CCNA – STP Questions
Here you will find answers to Spanning Tree Protocol Questions
Note: If you are not sure how STP and RSTP work, please read my STP tutorial and RSTP tutorial.
Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
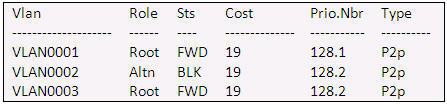
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
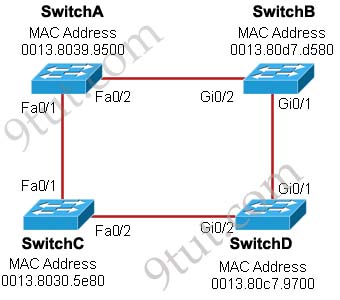
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again
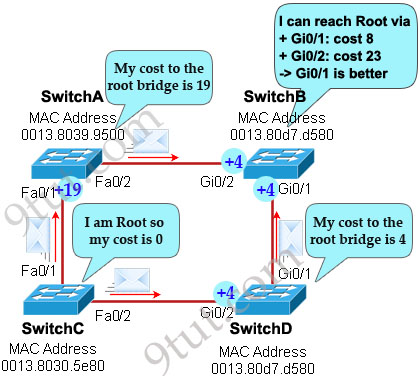
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
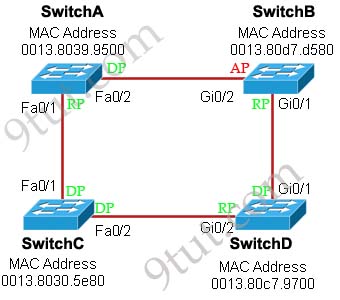
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 8
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 9
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
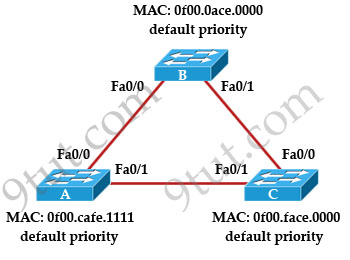
A. Switch A – Fa0/0
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.
On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.



@GK @9tut
There is no port status called blocking in RSTP instead it uses the term DISCARD.
There is a RSTP port role called DISABLED to indicate ports which are administratively shutdown
or are not capable of working due to some other reasons.
So correct answer is C and D.
In the case if you are not sure please refer ICND 2 wendell odoms book table 2-10 (Chapter 2 /page No :82)
@GK @9tut
Sorry there was some confusion about DISABLE status because in Cisco documents (http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cfa.shtml#edge) It clearly said that it is a STP status NOT RSTP STATUS.RSTP used DISCARDING instead of DISABLED.
SO I can only choose D !!!!!!!!!!!
9tut what do you think about it ?
@SMMS: I know answer A is not correct but it is the most suitable answer in this circumstance. Please read my comment above (on June 5th, 2011).
What is the function of the command switchport trunk native vlan 999 on a trunk port?
A. It designates VLAN 999 for untagged traffic.
B. It blocks VLAN 999 traffic from passing on the trunk.
C. It creates a VLAN 999 interface.
D. It designates VLAN 999 as the default for all unkown tagged traffic.
pls some one tell me the correct answer….my friend said in p4s dumps the answer is D…while here on 9tut its A…which one is it…they both seem correct…
@ 9tut
Ok .That’s correct I also believe it .A is the most suitable one.
Thanks
@ Deepti
native designate vlan 999 for untagged (NO TAGS APPLIED) frames. Not unknown tags.
@Deepti
correct ans is A Because default value of native VLAN is 1 .Vlan 999 is not default.
Hi, Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps at treepanel.ken@hotmail.com , i plan to take the exams at the end of sep.
Thanks.
Hi Guys. I have just finished my exam got 881, ACL to allow only B to access Finance Server, vtp , and eigrp, i think there is updates , because some questions were new for me,
read the entire this site 5 times and before going for exam….good luck
what is the right answer for question 2?
stp : listening, learning, forwarding, blocking , disabled
rstp: discarding, learning, forwarding, disabled
Thanks buddies….great work and explanation….when it explain with diagrams it seems to be so simple and easy to understand..
