CCNA – Hotspot
Here you will find answers to CCNA hotspot Questions
Hotspot Routing Question
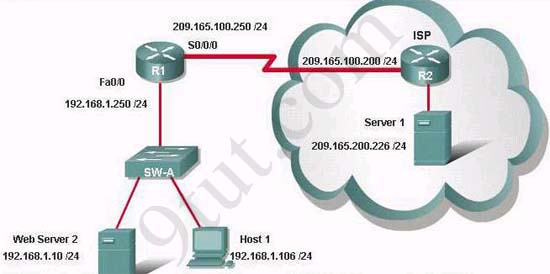
Question 1:
If the router R1 has a packet with a destination address 192.168.1.255, what describes the operation of the network?
A – R1 will forward the packet out all interfaces
B – R1 will drop this packet because it is not a valid IP address
C – As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will add 192.168.1.255 to its MAC table
D – R1 will encapsulate the packet in a frame with a destination MAC address of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
E – As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will forward it ti the device assigned the IP address of 192.168.1.255
Answer: B
Question 2:
Users on the 192.168.1.0/24 network must access files located on the Server 1. What route could be configured on router R1 for file requests to reach the server?
A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C – ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D – ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
Answer: A
Quetion 3:
When a packet is sent from Host 1 to Server 1, in how many different frames will the packet be encapsulated as it is sent across the internetwork?
A – 0
B – 1
C – 2
D – 3
E – 4
Answer: C or D(depending on your understand, please read the comments to understand why)
Question 4:
What must be configured on the network in order for users on the Internet to view web pages located on Web Server 2?
A – On router R2,configure a default static route to the 192.168.1.0 network
B – On router r2, configure DNS to resolve the URL assigned to Web Server 2 to the 192.168.1.10 address
C – On router R1, configure NAT to translate an address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to 192.168.1.10
D – On router R1, configure DHCP to assign a registered IP address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to Web Server 2
Answer: C
Question 5:
The router address 192.168.1.250 is the default gateway for both the Web Server 2 and Host 1. What is the correct subnet mask for this network?
A – 255.255.255.0
B – 255.255.255.192
C – 255.255.255.250
D – 255.255.255.252
Answer: A
Hotspot Frame-relay Question
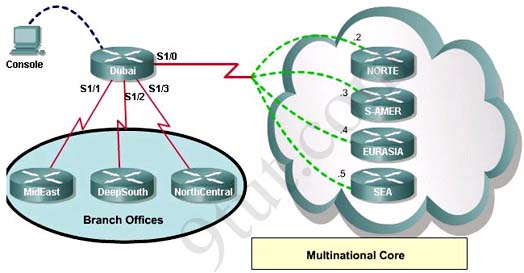
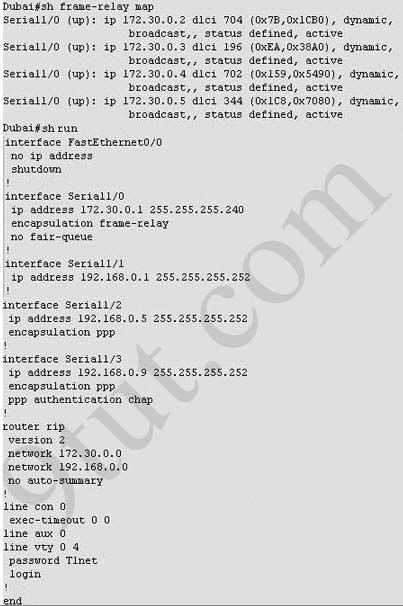
(In the old days, this question was a multi-choice question but Cisco upgraded it into a lab-sim question. Therefore, instead of listing all the configuration as above, you have to type show frame-relay map and show running-config to get its configuration)
Note: If you are not sure about Frame-Relay, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
Question 1:
What destination Layer 2 address will be used in the frame header containing a packet for host 172.30.0.4?
A – 704
B – 196
C – 702
D – 344
Answer: C
Question 2:
A static map to the S-AMER location is required. Which command should be used to create this map?
A – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 704 broadcast
B – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 196 broadcast
C – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 702 broadcast
D – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 344 broadcast
Answer: B
Question 3:
Which connection uses the default encapsulation for serial interfaces on Cisco routers?
A – The serial connection to the MidEast branch office
B – The serial connection to the DeepSouth branch office
C – The serial connection to the NorthCentral branch office
D – The serial connection to the Multinational Core
Answer: A
Question 4:
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router?
