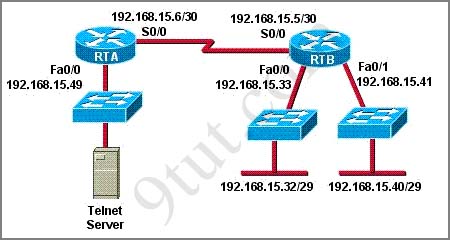
access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.15.32 0.0.0.15 any eq telnet
access-list 101 permit ip any any
A. source ip address: 192.168.15.5; destination port: 21
B. source ip address: 192.168.15.37 destination port: 21
C. source ip address: 192.168.15.41 destination port: 21
D. source ip address: 192.168.15.36 destination port: 23
E. source ip address: 192.168.15.46; destination port: 23
F. source ip address: 192.168.15.49 destination port: 23
Answer: D E
Explanation
First we notice that telnet uses port 23 so only D, E & F can satisfy this requirement.
The purpose of this access-list is to deny traffic from network 192.168.15.32 255.255.255.240 (to find out the subnet mask just convert all bit “0″ to “1″ and all bit “1″ to “0″ of the wildcard mask) to telnet to any device. So we need to figure out the range of this network to learn which ip address will be denied.
Increment: 16
Network address: 192.168.15.32
Broadcast address: 192.168.15.47
-> Only 192.168.15.36 (Answer D) & 192.168.15.46 (Answer E) belong to this range so they are the correct answer.
Question 2
Refer to the graphic. It has been decided that PC1 should be denied access to Server. Which of the following commands are required to prevent only PC1 from accessing Server1 while allowing all other traffic to flow normally? (Choose two)
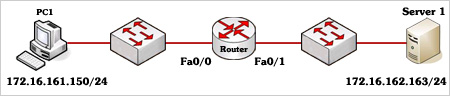
A – Router(config)# interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 out
B – Router(config)# interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
C – Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip host 172.16.161.150 host 172.16.162.163
Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
D – Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip 172.16.161.150 0.0.0.255 172.16.162.163 0.0.0.0
Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
Answer: B C
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Why would the network administrator configure RA in this manner?

A. to give students access to the Internet
B. to prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA
C. to prevent administrators from accessing the console of RA
D. to give administrators access to the Internet
E. to prevent students from accessing the Internet
F. to prevent students from accessing the Admin network
Answer: B
Explanation
Although the access-list is used to “permit” network 10.1.1.0/24 but the best answer here is “to prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA”. From the picture above, we know that 10.1.1.0/24 is the “Admin” network. This access list is applied to “line vty 0 4″ so it will permit only Telnet traffic from “Admin” to RA while drop all other traffic (because of the implicit “deny all” command at the end of the access list). Therefore we can deduce that it will “prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA”.
This access list only filters Telnet traffic (because it is applied to vty line) so it will not prevent or allow anyone to access the Internet -> A, D, E are not correct.
C is not correct as this access list allows administrators to access the console of RA.
F is not correct as this access list does not proceed TCP, UDP or IP traffic so the students still access the Admin network.
(Notice that the “command prompt” here implies telnet as telnet is the only way to remotely access RA)
Question 4
An access list was written with the four statements shown in the graphic. Which single access list statement will combine all four of these statements into a single statement that will have exactly the same effect?
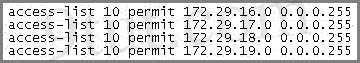
A. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.0.255
B. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.1.255
C. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.3.255
D. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.15.255
E. access-list 10 permit 172.29.0.0 0.0.255.255
Answer: C
Explanation
Four statements above allow 4 networks (from 172.29.16.0/24 to 172.29.19.0/24) to go through so we can summary them as network 172.29.16.0/22.
/22 = 255.255.252.0 so it equals 0.0.3.255 when converting into wildcard mask -> C is correct.
A, B, D are not correct as their wildcard masks are false. For example:
Answer A allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.16.255
Answer B allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.17.255
Answer D allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.31.255
Both the network address and wildcard mask of answer E are false as it allows the whole major network 172.29.0.0/16 to go through.