Echoing what Rogues Pierre mentioned
“Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the SwitchA & SwitchB. ts between It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative.”
Step 1. For switches connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost
to reach the root is the DP on that segment.
Step 2. In case of a tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the
lowest BID becomes the DP.
Based on this explanation, Switch B’s Gi 0/2 should be designated port and Switch A’s Fa 0/2 should be the alternate. They have unequal cost to the root bridge so we should follow step 1 first.
@Deepti
D. It designates VLAN 999 as the default for all unkown tagged traffic.—> this option is not correct because VLAN 1 is a default vlan and you cant change, configure or remove it.
So the correct answer is A.
correct —> It designates VLAN 999 for untagged traffic.
Isn’t the answer for Q9 faulty? As I understand it we could never have the value 32768 for it self, because we have at least VLAN 1 always so 32768 is wrong. Please correct me if I am wrong??
During the STP election process though, we don’t consider the vlans a switch has. So the BID would have a default priority of 32768 and the MAC Address.
Question 9
Q9 Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
i believe the answer is C which has a lower id than A!
@rose
look at the priority value plz, it’s not a multiple of 4096…
answer is A
@xallax
what is the result of the “no login” command?
ine vty 0 4
password c1sco
no login
A there is virtually a limitless supply of IP addresses
B Telnet access requires a new password at first login
C Telnet access requires a password
D Telnet access is denied
The dumps say D is correct
But from my understanding……when configuring telnet password, the ‘no login’ command should allow telnet acces without asking for a password.the correct option is not stated
@ayaj
line vty 0 4
enter line configuration for telnet/ssh lines 0 to 4
password c1sco
set the password for these 5 lines to c1sco
no login
do not ask for a password on login (big security issue!)
i don’t know where you found the question, but the possible answers don’t offer a correct variant.
you are correct on your assumption.
@xallax…..phew.thanks
@Ayaj
You & Xallax are both correct!! ‘password c1sco’ sets the password for vty 0 4 to c1sco. However, ‘no login’ tells you to not ask for a password. You are not prompted for the password that was set so telnet access is denied. I hope that helps!!!
In a STP configuration. For instance in a triangular topology, or Q7 above arrangement. Once the root bridge has been established.(Through election-exchanging of BPDU frames-BID) The switches facing the root bridge are automatically root ports. THAT IS GIVEN. The next step is to figure out which port becomes designated or blocked. I hope this eleminate some of the confusion.
@ Koffy
I beg to disagree that the switches facing the root bridge are automatically root ports. There is nothing automatic in the STP process.
Step 1: Determine all possible paths over which a frame, sent by the nonroot switch, can
reach the root switch.
Step 2: For each possible path in Step 1, add the costs of all outgoing interfaces
in that path.
Step 3: The lowest cost found is the cost to reach the root, and the outgoing
interface is that switch’s RP.
Step 4: If the cost ties, use the port priority tiebreaker, and if that ties, use the
lowest port number tiebreaker.
Nothing automatic on those steps. You still have to choose the lowest cost.
@Jeff
Please, don’t take it literally, when i say automatically. For instance, during exams, and you are press with time. the easiest way to figure out which ports are root port, that is after exchanging BPDU frames between switches and root bridge been elected. The switches facing the root bridge becomes root ports. Especially, in an arrangement just like Q7 of above topology; switches facing the root bridge becomes the root port. This saves you time from running all the calculations. Check Q7 and Q10 of above topology. This is just a little thing I picked up from the academy…..Off course, might be different in the real world.
On question 7 though, the root bridge is Switch C. So based on your explanation, how would you decide what would be the root port for Switch B? I mean you mentioned switches facing the root bridge becomes the root port. So which port is it?
@Jeff2
Regardless of what am saying, you have to understand that the election is done among the switches, not by you and I. But off course, as a network admin. you can always influence the election, and chose a particular switch you want to become the root bridge.
Back to your question. Q7.
Root bridge is switch C
Switch A Fa0/0 port become root port
Switch D Gi0/2 port become root port
Both ports on switch A and D are facing switch C, the root bridge.
Same applies to Q10. This is just a tip to get you out of a jam, when you are press with time during exams. But like i say, might be different in the real world.