A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
Answer: A or D (because maybe there are 2 versions of this question, depending on the output of “show running-config” command, please read the explanation below)
Explanation
This question is not clear for a long time but now maybe the trick was solved. What Cisco wants to ask is the word used as password, not the type of connection, so in the exam you might see some strange words for answers like “En8ble”, “T1net”, “C0nsole”. All you have to do is to use the command “show running-config” as wx4 mentioned below to find the answer.
wx4 commented:
Q4: if password required which?
in my example it was connection to North!
How to figure out which pw is required?
#show running-config
1. check the interface to the router you need connection to. If there is “ppp authentication” you need a password!
2. you will find the password on the top of your running-config output
check the area:
username North password c0nsole
username xxxxx yyyyy
username…
in my case it was c0nsole, in your case it can be no password needed or a different password.
If you are still not clear, please read anton‘s comment:
A big question I noticed here was about the FR Lab regarding the password. You have to perform a show running-config and look for USERNAME and PASSWORD.
i.e.
username South_Router password c0nsol3
username North_Router password t31net
Obviously this has to be en PPP encapsulation, if asked for a posible password for SOUTH_ROUTER you pick c0nsol3, and for NORTH_ROUTER you pick t31net. If you’re running HDLC, i would pick “no password is required”.



Question 4:
Please send me the correct Answer ?
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router?
A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
no password required. its hdlc
Hi,
Q3: D – 3
cos the question is “how many different frames” not “many different frame types”.
Q4: A – No password is required
cos “connection” could be 2 things:
- layer 2 auth: but here the S1/1 to MidEast is HDLC (no auth)
- vty connection: on the client side don’t need configuration, just on the server (dubai) side.
Q4, first : configuration should be done in mideast to allow connection with dubai. the question stated you are in mideast and i think it doesn’t say connecting “from” dubai.
second : About connection –> simply connected wether remote access (telnet), cdp or ping (icmp). So if i could ping dubai from mideast.. than it is a successful connection that is allowed (would need access-list to block, or physically disconnected).
assumption : link between mideast and dubai is up. so encapsulation would be HDLC. if this link is down, you don’t need any password since no way you could connect this two devices without editing encapsulation or troubleshoot physical link. So it must be : up & HDLC.
if you are in mideast and want to telnet dubai, you don’t have to configure anything in mideast. telnet as answer would be incorrect, since you ask to configure something.
I won’t choose T1Net either, why would i have to configure the same password as dubai. telnet password is locally significant.
I’ll go with “no password required”. even if that would make me non 1000 achiever;-)
Hi all !
What is the difference between a CSU/DSU and a modem?
A.
A CSU/DSU converts analog signals from a router to a leased line; a modem converts analog signals from a router to a leased line.
B.
A CSU/DSU converts analog signals from a router to a phone line; a modem converts digital signals from a router to a leased line.
C.
A CSU/DSU converts digital signals from a router to a phone line; a modem converts analog signals from a router to a phone line.
D.
A CSU/DSU converts digital signals from a router to a leased line; a modem converts digital signals from a router to a phone line.
Answer: D
If the answer is right, please give me any explanation please.
can modem converts analog signal into digital signal, always?
Is that right, I hope right, router to phone is digital into analog ??
Please clear my confusion,..
ccnaman
the phone lines as you know are analog , so the modem take the signal (digital) from the router (or even from a PC ) to the phone line and vice-versa (Modem is acronym of Modulation Demodulation ) ,as the CSU/DSU , does , it just the technology is different as phone lines and leased line are # .I hope this may help
Hi all!
Thank you for the mms.
Please answer or clear my thought?
On the net work 131.1.123.0/ 27 What is the last Ip address that can be assigned to a host?
1.131.1.123.30
2.131.1.123.31
3.131.1.123.32
4.131.1.123.33
Answer is 1.
my answer is 4. ??
examinar do not mention any subnets, he asked boldly last ip address is what?
So my answer is 4. ( last, one he provided very last one.
If he mention find the last from the 1st subnet, answer 1. is right.)
answer 2 and 3 are bcast and Nw respectively.
If anybody answer my confusion please?