Question 5
A network administrator wants to add a line to an access list that will block only Telnet access by the hosts on subnet 192.168.1.128/28 to the server at 192.168.1.5. What command should be issued to accomplish this task?
A – access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 23
access-list 101 permit ip any any
B – access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.240 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 23
access-list 101 permit ip any any
C – access-list 1 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 21
access-list 1 permit ip any any
D – access-list 1 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 host 192.168.1.5 eq 23
access-list 1 permit ip any any
Answer: A
Explanation:
First the question asks to block only Telnet access so the port we have to use is 23 -> C is not correct.
Next we need to block traffic from hosts on the subnet 192.168.1.128/28, which is 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 if we convert to wildcard mask (just invert all bits of the subnet mask,from 0 to 1 and from 1 to 0 we will get the equivalent wildcard mask of that subnet mask) -> so B is incorrect
In this case, we have to use extended access list because we need to specify which type of traffic (TCP) and which port (23) we want to block -> so D is incorrect because it uses standard access list.
Question 6
As a network administrator, you have been instructed to prevent all traffic originating on the LAN from entering the R2 router. Which the following command would implement the access list on the interface of the R2 router?
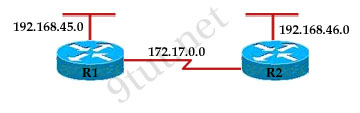
A – access-list 101 in
B – access-list 101 out
C – ip access-group 101 in
D – ip access-group 101 out
Answer: C
Question 7
The following access list below was applied outbound on the E0 interface connected to the 192.169.1.8/29 LAN:
access-list 135 deny tcp 192.169.1.8 0.0.0.7 eq 20 any
access-list 135 deny tcp 192.169.1.8 0.0.0.7 eq 21 any
How will the above access lists affect traffic?
A – FTP traffic from 192.169.1.22 will be denied
B – No traffic, except for FTP traffic will be allowed to exit E0
C – FTP traffic from 192.169.1.9 to any host will be denied
D – All traffic exiting E0 will be denied
E – All FTP traffic to network 192.169.1.9/29 will be denied
Answer: D
Explanation:
There is always an implicit “deny all” command at the end of every access list, so if an access list doesn’t have any “permit” command, it will block all the traffic.
Note: This access list is applied on outbound direction so only packets exiting E0 will be checked. Packets entering E0 will not be checked and they all are allowed to pass through.
Question 8
The access control list shown in the graphic has been applied to the Ethernet interface of router R1 using the ip access-group 101 in command. Which of the following Telnet sessions will be blocked by this ACL? (Choose two)
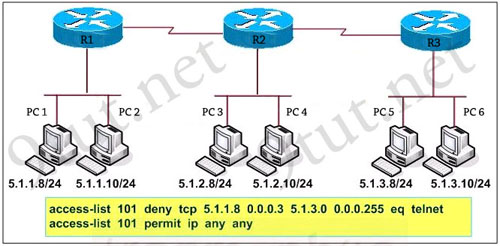
A – from host PC1 to host 5.1.1.10
B – from host PC1 to host 5.1.3.10
C – from host PC2 to host 5.1.2.10
D – from host PC2 to host 5.1.3.8
Answer: B D
Explanation
Below is the simple syntax of an extended access list:
access-list access-list-number {deny | permit} {ip|tcp|udp|icmp} source [source-mask] dest [dest-mask] [eq dest-port]
Notice that this access list is applied to the Ethernet interface of R1 in the “in direction” so in this case, it will filter all the packets originated from E1 network (host PC1 and PC2) with these parameters:
Source network: 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 which means 5.1.1.8/252 (just invert all the wildcard bits to get the equivalent subnet mask) -> Packets from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 will be filtered.
Destination network: 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 which means 5.1.3.0/24-> Packets to 5.1.3.0/24 will be filtered
Therefore packets originated from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 and have the destination to the host 5.1.3.x (via Telnet) will be denied.
Question 9
The following configuration line was added to router R1
Access-list 101 permit ip 10.25.30.0 0.0.0.255 any
What is the effect of this access list configuration?
