Frame Relay Tutorial
Let’s start this article with the question: Why do we need Frame Relay?
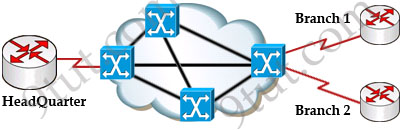
Let’s take a simple example. Suppose you are working in a big company and your company has just expanded to two new locations. The main site is connected to two branch offices, named Branch 1 & Branch 2 and your boss wants these two branches can communicate with the main site. The most simple solution is to connect them directly (called a leased line) as shown below:

To connect to these two branches, the main site router, HeadQuarter, requires two serial interfaces which a router can provide. But what happens when the company expands to 10 branches, 50 branches? For each point-to-point line, HeadQuarter needs a separate physical serial interface (and maybe a separate CSU/DSU if it is not integrated into the WAN card). As you can imagine, it will need many routers with many interfaces and lots of rack space for the routers and CSU/DSUs. Maybe we should use another solution for this problem? Luckily, Frame Relay can do it!
By using Frame Relay we only need one serial interface at the HeadQuarter to connect to all branches. This is also true when we expand to 10 or 50 branches. Moreover, the cost is much lesser than using leased-lines.
Frame Relay is a high-performance WAN protocol that operates at the physical and data link layers of the OSI reference model. It offers lower-cost data transfer when compared to typical point-to-point applications, by using virtual connections within the frame relay network and by combining those connections into a single physical connection at each location. Frame relay providers use a frame relay switch to route the data on each virtual circuit to the appropriate destination.
Maybe these terminologies of Frame Relay are difficult to understand so we will explain them in more detail in this article.
DCE & DTE
The first concept in Frame Relay you must grasp is about DTE & DCE:
+ Data terminal equipment (DTE), which is actually the user device and the logical Frame-relay end-system
+ Data communication equipment (DCE, also called data circuit-terminating equipment), which consists of modem and packet switch
In general, the routers are considered DTE, and the Frame Relay switches are DCE. The purpose of DCE equipment is to provide clocking and switching services in a network. In our example, HeadQuarter, Branch 1 & Branch 2 are DTEs while Frame Relay switches are DCEs.
Virtual Circuits
The logical connection through the Frame Relay network between two DTEs is called a virtual circuit (VC). The term “virtual” here means that the two DTEs are not connected directly but through a network. For example, the HeadQuarter & Branch 1 (or Branch 2) can communicate with each other as if they were directly connected but in fact they are connected through a Frame Relay network with many Frame Relay switches between them.
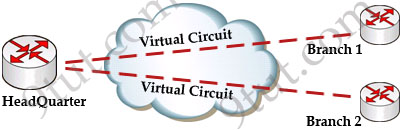
There are two types of VCs
+ switched virtual circuits (SVCs): are temporary connections that are only used when there is sporadic data transfer between DTE devices across the Frame Relay network. SVC is set up dynamically when needed. SVC connections require call setup and termination for each connection.
+ permanent virtual circuits (PVCs): A predefined VC. A PVC can be equated to a leased line in concept.
Nowadays most service providers offer PVC service only to save additional costs for signaling and billing procedures.



It seems easy when you’re reading it, because the examples are simple.
When you are given network diagrams, sometimes the frame relay connection is portrayed as a solid line from router to router, implying a physical connection (as in the leased line example at the top) when this is not actually the case.
The first thing to do in these cases is work out where the frame relay cloud is situated, and (from the routing perspective), focus on the endpoints of each VC.
If you are dealing with a full mesh or ‘hub and spoke’ design, you can ignore the connections within the cloud itself. This is only important for a partial mesh where more than one router is taking on a distributive role.
When you are also required to perform configuration, it may help to use your note-taking materials in the exam to construct your own diagram. This way, you can keep the question on screen with your console, while having a diagram that you can edit if required.
Great work!