For Ccnaman
You are given the network address of 131.1.123.0 with a /27. the last address must be within the .0 network therefore 1 is the answer.
you have given this network 131.1.123.0/27
so it your subnet network here : 131.1.123.0
since it /27 , so the block size 0, 32, 64 , 96 and so on
and in the question u have been asked is to use the last valid IP on this network or on this first subnet (131.1.123.0) which is 131.1.123.30 as thre range again is (0-30) and .31s the broadcast for this network (or this subnet .0)
and you answer , u took the the first ip on the second subnet .32 )
which its range (33-62) Broadcast .63
Thanks
Users on the 192.168.1.0/24 network must access files located on the Server 1. What route could be configured on router R1 for file requests to reach the server?
A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C – ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D – ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
For this question option C should be correct. How can be Question A is the correct choice?
Please Explain its Urgent!
Dear 9tut:
Users on the 192.168.1.0/24 network must access files located on the Server 1. What route could be configured on router R1 for file requests to reach the server?
A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C – ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D – ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
For this question option C should be correct. How can be Question A is the correct choice?
Please Explain its Urgent!
Option C ,it’s not the correct answer because you need the next hop for the 209.165.200.0 network which is s/0/0/0 i.e 209.165.100.250/24
Ok, janazeb and Pete, if it’s urgent you need to go ahead and start reading more about the static routing, that’s a topic mentioned even before dynamic routing so for you to spend time on this website right now will actually be detrimental to your studies. Go back to the books if you really want to use your cert for any good. I will give you a freebie this time around ;)
Users on the 192.168.1.0/24 network must access files located on the Server 1. What route could be configured on router R1 for file requests to reach the server?
A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C – ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D – ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
The only viable answer is A.
It can’t be B because R1 doesn’t have an interface with address 209.165.200.226
It can’t be C because R1 doesn’t have an interface with address 192.168.1.250, but it does have an interface with 209.165.100.250 (but that’s not what the answer says).
It can’t be D because we are not trying to go to the 192.168.1.0 network (it’s not the network where the server is).
But A, will allow any address go out to s0/0/0 and that would work, the R2 will take care of the rest…
Now, don’t forget to read that book. It’s good for you and it will help you long term. I promise. ;-)
Q1 Answer 1 seems incorrect.
a ping to .255 results in a broadcast ping:
—-#ping 192.168.5.255
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.5.255, timeout is 2 seconds:
Reply to request 0 from 192.168.5.54, 1 ms
Reply to request 0 from 192.168.5.11, 1 ms
Reply to request 0 from 192.168.5.13, 1 ms
Reply to request 0 from 192.168.5.10, 1 ms
Reply to request 0 from 192.168.5.15, 1 ms
Reply to request 0 from 192.168.5.12, 1 ms
….
cheers,
harb
@harb
the q.1 says if the router receives a packet with dest. add. of
- The b-cast add. – what happens …
it is dropped routers dont pass a broadcast address…
please all can any one make this lab on packet tracer and send it to me
E-mail : eng.mostafa_mahmoud99@yahoo.com
hai to all..!
i am preparing for ccna exam.
can you help me which material or website will help to me.
and also tell me please from which website questions will come to my exam ..
please please.
E-Mail:make_frnd@yahoo.com
With regards to Q4… I had the same ques on another practice test and the answer was “no password required”. This one says Telnet.
I cannot find info on this anywhere, not even in the ccna book(Todd Lammle 640-802) I saw the same ? on the actual test I recently took(score=770) and not sure if I got it right or wrong?
Please help…?…
I am going to take my exam tomorrow. Pls let me know latest updates on 640-802 CCNA
hasy do tell me how ws your exam….i am going to take it on this 14th..
ur a fresher too???
reply @ my email id “kundankumar1989@rediffmail.com”
Hay, does anybody know when in the real exam do we need to issue
“#show frame-relay map” command to view the map. or is it being given as part of the question like it shown at the top????
Took the test last week. It was given – no need to type it in. The only sim that required me to type in commands was the VLAN/Switch question(5 questions given from a diagram which requires to click on SW3 and do your “sh” commands).
Also, the two sims(obviously) – I had the EIGRP and ACL sim.
Thanx mate…. that was really helpful, I’m taking the exam on 14th
cheers….
STudy hard! Wish you the best.
@ kiran
9tut would be right in guessing the questions most of the time. Since you’ve asked about the material as well, you seem to be serious in developing concepts as well.