A – permit all packets matching the first three octets of the source address to all destinations
B – permit all packet matching the last octet of the destination address and accept all source addresses
C – permit all packet matching the host bits in the source address to all destinations
D – permit all packet from the third subnet of the network address to all destinations
Answer: A



HELP!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
plz can someone help, i am writing my CCNA on tuesday 4/12/12, i need the current questions and answers to enable me to pass. thanks in advance
my email is listofred@yahoo.com or listofred@gmail.com
URGENTLY!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Brain plz can u help with some the questions and answers. listofred@yahoo.com or listofred@gmail.com. thanks in advance
@9tut
subnet mask and increment value is wrong for QUS 1 /29=255.255.255.248 .
@Suresh :
you mixed the network covered by the ACL and the network address of RTB LANs.
The subnet mask and the increment value are correct in @9tut’s explanation.
9tut,
The explanation of Q4 is still not broken down enough to where I can understand the summarization part. I know how to arrive at the wild card mask but I do not understand the summarization aspect as I thought it was a /20 which aparently is wrong according to the answer above. Thanks for your help.
@Jamerican: The subnet mask in this case is /24. We need 4 networks so the number of bits to summarize is 2 (2^2 = 4). So /24 – 2 = /22. The process of summarizing networks is reverse to subnet them.
Hi guys! Can someone please sent me dumps in PDF or Word format from sekhar and brah. I am failing to open them using VCE. My ccna exam is on the 11th of december. One more thing what is the difference between 640-802 with official practice exam and just 640-802? I’ve seen these 2 exams when i opened the Pearson VUE to schedule my exam and i am confused. I want to know which one to choose. brentrobertson7@gmail.com
Hi guys! Can someone please sent me dumps in PDF or Word format from sekhar and brah. I am failing to open them using VCE. My ccna exam is on the 11th of december. One more thing what is the difference between 640-802 with official practice exam and just 640-802? I’ve seen these 2 exams when i opened the Pearson VUE to schedule my exam and i am confused. I want to know which one to choose. brentrobertson7@gmail.com
i failed to understand the explanation on question 8. Anyone with other solution please elaborate!
@brent
The keyword here is “in”. That means denying all packets coming in to the router Ethernet interface. Since answers A and C are trying to send packets on the same LAN the packets have to pass through the routers interface and return to the host (PC1 or PC2) which is on the same LAN and that’s where the coming back “in” through the Ethernet interface would be denied making B and D the correct answers. Answers B and D are traveling out the interface back not coming “in”.
@brent
Actually, i am wrong but the explanation is correct. I had to read it again.
sir how can i known the subnet mask is/22 of class b
according to question ? four 4
@anil
Because you are working out of the 3rd octet so you need to find a block size that will work with 16,17,18 and 19 which is 4…..(128,192,224,240,248 and your subnet mask 252. This 252 gives you a block size of 4 = your 16,17,18, and 19). The 3 you see in answer C is the wildcard mask which is one less than the block size.
16 = 0
17 = 1
18 = 2
19 = 3
yes, when it comes to wild card masking its important to know the block size, the mask is always one (1) less to the block size or we can call it the magic number.
Example a block size of 64 would be 63 , a block size of 32 would be 31 and so on.
thnks to 9tut . Im hoping to do my CCNA soon.
can some1 pls help me about q8? it should be A cause of the statement 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3. can someone explain this plz. im confuse.
Hi Can Someone explain to me Q8 i dont understand why D is one of the Answer
Thanks.
the answer to que 8 makes no sense coz l thot we were blocking the source”into the router”!,but the answers belong to the destination!
@ricccc@oli
deny 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 from this u identify they block the network not host..first find the subnet mask here /30 the incremental value is 4 it is 2nd subnetwork id blocking range for this 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11. similarly the destination network u compare the same formula 5.1.3.0..
@ricccc@oli
extend accesslist compare all those things in destination like (souce ip, destination ip, protocol, oure port, destination port ) but standard accesslist compare only source ip in desination only…
TY 9tut.