And off course, as for switch B would have AP and RP base on topolgy. Switch B is not facing the root bridge. Switch B is sitting across from root bridge. I hope am not confusing you. Let me know if you need more clarity. Thanks.
@Koffy,
actually I had an issue with Q7 if you look at the discussion here. Let’s look at the link between switch A and B. The Fa 0/2 of A is connected to Gi 0/2 of B. Switch B will reach the root with a cost of 8 and A with a cost of 19. So between those 2, shouldn’t Gi 0/2 become the DP and Fa 0/2 becomes the AP? I didn’t enroll with a learning center or anything so maybe you could explain that to me. I already passed the ICND2 exam by the way. Q7 is just confusing me on the port roles between A and B.
I have a question that has been nagging me lately and I couldn’t find an adequate answer on the web, here it comes……
the LOGIN command has not the same effect on the vty line and the console line!!! If I put LOGIN on both of them without setting a pasword, then the vty lines will reject any login as expected. But when it comes to the console line, it will not have any effect.
I find this behaviour, starange enough, logical and acceptable. Otherwise we would end up doing password recovery, right??? But 1 thing is not answered yet. It should have been prohibitted to enter the command before creating for the console line, otherwise it is misleading to say that the command has the same effect on both vty and console line. What do you say people, please I need your reflection on that!!!
@Jeff2.
This what I’m going to do to clarify things for you. I will try to brief you a little bit on STP concept. Once you get a hang of it, would make your understanding and how to approach STP a little easier. This will take a bit of time, so bare with me. Okay buddy.
Electing a root bridge, and knowing which ports becomes RP/DP/AP is all done by the switches. This is a process where all switches exhange their BPDU(Bridge Protocol Data Unit) This is STP hello packets sent out at configurable intervals-every 2secs. Each BPDU contains the BID(Bridge ID) that identifies the switch that send the BPDU.The BID contains a priority value, the mac address of the sending switch, and an optional extended system ID. STP uses STA Spanning Tree Algorithm to determine which switch ports on a network need to be configured for blocking to prevent loop from occuring. Redundancy is the prime focus in STP. Availability. Just bareinmind, frames unlike IP packets have no TTL(Time To Live) If not terminated properly on a switch network, would continue to bounce from switch to switch endlessly, or until a link is disrupted and breaks the loop. On this note STP has to be effective on a network.
Q7 above is using mac address which much easier to solve if you understand MAC ADDRESS.(Alphanumerical). Once you determine which switch is the root bridge, the rest fall in place. Now lets take a look at the links. 10Gbps has cost 2(Gigi Link), 1Gbps has cost 4(Gigi Link), 100mbps has cost 19(Fast Ethernet Link), 10 mbps has cost 100(Ethernet Link)
Switch C is the root bridge, has a cost 0. Switch A has Fa0/0=cost 19 to reach the root bridge, switch D has Gigi link Gi0/2=cost 4 to reach the root bridge. Now switch B is trapped. Switch B has to figure out which is the quickest way to arrive at the root bridge. Switch B has two Gigi link Gi0/1 and Gi0/2, each has a cost 4. Now, imagine you are switch B (bareinmind, fast convergence) which direction will you chose to get you quickest to the root bridge? I think the picture is clear which direction to take.
Base on your question, I think you are confusing the election of which switch becomes the root bridge base on mac address, and the links to determine which switch would have a block port.
For B to reach the RB thru A is 19+4=23, and B to reach the RB thru D is 4+4=8. It is obviously the port Gi0/2 become the blocked port. Please, think of “fast convergence” Switch B under no any circumstance would have a DP. The switches facing the root bridge will have RP/DP respectively. Lastly, as a network admin. you can always influence the election process, and chose a switch you wish to become the RB. I hope this long and boring lecture helps a bit.
@Koffy
Again, I already earned my CCNA so I am familiar with STP and a lot of what you have written. My only concern on Q7 is the port roles of the Switch A and B segment (Fa 0/2 and Gi 0/2 respectively). Just that and nothing else. This is how it was explained here:
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port.
Again, I am talking about the A and B segment ONLY. For that, the first rule is:
Step 1: For switches connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost to reach the root is the DP on that segment.
