CCNA – STP Questions
Here you will find answers to Spanning Tree Protocol Questions
Note: If you are not sure how STP and RSTP work, please read my STP tutorial and RSTP tutorial.
Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
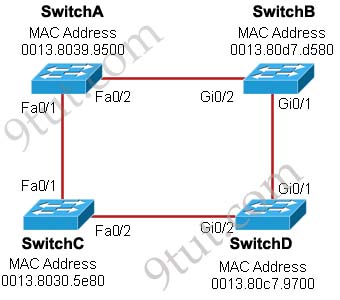
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again
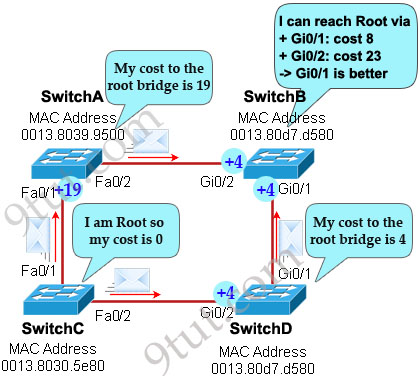
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
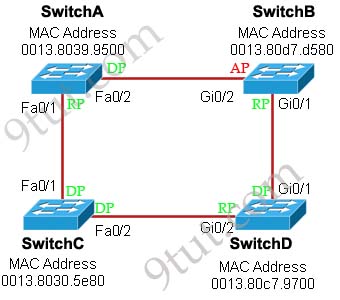
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 8
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 9
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
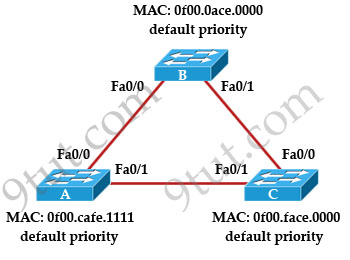
A. Switch A – Fa0/0
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.
On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.



hi,
Regarding Q.2
The RSTP groups blocking and listen states ,so the right answer is : A & E
please want to confirm that answer.
Hi, can anybody care to explain question 10?
@ Mick
First find the root bridge with the lowest BID(Prio+MAC add)….In this case it is the switch B. Remember that all the ports of the root bridge are always Desg…ie in this case Switch B – Fa0/0 and Switch B – Fa0/1….
Now the the ports to which the the other switches are directly connected to becomes the Root ports…..in this case . Switch A – Fa0/0 and Switch C – Fa0/0
Now what remain is to find the one Blocking or the Altn port so that we dont have a Loop..
The ALTN port will be the remaining port of the highest BID….in this case Swicht C…..ie Switch C – Fa0/1……
n we mark the remaining port of the Switch A ie Switch A – Fa0/1 as Desgn….cos it has lower BID than switch C
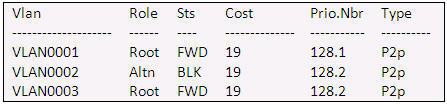
To summarise
Switch A
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
—————- —- — ——— ——– ——————————–
Fa0/0 Root FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.2 P2p
Switch B
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
—————- —- — ——— ——– ——————————–
Fa0/0 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.2 P2p
Switch C
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
—————- —- — ——— ——– ——————————–
Fa0/0 Root FWD 19 128.1 P2p
Fa0/1 Altn BLK 19 128.2 P2p
Hope u understood…ne doubts then ask….
Sorry @CL…Question 10…
Hi Niwsa,
now i get it…thx a lot for the sharing!
Q2- Blocking is NOT a port state in RSTP, that should be Discarding
3 RSTP Port States: Discarding, Learning, Forwarding only
vs
4 STP Port States: Blocking, Listening, Learning, Forwarding
Note Controversy: Disabled is not considered a true STP or RSTP port state due to the fact it indicates interface is inactive whereby Spanning-Tree has no participatory role.
@Mike: Yes I agree with you that RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state may be considered the best alternative answer.
great sharing……..thank to all guys….
Q.7 not that it changes the outcome of the logic, but SW-B and SW-D have the same MAC: 0013.80d7.d580. It did confuse me some untill I understood the logic.
This site is great in helping to fill in the blanks, I see more of how to do it the right way here than seeing the wrong way to do it and trying to figure out why it is wrong.
How can you know it is wrong if you never see it right/correct.
@kapptaink: Thanks for your detection. I updated that image!
Hello, first id like to thank you for the website, it’s a great work!
I have a question concerning the Q7 : why is the SwitchD advertising a cost of 4 to the SwitchB, while it’s connexion to the root SwitchC is at 100Mbps? Shouldn’t it advertises the link cost (19) instead of it’s interface cost(4)?
Q.10
plz explain comparison for bridge id for switch C & A..