Today I have passed the CCNA. (860/825)
50 questions 3 labs (VTP, EIGRP, ACL). 35 from 9tut.
Also thanks a lot Brar and Sekhar (still valid from examcollection)
Ty again 9tut
Can any one explain how they got the answer at question 8
Question 8 Explanation:
The access list is extended known by the 101. Therefore it will block traffic from the source address or address range, to the destination address or address range. It can also block specific protocols, in this case telnet.
So the command access-list 101 deny tcp 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 eq telnet says this:
Access list 101 is extended, I want to deny something(or all of, in this case something((telnet))) the tcp protocol. I want to deny the source addresses 5.1.1.8 through 5.1.1.11.
It is the 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 because of the wild card mask 0.0.0.3.
I want to deny the source addresses listed above from the desination addresses 5.1.3.0 /24 Which is 5.1.3.0 – 5.1.3.255. Again the range is known from the wild card mask 0.0.0.255.
And I only want to block them on TCP protocol of telnet.
S0 the lists states it will block anything coming from the source 5.1.1.8 — 5.1.1.11 and going to the destination address range of 5.1.3.0 — 5.1.3.255 and it will only block them if it is using the telnet port as the destination port number.
é VERDADE A QUESTÃO NUMERO 8 ESTA TOTALMENTE CONFUSA!
question no: 8 is totally confusing…. is it right answer????
Hi ,
regarding question 1:
For network 192.168.15.32/29 ,How come the subnet mask is 255.255.255.240? shouldn’t it be 255.255.255.248 ? Please explain someone
@arif Those are LAN subnets. The ACL rules can apply to multiple hosts from different subnets with different masks.
Remember that masks applied to network addresses (prefixes – ex. /26) define some IP ranges. You just need to calculate the IP ranges and see where the rules apply.
Regarding Q8.
From “5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3″ statement in ACL, we get “5.1.1.8/255.255.255.252″ ; which is THE network, not host.
In 5.1.1.8/30 network, possible hosts are :5.1.1.9 and 5.1.1.10, while ‘.11′ is broadcast address for ’5.1.1.8/252′.
The IP address derived for hosts above thus contradicts the pictorial representation.
I.e PC1 should have been : 5.1.1.9/30, while PC2=5.1.1.10/30
Or it could have been ’5.1.1.8/30′ at the network level as well.
Please note that the options in ANSWER don’t refer to above complexities, rather just PC1 and Pc2. SO, we are good :).
Now take a look @ Destination -> 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 => 5.1.3.0/24 implies, 254 hosts in this subnet. And, as you see, these (Destination) hosts include 5.1.3.x (where x= 1-to-254). I.e Answer D(5.1.3.10) and D(5.1.3.8)
oops: I meant “I.e Answer B(5.1.3.10) and D(5.1.3.8)”.
i have doubt in inbound,outbound interface ….
Qus 2. i have set interface fa0/0 out bound…it show request time out…
and else i set interface fa0/0 in bound …it s show destination host unreachable….
what is the correct answer…what is different for these output…
can you help me 9tut……
Question 8
Because there is a switch in between. it guess it doesn’t need the router. The traffic flows via mac adres into the switch port and send out the switch port to the second PC (same domain)
remember that on a layer 2 network IP adressen don’t get used ( just packed into the frame ).
Pretty horrible questions because you might think its A. I think it can be answer better only by using the hardware in real life.
correct me if i am wrong
Q8:
oh btw
Source and destination that gets blocked are not matched for A … so PC1 can telnet to PC2 and gets allowed. so it’s a AND and not a OR statement.
Source is matched but not the destination so ….
regarding question 1:
For network 192.168.15.32/29 ,How come the subnet mask is 255.255.255.240? shouldn’t it be 255.255.255.248 ?
I don’t understand “The ACL rules can apply to multiple hosts from different subnets with different masks.