Step 2: In case of a tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the lowest BID becomes the DP.
- Odom book
Switch B will reach the root with a cost of 8 while A with a cost of 19. It’s not a tie so we can apply step 1. The explanation here used step 2 but the cost again is not a tie. Based on this explanation, shouldn’t Switch B’s Gi 0/2 be the DP?
This is a STP tutorial from the Cisco learning network. https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/docs/DOC-6646. If you would browse on the last page, the bottom switch have a RP and 2 DP even though it is not facing the root bridge. It relied on the cost.
@Jeff2
Well, you do have a point there. STA would not permit what you are suggesting though. The way the switches are arranged and their link cost plays a big part in B port roles. STA finds the shortest path to the RB. B has to go thru A or D to the RB. But off course, if D is out of the picture, that changes the whole port roles. B becomes RP/DP. And A becomes RP/AP. As long as D stays in the picture, and B Gi0/2 is facing A Fa0/2 your suggestion won’t fly.
My advice is you read some more about how STA works.
@Koffy
You have some interesting comments that I need explanation for…
“..For B to reach the RB thru A is 19+4=23, and B to reach the RB thru D is 4+4=8. It is obviously the port Gi0/2 become the blocked port. Please, think of “fast convergence” Switch B under no any circumstance would have a DP. The switches facing the root bridge will have RP/DP respectively…”
According to the book “LAN switching and wireless”, the switch behaves differently depending if the costs to the RB are the same or not. If they are the same the decision would be rather easy. Read the following from the book, on page 266.
” When the switch decides to use one port over another for the root port, the other is configured as a non-designated port to prevent a loop from occuring. ”
According to your comment switch B would never ever have a DP due to its location on the topology. But that can’t be right. Isn’t it the path costs that decides the port roles and not how many switches you traverse to reach the root bridge??? Please expalin. Thanks.
@Bruno
Please take a close look at the topology above. There are two steps to it. The first step is the election of RB(Mac address)
The second step STA has to decided which port become blocked port.(base on path cost to RB). STA will not allow Switch B go through Switch A to the RB(cost 23) Switch D is a preferred route.(cost 8). As it stands, since B will go thru D and not A, then B Gi0/2 facing A Fa0/2 become blocked port. …Redundancy-loopless….If for any reason B Gi0/2 port is open, will create a loop. I’m still saying base on the arrangement of the switches in the above topology, switch B Gi0/2 port will not be DP, but AP(blocked port) as long as it is facing A Fa0/2 port. You may try rearranging the switches and eventually will have both ports on B as RP/DP. Thanks.
@ Koffy
“STA would not permit what you are suggesting though… As long as D stays in the picture, and B Gi0/2 is facing A Fa0/2 your suggestion won’t fly.”
I don’t understand what you are trying to tell about the presence of switch D. Do you agree that Switch B’s cost to reach the root is 8 and A is 19?
What I meant was , if Switch D is not present, then switch B will be directly connected to Switch C RB, and that changes the whole port roles. Base on the current path cost, Switch D ports(cost 4) becomes RP/DP respectively, and switch A ports(cost 19) becomes RP/AP respectively.
You ask me if i do agree that Switch B’s cost to reach the RB is 8 and A is 19. Yes, I do. But remember, the reference point in the above topology is Switch C.
B thru D to C RB=8(4+4)
B thru A to C RB=23(4+19) Therefore switch B to RB is 8 OR 23. And switch A to RB is 19.
Please, my comment here is solely base on Q7 above , and how the switches are arrsnged, path cost, types of links and so on. This instance might not be appicable in other topoligical arrangements, like in the real world, where you may encounter 10,20,50 100 or 1000′s of switches. Thanks.
@kOFFY:
The explanation part of the solution tell us that that port is blocked because the Bridge ID is lower than A’s. Do you agree with that expalanation??
@Bruno
Sir, I don’t quite agree with you. BID of a BPDU frame contain three seperate fields: Bridge Priority, Extended system ID, and Mac address. So far all we have is the switches mac addresses. I assume all the switches are configured with default priority value(32768). Also, keep in mind, the switch with the lower BID wins the competition, not the other way round.