@rohini :
Bridge ID of switch A = 32768:0f00.cafe.1111
Bridge ID of switch C = 32768:0f00.face.0000
MAC address 0f00.c—.—- is lower than 0f00.f—.—-
@Clément: Switch C only advertises its cost (0) to SwitchD and Switch D plus that cost with the cost at its local interface Gi0/2. Because Gi0/2 is a 1Gbps so its cost is 4.
hello,
in question 7 the last exibit is false no ?
between switch C and Switch D it’s not a gigabytes link but a fast link (the link according to the lowest speed no ?)
C have a fast port and D a giga port link is fast not giga so cost are 19 not 4.
But answer are not changed…hopefully
Q7
in question 7 is told that
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> C is not correct.
but this is true if all links will be the same and is about port 1and 2 only to switch B
if all links will be the same port Fao2/ of Switch A never be alternetive
here we have gigabit ports and fast ports and cost told us which link willbe alternate
(root + mac adress told us which port choose if cost from two direction wilbe the same)
@9tut : thanks fo the answer. In fact I understand the fact that the switch communicates its interface cost, but how can the STP be efficient if only the interface speed is considered and not the link speed? I mean 1000Mbps to 1000Mbps link is faster than a 100Mbps to 1000Mbps, in this case, the frames could be transfered to the slower link. Do you have to configure the cost manually in this case or the STP is “smart” enough to chose the better link? I don’t know if I’m understandable, english isn’t my mother tongue and it would be clearer with a schema.
Anyway, the important thing is that I passed my exam Tuesday and that the website helped me a lot. Thanks !
@Clément: In some cases, STP can use lower link but it is very rare. As an administrator maybe you will never try to link a 100Mbps with a 1000Mbps port.
However, we can manually configure the port cost on each interface so we can use any link we want to route packets on.
In Q 9
The correct ans is C Coz it haz the lower Bridge ID
Sorry for the post, The priority is higher……
hi all, can some one enlight me of how to solve this problem:
If u have any slight idea of how to solve it, kindly share the same :)
Given:
there are 2 switches A and B. Default priority for both. But Mac addr of A is logicaly less than B.
These switches are connected together by 2 fast ethernet connections(showing redundancy).
fa0/1 of switch A=> fa0/2 of switch B
fa0/12 of switch A=>fa0/11 of switch B
At the end of RSTP election,out of these 4 ports which port plays a discarding role???
OPTIONS:
1 Fa0/1 of Switch A
2 Fa0/12 of Switch A
3 Fa0/2 of Switch B
4 Fa0/11 of Switch B
Answer: 4. Fa0/11 of Switch B
Please tell me the logic behind backup port role in RSTP and how a port is elected to be a backup port.
Re Q 7.
I recreated the network in Packet Tracer 5.3.1 and used the vlan1 addresses in the order they appear, the lowest being C, 2nd lowest A, 3rd lowest D, and highest B.
The port states matched exact. However, the route costs were different than the example given in the explanation.
The Gi to fa costs were 19, not 4. Gi to Gi was 4.
I was puzzled by the explanatio, the Gi bit links HAD A COST of 4 but Switch A did not use fa0/2 aS A ROOT because the total cost would have been 12, less than the 19 of fa 0/1 on SwitchA.
I made the trunks from A->B & C->D Gi links, the cost was 4 (duplicating the costs in the example), and SwitchA used Gi port for root, not fa0/1. Fa0/1 became ALT.
Granted that Packet Tracer is using STP, not RSTP, but the logic is the same and only the speed is faster.
Hi!
Whats is the lowest value of these two:
0010:7bcc:733A
0010:7bcc:7347?
And why?
in Question 5
why the answer is not1 ( A ) ????!!!!
@ Cisco
The lowest number is 0010:7bcc:733a
The numbers are identical until the last two numbers on the right. In the 11th digit there is a 3 & a 4 respectively, 3 is the lower number so that MAC is the lowest. The lowest unique alpha-numeric digit to the left, makes it the lowest number or mac address.
@ abdelrady
The question is why fa0/10 is not the root port for vlan10.
It is true that more than one port is connected to the root but it does not tell you why fa0/10 is not the root port.
This port has a higher cost than the other port so this is an alternate port. If the port cost were = than the lower MAC would be desg and the higher would be alt.
@ Nad – Concerning STP or RSTP, all lower numbers are good. When STP or RSTP has to choose between two numbers it will always favour the lower number. So, Switch A has a lower or less MAC address than Switch B so RSTP will choose Switch A as the root switch. The root switch never ever blocks ports. They are always in a forwarding state and they are always designated ports. So if a port is going to be blocked it’s going to be on Switch B. You are given a choice between Fa 0/2 and Fa 0/11. Again RSTP will favour the lower number. In this case it’s Fa 0/2. It will elect this port as the root port and put it into a forwarding state. Fa 0/11 will then go into a blocking state to prevent loops.
What is the function of the command switchport trunk native vlan 999 on a trunk port?
