RIP Tutorial
In this tutorial we will learn about RIP routing protocol
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector routing protocol. RIP sends the complete routing table out to all active interfaces every 30 seconds. RIP only uses hop count (the number of routers) to determine the best way to a remote network.
Note: RIP v1 is a classful routing protocol but RIP v2 is a classless routing protocol.
Classful routing protocols do not include the subnet mask with the network address in routing updates, which can cause problems with discontiguous subnets or networks that use Variable-Length Subnet Masking (VLSM). Fortunately, RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol so subnet masks are included in the routing updates, making RIPv2 more compatible with modern routing environments.
Distance vector protocols advertise routing information by sending messages, called routing updates, out the interfaces on a router
Key points:
+ RIP uses hop counts to calculate optimal routes (a hop is a router).
+ RIP routing is limited to 15 hops to any location (16 hops indicates the network is unreachable).
+ RIP uses the split horizon with poison reverse method to prevent the count-to-infinity problem.
+ RIP uses only classful routing, so it uses full address classes, not subnets.
+ RIP broadcasts updates to the entire network.
+ RIP can maintain up to six multiple paths to each network, but only if the cost is the same.
+ RIP supports load balancing over same-cost paths.
+ The update interval default is 30, the invalid timer default is 180, the holddown timer default is 180, and the flush timer default is 240.
A big problem with distance vector routing protocol is routing loop
A common problem that could occur with routing protocol is that a routing loop. Let’s take a look at how a routing loop occurs.
——————–
Here we have routers A, B and C. Notice that at the beginning (when a routing protocol is not turned on) there are only directly connected networks in the routing tables of these routers. For example, in the routing table of router A, network 1.0.0.0 has already been known because it is directly connected through interface E0 and the metric (of a directly connected network) is 0 (these 3 parameters are shown in the routing tables below).
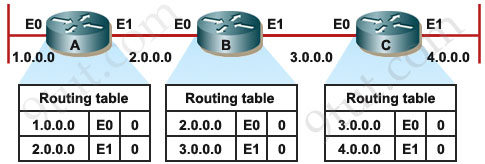
Also B knows networks 2.0.0.0 & 3.0.0.0 with a metric of 0.
Also C knows networks 3.0.0.0 & 4.0.0.0 with a metric of 0.
Now we turn on RIP on these routers (we will discuss the configuration later. In the rest of this article, we will call network 1.0.0.0 network 1, 2.0.0.0 network 2 and so on).
RIP sends update every 30 seconds so after 30 sec goes by, A sends a copy of its routing table to B, B already knew about network 2 but now B learns about network 1 as well. Notice the metric we have here for directly connected networks, since we’re using RIP, we’re using a metric of hop count. Remember a hop count (or a hop) is how many routers that these packets will have to go through to reach the destination. For example, from router A to network 1 & 2 (which are directly connected) it goes to 0 hop, router B has now learned about network 1 from A via E0 interface so the metric now will be 1 hop.
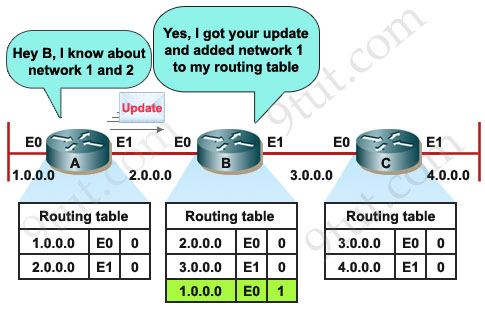
Each router receives a routing table from its direct neighbor. For example, Router B receives information from Router A about network 1 and 2. It then adds a distance vector metric (such as the number of hops), increasing the distance vector of these routes by 1.
B also exchanges its routing table with A about network 2 and 3.