For a killer understanding of everything, follow this path:
1. 1st watch:
CBT Nuggets’ CCNA CCENT ExamPack 640-822 ICND1 by Jeremy Cioara
CBT Nuggets – CCNA ExamPack 640-816 ICND2 by Jeremy Cioara
2. Then download and read Cisco Networking Academy’s official course material for CCNA exploration. It will be 4 parts:
Network Fundamentals
Routing Protocols and Concepts
LAN Switching and Wireless
Accessing the WAN
3. Then check 9tut, TestInside and CertKing etc to test your understanding.
There is no point in mugging up the dumps without knowing the concepts. Networks are a beautiful thing that’s worth spending your time upon.
@ ccnaman
Hi all !
What is the difference between a CSU/DSU and a modem?
A. A CSU/DSU converts analog signals from a router to a leased line; a modem converts analog signals from a router to a leased line.
B. A CSU/DSU converts analog signals from a router to a phone line; a modem converts digital signals from a router to a leased line.
C. A CSU/DSU converts digital signals from a router to a phone line; a modem converts analog signals from a router to a phone line.
D. A CSU/DSU converts digital signals from a router to a leased line; a modem converts digital signals from a router to a phone line.
Answer: D
If the answer is right, please give me any explanation please.
can modem converts analog signal into digital signal, always?
Is that right, I hope right, router to phone is digital into analog ??
Please clear my confusion,..
ccnaman
———-
Digital means system using discontinuous or discrete values while analog means continuous signalling.
In plain terms think of digital signal as:
Something relating to two digits 0 and 1
Some thing JUMPING to NEXT value instead of TRANSFORMING into it e.g. time on your digital clock
Weight on you digital scales
Think of analog signal as something continuous like:
Electrical sine wave
Hours, minutes and seconds hand travelling all the way to next mark
Pointing needle travelling all the way from 0 to your weight on your mechanical scales
A modem (Modulator-Demodulator) works both ways. Remember old dial-up days when you used to plug-in your phone RJ-11 connector into the modem to go online? In that situaltion it converts the DIGITAL data from your computer into modulated electrical signals for travelling over telephone channel (POTS – ANALOG). The ISP can have whatever equipment but you take data back via same phone-line where your modem demodulates the electrical signal to recover digital data.
A. False: Modems don’t connect to leased lines
B. False: CSU/DSUs don’t connect to phone lines nor modems to leased lines
C. False: CSU/DSUs don’t connect to phone lines
D: True
Any info on question 4?? Is the “real” answer telnet?? Its gotta be, no?
About question 4:
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router?
A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
On Dubai router we have password just for Telnet connection ( see on the bottom of sh run command for Dubai router) and that is it.
If we have to log from MidEast router to Dubai router then we have to use telnet password.
But I agree question is not quite clear.
The question says… “to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router?”
It says nothing about a “telnet” connection. Simply “A” connection. So I believe it would not require a PW. Unless the question asked for a “telnet” connection.
Thank u all for your input. I hope I don’t get this question on the test again.
thanku 9tut
Hi all, i am preparing for CCNA exam so could anyone of you sugguest me about materials..?
from where i could get those mashti and acme dumps? plz help me
i gave my ccna on dec 18th.. m so greatful n thankful to pass4sure ESP 9TUT.. 9TUT has been doing a great job.. sims were eigrp,access-list,vtp (all from 9tut)..Go thru 9tut before u appear for the exam..
Thanks 9tut..keep rrrrockinggggggg!!!!
pakistani sir itne panlun hyy..kuch btate he nae hain bus student atay jain or paise milte jae in ko…..dagardallllllliiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii k ptr hain.
hmm i think question 4 in frame relay actually tests you for the fact that you can’t telnet somewhere if you didnt set password on that router for the telnet connections. You also have this question among 600+ questions in testinside/pass4sure etc.
Can somebody explain question 2 as the answer says A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
thanx in advance
@pavan
its is default static route to the destination you want to reach server
ip default static route – 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 interface its reaching destination
we have the ip address of 192.168.1.106 which is ip address of the host 1
CORRECT ME IF I AM WRONG CHEERS!!
Hey Guys!
>>harb
>>December 2nd, 2010
>>Q1 Answer 1 seems incorrect.
Confirm, the answer is incorrect. Cirect answer is D
hello
i failed my exam on the 23rd of dec 2010 that was devastating
im gonna reset my exam as soon as possible
i failed it because of a hotspot question and now im freeked out i can hardly concentrate
Hello,
I want to comment question 4(frame relay) as I had it today in my ICND2 exam. Actually in the test the runing config of DUBAI had an entry for chap authentication like:
encapsulation ppp
ppp authentication chap
username Mideast password C0nsole
So the answer is pretty obvious. I think here on 9tut those lines were omited or if not in this case the answer is : no password required.