A. It designates VLAN 999 for untagged traffic.
B. It blocks VLAN 999 traffic from passing on the trunk.
C. It creates a VLAN 999 interface.
D. It designates VLAN 999 as the default for all unkown tagged traffic.
Answer: D
is this answer correct
@dinesh
corect answer is: A
every untagged traffic will go to the native vlan.
imagine R1 with Fa0/0 send trafic to a trunk link..if u configure native on that switch port..lets say switchport trunk native vlan 999, all the trafic will go to vlan 999 (vlan 999 can be ur management interface).
every tagged traffic, lets say fa0/0.100 without native will be dropped by the switch. u can do this to work by puting on router this: encapsulation dot1q 100 native and all traffic will be forwarded also to vlan 999.
just practice and u will get the idea.
For questions 7, my understanding is that the designated port is the switch port that advertises lowest cost Hello onto a LAN. For the LAN between switch A and switch B, switch A advertises a hello with a cost of 19 out Fa0/2 and switch B advertises a cost of 8 out of Gi0/2 so the designated port should be Gi0/2 on switch B. Is this understanding correct?
Im confused about STP vlan and regular vlan. Why do we need to use sho spanning-tree vlan (#) Does one STP cover all vlans? Thanks
can somebody please explain question #5
I am going for exam on 25th of July, Please send me latest dumps at nikos_g_s@hotmail.com
@ dinesh
The answer has to be A.
The purpose of a vlan ID is so that trunk links can identify which vlan they belong to. The vlan ID also adds extra processing to read the ID and increases latency/delay in transmission.
The purpose of the native vlan is to accomodate traffic that does not have a vlan ID and reduce the processing time required. This allows traffic that needs to flow in real time (video/audio) to do so without the delay/latency involved with reading a vlan ID.
The answer cannot be D. ” It designates VLAN 999 as the default for all unkown tagged traffic.”. If the traffic is tagged then it cannot be unknown traffic, it will have a vlan ID.
my response is for ? 7… I think the question should ask for the correct 4 answers NOT only 3 correct answers when there are really 4 answers that are correct. The correct answer here is A,B,C,F… the explanation for the ? is correct…
BTW .. this site is awesome and i really appreciate your time and effort in this site. I believe this site to be just as helpful, if not more helpful, as the practice tests floating around the net.
thanks for all of your work.
Habib…. you do not need to be registered with Cisco to DL the PT 5.3.1…. This site is really all you need to help you. Honestly… if you test is in 2 weeks as you stated, you should really just be brushing up on everything. I found ALOT of my questions from the 640-802 exam on this site.. (some of which were word for word…
when i was brushing up for mine ( which I made a 910 ) I found that me writing on paper the different topics I found to give me the most problems, helped tremendously.. I dont know if it was the muscle memory from the writing or just the focus and concentration to write this stuff down helped…
hope you do well on your exam…
Thanks David A,
I agree with you that 9tut is really useful for those who are preparing their self for CCNA exam and thanks from those who make this website, but I couldn’t find the link to download PT 5.3.1, could you please assist me?
can somebody exlain to me the following terms mngmt vlan,default vlan,native vlan
@HABIB: Please try searching with google.com you surely find a link.
how to find out whether it is rstp or stp from outputs
@9tut
I think you should reconsider the explanation for question 7. I don’t think that the designated port is selected based on the MAC address.
The key thing here is that the link between Switch C & Switch D is different in speed and because the question said “no other configuration changes have been made”
=> Switch C and Switch D will negotiate to use 100 Mbps as the speed used on that link
=> This makes the root path cost changes
=> The consequence is the cost advertised by Switch B will be higher than Switch A
=> This will make the Fa0/2 on Switch A the Designated Port
Finally, the answer is correct, but I think the explanation is not. I post this comment because STP confused me a lot and I think it confused others also. Hope you will consider this comment.
Thank you.
Ah, one more thing, I did test this scenario and It worked out as I expected. When A Gigabit link connected to FastEthernet link, both sides have cost 19.
@9tut:
Leave it, I was wrong about STP does not use the MAC address. Sorry T_T
can anyone explain me Q.10.
the options of C and D are rite coz of switch B having the lower mac address, but hw is that possible of option B. pls xplain me….
@Giridhar: I updated Q.10 with the explanation, please check it.
Q7 I agree with the answer but not the explination and I am still confused after reading the discussions.
The explination of the last part states.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the porSwitchA & SwitchB. ts between It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative.
I belive we still use path cost to determine the designated port and so Fa0/2 is the designated port for that segment because
If we had a configuation like q10 which has equal path costs we would use the lowest MAC address?
Any thoughts, Thanks
Q2. Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
I getting two different responses for this question. Here the answer is A and D but other dumps are saying C and D is the answer. Which is the correct answer and why?
correct: A, D.
a disabled port is a port that is in “down / administratively down” (had the *shutdown* command applied to it). this kind of ports can not participate in the RSTP root/designated port election.
@Xallax thanks for the explanation. Can I say that RSTP convergence is when 2 switches decide which port would be forwarding and blocking.
yes, convergence is when the switches agreed who the root bridge is, which ports lead to the root, which ports are blocked and which of the blocked ports are backups