Thank you so much!
said Ed Perrott, there are actually numerous patchwork purses you can pick from. were piped over a distance of 16km to a tailing dam sited in Lohan Valley about 980m below the mine.?
i want to download this in pdf document how can i download it\.
thanks a lot for the tutorial, it clarified things…
so there is a frame-relay encapsulation type “cisco” and an LMI type “cisco” as well. 2 different things but the same name..
hi there,
I have appreciate your explanation and the tutorial was simple and nice to understanding .
thanks
madja
Thank you for a well explained and presented article
very easy for study
This is very easy to understand and usefully for a newbie like me. THANK YOU!
arrr
Hi,
Very nice explanation.Really helful.
I think there is a small mistake in diagram labeling. For branch-2 DLCI 51, but in diagram it shows DLCI -49..
Nasir uddin Pavel
Linux pathshala
Hi,
Very nice explanation.Really helful.
I think there is a small mistake in diagram labeling. For branch-2 DLCI 51, but in diagram it shows DLCI -49..
Nasir uddin Pavel
Linux pathshala
@Linux Pathshala: It is not a mistake. The DLCI 49 is used on Branch 2 for traffic to the HeadQuarter.
plsssssssssssss help for dis exami need dumps oooo
what is the difference b/w RARP and InARP…?
@ Adex
if u need CCNA 200-120 dumps i will provide of other then sorry…
HI
Very nice explaniation
But I have a question
For branch-2 DLCI 51, but in diagram it shows DLCI -49..
It is not a mistake. The DLCI 49 is used on Branch 2 for traffic to the HeadQuarter.
why HQ & branch-1 DLCI is 23 both sides, and HQ DLCI 51,For branch-2 DLCI is 49.
what about it if I had more than 2 branches
are those standards
Thank you
@jefdezp: It is not a mistake. We implied DLCI is a random number used by both devices so they can be the same (DLCI 23 between HQ & Branch1) or different (DLCI 51 & 49 between HQ & Branch2). If more branches are added they just use other DLCIs, provided they are different at the local routers.
In Frame Relay InARP is the extension for ARP whereas RARP is the Reverse Address Resolution Protocol.
nice
very easy explanation.. thanks
HI
very nice tutorial
Frame-relay is not a problem to me, is easy to work with it dose not require that much typing commands. good luck guys.
Excellent tutorial
Great article. A little confusion here—why do we need DLCI when we already have PVC Number?
superb tutorial
hi guys ! who are asking dumps over and over.
let me tell you
check everything on this site! Enough to pass!
You guys are awesome. God bless you dear.@9tut
nice explanation
Very nice explanations with simple understanding examples ..i love it
VCE PLAYER 1.1.7 crack is needed for my exams , can any one help ?
or is there other application which can open VCE files ?
thx in advance to send info on tn.touareg@live.fr
Did anyone do Boson simulations? I mean there are ICND1 ,ICND2 and CCNP for old syllabus. Is CCNP frame relay of Boson applicable to new CCNA(200-120) ?
Great work. thanks alot
the exam has changed. the dumps is now uselesss
what is the types that frame relay network transfer data?
Great piece of work! Full of information.
how bout CSU/DSU. how does it work?
got the frame relay concept..
This is the simplest way for explaining things in detail.
Hi, I think there is a mistake in the Quiz 11 question 43 about frame-relay mapping.
You have this situation.
R1 DLCI 100——————————————————–R2 DLCI 200
IP: 172.16.100.2/16 172.16.100.1
The configuration on R1 was : #frame-relay map ip 172.16.100.1 100 broadcast
Which in my concept is good!!
But in the quiz answers when you choose : “incorrect map statement ” then you have it right. But actually the configuration was good!!
Great tutorial!
VCE player higher version 1.1.7 or above , needed for my exam prctice. please help me >>>
my email : sarohan.sanjaya@gmail.com
I passed my icnd 1 last year August. this site played a huge part to that. Now im ont Icnd 2 in the nearest future. Thumbs up to the admin of this site
if you are only concerned with this MATERIAL because you want to pass the test…you have NO BUSINESS administering a live production site.
GET understanding first…and the exam will just be another boring example to you and you’ll be able to concentrate on TROUBLESHOOTING TECHNIQUES and how to GET to the answers effectively and quickly.
-M
wonderfull work thanks many
syed, to download to pdf, simply select entire text and right click (if you are using chrome) and choose print; one of your printers needs to be set up as a pdf output; it will save to that file then print
helpful thaxs
helpful thaxs
Simple and clear
nyce