Answer hot spot question 3
is D
Explanation:
First:Host1 encapsulates the packet into frames and forwards to theswitch.
Switch in turn forwards the same frame. to router R1.
Second:Router R1 receives the frame. on one interface and it is encapsulates into new packet once it leaves the router R1 towards the direction of server1.
Third:R2 receives this packet and it also encapsulates the frame. into new packet when it is forwarded to server1 on different interface of R2.
Therefore the packet is sent using three different frames to reach from Host1 to server1.
Q4: “in how many different frames will the packet be encapsulated”
frame – layer 2 PDU (Protocol Data Unit)
packet – layer 3 PDU
I think answer E is correct because 4 different destination MAC adresses are used as it is sent across the internetwork.
Thanks Anonymous. That makes ALOT more sense because blindly assuming that they are talking about the telnet session (vty) password just felt so WRONG. HDLC requires no authentication and if they were talking about a telnet connection then they would have said “telnet” or “virtual terminal”…
I’m gonna stick to the facts on this one.
whats the correct answer for this
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router?
A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
Please help
Refer to the exhibit, according to the routing table, where will the router send a pkt destined for 10.1.5.65
int next hop
10.1.5.0/24 e0 10.1.1.2
10.2.5.64/28 e1 10.1.2.2
10.1.5.64/29 s0 10.1.3.3
10.1.5.64/27 s1 10.1.4.4
a. 10.1.1.2
b.10.1.2.2
c.10.1.3.3
d.10.1.4.4
According to me the 10.1.5.65 is available as a host on all the four subnets.
Dear 9tut,
Question 4:
What must be configured on the network in order for users on the Internet to view web pages located on Web Server 2?
A – On router R2,configure a default static route to the 192.168.1.0 network
B – On router r2, configure DNS to resolve the URL assigned to Web Server 2 to the 192.168.1.10 address
C – On router R1, configure NAT to translate an address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to 192.168.1.10
D – On router R1, configure DHCP to assign a registered IP address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to Web Server 2
I consider option c wrong, why?
Internal servers always configured with a static address and not a dynamic address so that, network/host outside the internal network can get easy access to it.
I consider option B correct, Why?
DNS and url resolution deals with static address. It maps the internal address to a static public address, so that host outside the network can get access to it. The flow is like this:
Outside host ->public address of Server2 -> internal address of server2. when configuring the DNS, it is the public static address that is always used.
Please, correct me if I am wrong, I am waiting for your confirmation
Regards
JKano
Dear 9tut,
Quetion 3: Hotspot
When a packet is sent from Host 1 to Server 1, in how many different frames will the packet be encapsulated as it is sent across the internetwork?
A – 0
B – 1
C – 2
D – 3
E – 4
I consider option D to be the correct answer, Why?
There are two ethernet encapsulation and One wan encapsulation. But the two ethernet encapsulation changes the source and destination and new FCS is calculated. That distinguish their encapsulation. In total :
2 different ethernet encapsulation + I wan encapsulation = 3 different encapsulations
Best regards,
JKano
Please forgive the long post, but my conscience cannot let me pass this opportunity for Cisco exams to steer you wrong if you answer this question as B and you pass the exam. :)
This is a very good but very horrible question, because of the word “has”. Did the router receive this packet or did the router generate the packet? From which interface? This might lead you to think, “if it transmitted the packet, it would be one way, but if it received the packet, it would be an other way.”
==>Either way, the router will not discard the packet.ipconfig
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : strance.net
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.254.2
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.254.1
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>route print
================================================================
================================================================Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.254.1 192.168.254.2 20
So, we know that our packets for R8 will go to R1 because R1 is our default gateway. Also note that ICMP should report a TTL of 253 (255-2) on our ICMP echo replies: (nul)->255 from W1 to R1; 255->254 from R1 to R5; and 254->253 from R5 to R8.
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>ping 155.1.58.8
Pinging 155.1.58.8 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 155.1.58.8: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=253
Reply from 155.1.58.8: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=253
Okay, good. Now we will perform the same test for the LAN of R8. We also have TTL=253 here, because the IP packet did not //traverse// another Layer3 device (TTL is decremented when packet is received on a device, so local “routing” will not affect TTL):
Reply from 155.1.8.8: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=253
Reply from 155.1.8.8: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=253
And now we will traceroute to both unicast addresses, to have a “baseline” of network path.