The reason B’s Gi0/2 is blocked-AP is due to the position of the switch in relation to the RB. And bareinmind, that port is called Alternate Port. If for any reason the trunk link between switch B and D fail, STA will be forced to use the Aternate Port of switch B(the blocked port). Switch B plays a very important role in the above topology.
Please, read some more on how STA works. The above topology is not that complicated. It is only four switch configuration. Thanks.
@ Koffy
“The reason B’s Gi0/2 is blocked-AP is due to the position of the switch in relation to the RB”. You ask Bruno to read some more on STA but there is nothing in it that mentions a port can be designated as blocked due to its position.
@Jeff2
Please, you must read all on STP, STA inclusively. I’m sure you guys are well familiar with the concept, but it wouldn’t hurt to go back and read all on STP.
Please, just hear me out. Let’s break the above topology in a couple of scenarios (segements).
1. Switch B, Switch D, Switch C.(In relation to RB-C) This scenario will result into a tie.(Port ID values)
2. Switch B, Switch A, Switch C (In relation to RB-C) In this scenario Switch A becomes RP/AP.
3. Switch A, Switch D, Switch C (In relation to RB-C) In this scenario Switch A becomes RP/AP.
Now, lets look at the above topology in its original configuration-four switches, in a square arrangement, or rectangular arrangement.
Switch B has two paths to the RB-C.
Path #1. through D=cost 8
Path #2. through A=cost23.
Preferred path D.
Since switch B is position in between Switch D and switch A, the rule will force switch B to have one of its port blocked. The path with the cost 23 to RB be blocked. For the sake of fast convergence, and shortest path to the RB.
I am answering nad’s question:” Given:
there are 2 switches A and B. Default priority for both. But Mac addr of A is logicaly less than B.
These switches are connected together by 2 fast ethernet connections(showing redundancy).
fa0/1 of switch A=> fa0/2 of switch B
fa0/12 of switch A=>fa0/11 of switch B
At the end of RSTP election,out of these 4 ports which port plays a discarding role???
OPTIONS:
1 Fa0/1 of Switch A
2 Fa0/12 of Switch A
3 Fa0/2 of Switch B
4 Fa0/11 of Switch B
Answer: 4. Fa0/11 of Switch B”
Fa0/11 on switch B is higher than f0/2 so fa0/11 is in discarding mode. When no other info in provided, you compare the physical interface number. the lower number is the DP, the higher is the blocking (discarding mode.)
Thanks for question 7 9tut – It is a great explanation on how RSTP works in the election of RP and DP…
H.
Koffy – Wow – I did not read this entire thread… I will try to set this up in my lab – I didn’t think about the tie…
Again, I am talking about the A and B segment ONLY. For that, the first rule is:
Step 1: For switches connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost to reach the root is the DP on that segment.
Step 2: In case of a tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the lowest BID becomes the DP.
- Odom book
May be set this up in Packet Tracer…? I will try…
Hi, thanks for the site is awesome, I am having my test in the next few days and it has been of great help.
I have a doubt regarding Q7, can someone tell me which is the cost of the link between fa0/2 of SwA and Gi0/2 of SwB, 19 or 4?
thanks.
I think question 7′s explanation is wrong! but answers may be correct if:
“SwitchC, Fa0/2, designated”, instead of “SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated”
does anybody agree?
When of the questions in dump 486 ask for the two port states when RSTP is converged…The dump says C & D are correct (WRONG) should be A & D FYI
a.blocking
b.learning
c.disabled
d.forwarding
e.listening
thanks 9tut , The question 7 his explanation wonderful. Very helped me .
HI I have this question
whats the function of command switchport trunk native vlan 999 on trunk port ?
A- It block vlan 999 traffic from passing on the trunk
B- It creates a vlan 999 interface
C- It designate vlan 999 for untagged traffic.
D-It designate vlan 999 for as the default for all unknown tagged traffic
I answered it and choosed option C but in the dumps it choosed D
is that correct and why ?
the default vlan for untagged traffic is vlan 1, with that command you are changing the default vlan for untagged traffic to vlan 999. That is ma idea…
I have learned a lot from question no 7, thank a lot 9tut.