Remember that masks applied to network addresses (prefixes – ex. /26) define some IP ranges. You just need to calculate the IP ranges and see where the rules apply.”
pls ,Do not you tell me in detail anyone? Thank
Hello pals, I plan sitting for CCNA by February this year, can anyone send me the latest dump please.
sammyhero@gmail.com
Tnx
Could someone send me the last dumps please? mgiurni@gmail.com Thank you in advance!
Could anybody send the latest dumps to me please? i will take the exam the next week naylinnisme@gmail.com . Thanks..
@Wally:Quesiton8: You can connect multiple hosts to a HUB and connect thereon to Router Ethernet port. Also, note that ACl acts @ L3, not L2.
@sainyi:Question1: ACL statement has wildcard mask = 0.0.0.15 , which 255.255.255.240 subnet mask.
Question 1, Subnet mask should be 255.255.255.248, with total of 8 hosts per subnet. so the range should be 192.168.15.32 to 192.168.15.40…..
BUT take a look at the Accesslist in the question. The Accesslist has a wildcard mask of 0.0.0.15 which is 255.255.255.240 so it will allow hosts from Range 192.168.15.32 thru 192.168.15.46.. I know Cisco sucks when it comes to asking sane questions.
Question #4:
Is this about “route summarization” or just counting the number of bits needed to cover the number of networks? If it is about route summarization, can you please explain why the summarized network is “not” 172.29.16.0/20? No matter how/what I try, I end up with 20 as the number of common higher-level bits, not 22.
We don’t have any common bits between positions 3 and 0 inclusively. There are 4 common higher-level bits in the 3rd octect (they are at at position 7, 6, 5, and 4). Adding those 4 to the obvious 16 bits (for the first 2 octects) yields to a total of 20 common higher-level bits, hence my /20.
Am I trying too hard or have completely missed the point here? Any clarification will be greatly appreciated.
@Shafie:Q1: You may want to summarize 192.168.15.32/29 & 192.168.15.40/29 at RTB to get 192.168.15.32/28….same as 192.168.15.32 0.0.0.15 in ACL statement.
@Anonymous:Q4: While summarizing 3rd octet = 16 to 19, Bit3 and Bit2 are also common. So, total common bits = 6. Adding it /16 would become /22.
guys refering to question 8, the access list blocked the hosts on rthernet interface of the R1,and according to the statement and question “The access control list shown in the graphic has been applied to the Ethernet interface of router R1 using the ip access-group 101 in command. Which of the following Telnet sessions will be blocked by this ACL? (Choose two)” only hosts with addresses 5.1.1.9 and 5.1.1.10 will be blocked, any better explanation here,I am confused thanks
@Renolph:Q8: ’5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3′ is equal to 5.1.1.8/30. In 5.1.1.8/30 subnet, we’ve only 2 hosts = 5.1.1.9/30 & 5.1.1.10/30 with 5.1.1.11/30 being directed broadcast for 5.1.1.8/30 subnet. In destination end of ACL, we’ve ’5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255′, which will =5.1.3.0/24 subnet. Thus answers B & D.
@9tut
Question 7
Explanation wrong!
Yes, implicit deny will drop all traffic. But option C could not be correct one, if add “permit any any”. Because Acl has been applied on OUTBOUND direction of that interface! please correct me if i’m wrong! Thanking You!
@Pijush:Q7: You are right.
On the contrary, “If we use the command ‘access-list 135 permit ip any any’ at the end of this access list”, then FTP traffic from 192.169.1.9 to any host will be ALLOWED. Simply because of direction of ACL apply on eth0 and SRC/DST addresses in the packet:).
@Pijush, @shanks: Yes, the explanation is not correct. Thanks for your detection, I updated it.
Gonna make my exam next month, i still need practice… But can someone send new dumps for my email? Thanks !
gabrielsmello@gmail.com
can someone explain question no. 2 why it’s b,c is the answer?
Hello Good people, my CCNA exam is next week, could someone send me the lattest dumps please
my email address is nswai15@yahoo.com
I will really appreciate it.
if could get latest dumps. i would appreciate also
rayjr75@yahoo.com
What is happening to CCDA 9tut website. It appears to be done. Can anyone alert the webmaster because I don’t know how. Thanks in advance for your help.