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>tracert 155.1.58.8
1 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms r1.strance.net [192.168.254.1]
2 2 ms 1 ms 2 ms r5.narodna.net [155.1.15.5]
3 5 ms 3 ms 2 ms r8.narodna.net [155.1.58.8]
Trace complete.
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>tracert 155.1.8.8
1 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms r1.strance.net [192.168.254.1]
2 2 ms 1 ms 2 ms r5.narodna.net [155.1.15.5]
3 5 ms 3 ms 2 ms r8.narodna.net [155.1.58.8]
Trace complete.
155.1.58.0/24 is Net-C from R5 to R8. 155.1.8.0/24 is the LAN on R8. But notice that the traceroute to 155.1.8.8 also stops at 155.1.58.8. This is because the interface is on the same end device, so the closest IP address to the ICMP Echo Request source will be the one to return the packet.
R8>show ip route connected
C 155.1.8.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 155.1.58.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
R8>
Now we will ping and traceroute to the BROADCAST address. Notice that the Net-C address of R8 is still the same IP Address to respond to the ICMP Echo Request. We see one minor difference in the traceroute:
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>ping 155.1.8.255
Pinging 155.1.8.255 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 155.1.58.8: bytes=32 time=48ms TTL=253
Reply from 155.1.58.8: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=253
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>tracert 155.1.8.255
Tracing route to 155.1.8.255 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms r1.strance.net [192.168.254.1]
2 2 ms 2 ms 1 ms r5.narodna.net [155.1.15.5]
3 2 ms 1 ms 3 ms r8.narodna.net [155.1.58.8]
4 7 ms 1 ms 1 ms r8.narodna.net [155.1.58.8]
Trace complete.
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>
==>Notice that the traceroute to 155.1.8.255 has an extra hop at 155.1.8.8<== And TTL is still 253, hmm. This is when the packet gets sent to the LAN of 155.1.8.0/24.
In the UNICAST traceroute, the IP address is on the same end device, so R8 can respond to Workstation-1 with ICMP Echo Reply.
However, in the case of traceroute to the BROADCAST address, R8 knows that the IP address is //connected// to itself, but it is not itself, so it must forward the packet. But to where? There is no ARP entry for 155.1.8.255. So it must send an ARP request for 155.1.8.255, to the Layer2 broadcast of FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
Networks have so many firewalls and ACLs these days, that we get lazy about remembering how ethernet works. The "split-horizon" rule of Ethernet is "When an ethernet interface (router or switch) receives a frame for an unknown destination, it forwards the frame out all of the interfaces except the one on which it was received." So, in this case, R8 is permitted to send the broadcast out to the LAN. R8 sends to FFFF.FFFF.FFFF as destination, with its LAN MAC as source. Server-1 replies to the frame that was sent from R8's MAC to FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. Servr-1 uses its own MAC address as source, and R8 MAC as destination. This is where the FFFF.FFFF.FFFF "disappears," and so the packet is able to come back into R8 as a Unicast packet.
Also, notice that in the case R1 and R5 routers both forwarded the broadcast packet towards R8, because they never knew that it was a broadcast.
R1 and R5 never saw this traffic as "broadcast" because W1 used the unicast MAC of R1 as destination, and its own MAC as source. R1 used its own MAC as source, and R5 MAC as destination. R5 uses its MAC as source, and R8 MAC as destination, etc. The transit routers did not have any idea that anyone was sending a broadcast.
Once the traffic arrives at R8, R8 must send the broadcast out the LAN interface, because the source frame at R8 was not an ethernet broadcast. Think about how ARP works.
The rule of "Routers do not forward broadcasts" is really "Routers do not forward Layer2 ethernet broadcasts, from one of their own Layer3 interfaces to another of their own Layer3 interfaces." Anything except for that is allowed. Again, if the router did not send Layer2 broadcasts, how would it ever discover any ARP entries?
As a final example, here we have router 7. It is connected to R5 from above. There are no ACL's on the interfaces. See how R7 cannot ping its own broadcast addresses, but R5 can ping the broadcast addresses of R7:
R7#show ip route connected
155.1.0.0/24 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 155.1.57.0 is directly connected, Vlan57
61.0.0.0/21 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 61.237.56.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.0.0.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
C 192.168.255.0/24 is directly connected, Vlan255
R7#
R7#ping 10.0.0.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
…..
R5#ping 10.0.0.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.0.0.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
You can see this in real life on your own network as long as you are separated by one Layer3 device (and network security ACL's allow it). Simply find the broadcast of a remote network, and ping that address. If you are on the same Layer3 device, you won't be able to ping. If you are on a different Layer3 device, the originating routers will swap the MAC addresses, and the terminating routers will never know that it was intended as a broadcast. Even on your local network, find your broadcast address and ping it. If workstations are not configured to block ping, you will see quite a number of replies.
Sorry again. My post got cut – probably because of its rediculous length :) Here is the first part of the post, with the networks:
This question is really testing your knowledge Layer2/Layer3 interaction in the OSI model. The “correct” answer could seem to be “B”, but the correct answer in real life is “D” and I will explain why below. This happens over Ethernet as well as Serial links.
Cisco might mark Answer D as incorrect, as this question at first appears to be testing fundamentals of subnetting and not testing fundamental of Layer2 forwarding.
But, maybe Cisco wants to REALLY test understanding here and will mark Answer D as correct. In any case, I will just hope that I did good enough on other questions to pass, and I will choose what I know is correct in real life. Hopefully this question is one of the 5 ungraded beta questions in the exam.
Now, the reason of Answer D:
Below is a network configured with Workstation-1 at left, with Server-1 at right. Router-1, Router-5, and Router-8 are transit routers in the path. Net-B, between R1 and R5, is a Serial HDLC link.
(W1)——-(R1)——-(R5)——-(R8)——-(S1)
Net-A Net-B Net-C Net-D
The lab is on real Cisco equipment, not on simulator such as Boson, PacketTracer, etc. Simulators are GREAT, btw, to this is not to say that simulators are not good, but this is how a real Cisco network responds to the conditions.
Hostname, IP address, and OSPF as routing protocol have been configured (Routing protocol does not matter, it could be RIP). All other configurations are default.
Firstly we will list the IP addresses in use. There is a /24 network between all devices, according to the names of the routers on the network. And each router uses an IP according to its name. Example, 155.1.15.0/24 is Network-A, between R1 and R5. R1 is using 155.1.15.1 and R5 is using 155.1.15.5
Also on each router there is a local /24 network for LAN, according to the number of the router, and the Router is using IP address according to its number. e.g. Router-8 LAN is 155.1.8.0/24 and the IP is 155.1.8.8/24. Every network is /24, which means that .255 is the broadcast address.
Network Addresses:
Network-A:192.168.254.0/24
Network-B:155.1.15.0/24
Network-C:155.1.58.0/24
Network-D:155.1.8.8/24
Node Addresses:
Wrkstn-1: 192.168.254.2 (to R1 Network-A)
Router-1: 192.168.254.1 (to LAN Network-A)
Router-1: 155.1.15.1 (To R5 Network-B)
Router-5: 155.1.15.5 (To R1 Network-B)
Router-5: 155.1.58.5 (To R8 Network-C)
Router-8: 155.1.58.8 (To R5 Network-C)
Router-8: 155.1.8.8 (To LAN Network-D)
Server-1: 155.1.8.10 (To R8 Network-D)
From Worksatation-1 we will //show IP address// and //show IP route//, to ensure we are using Router-1 as default gateway. Then we will perform two tests, one test against the “unicast” IP address and one test against the “broadcast” IP address.
First test will be to ping to Router-8, to see if we have “unicast” connectivity. Then we will traceroute to Router-8, to see the path.
Second test will be to ping the broadcast address that should be on Router-8. Then we will traceroute to that broadcast address, to see if it follows the same path as the unicast traceroute.
Workstation-1:
C:\Documents and Settings\Dood>ipconfig
…
HELP ME ON QUESTION 1…I don’t understand..shouldn’t the answer be D?? because it is a broadcast address packet..so it will encapsulate it in Ehternet frame with FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF to forward it to all hosts within a network???
Why would it drop the packet??? Please help me on this!!!
Question 4:
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the Dubai router?
A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
So what the heck is it?? 9tut says D, but as you all say, looking at it close, I guess you dont need a password. I had this question and I choose T1net..but I failed the exam overall with a 771. Is it A or D????? Man this one sucks!!