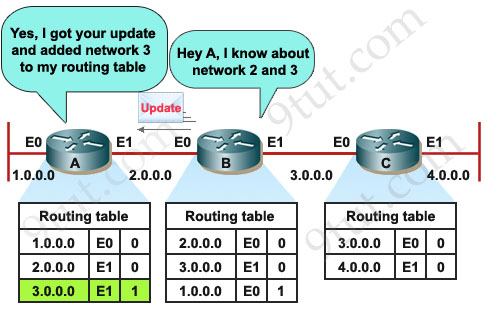
B then passes the routing table to its other neighbor, Router C.
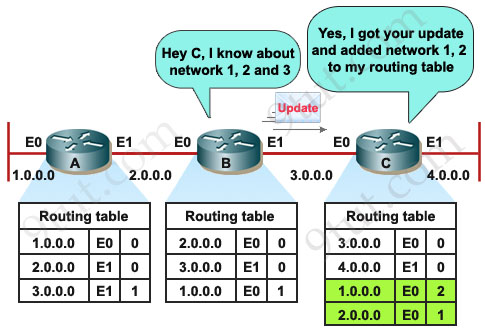
C also sends its update to B and B sends it to A.
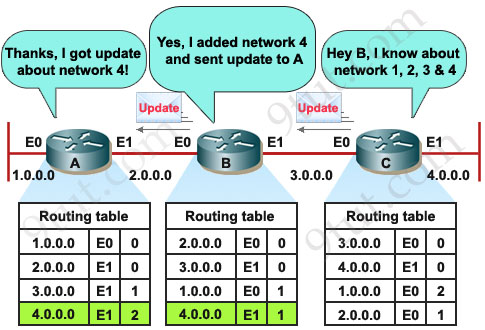
Now the network is converged.
Now let’s assume network 4 down suddenly.
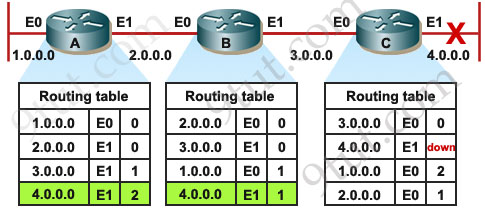
When network 4 fails, Router C detects the failure and stops routing packets out its E1 interface. However, Routers A and B have not yet received notification of the failure. Router A still believes it can access 4.0.0.0 through Router B. The routing table of Router A still refects a path to network 10.4.0.0 with a distance of 2 and router B has a path with a distance of 1.
There will be no problem if C sends an update earlier than B and inform that network is currently down but if B sends its update first, C will see B has a path to network 4 with a metric of 1 so it updates its routing table, thinking that “if B can go to network 4 by 1 hop than I can go to network 4 by 2 hops” but of course this is totally wrong.
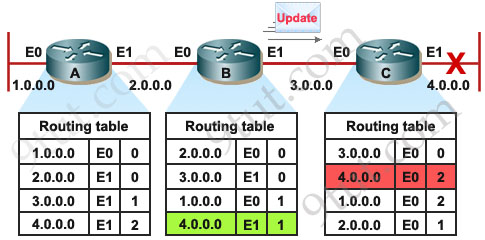
The problem does not stop here. In turn, C sends an update to B and informs it can access network 4 by 2 hops. B learns this and think “if C can access network 4 by 2 hops than I can access by 3 hops”.
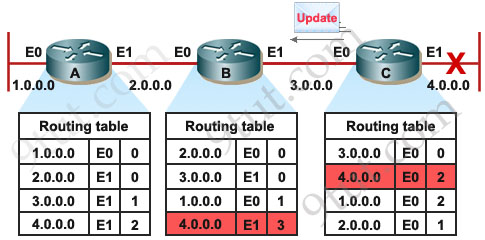
This same process occurs when B continually sends its update to C and the metric will increase to infinity so this phenomenon is called “counting to infinity”.
Below lists some methods to prevent this phenomenon:
SPLIT HORIZON:
A router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came, routers keep track of where the information about a route came from. Means when router A sends update to router B about any failure network, router B does not send any update for same network to router A in same direction.
ROUTE POISONING:
Router consider route advertised with an infinitive metric to have failed ( metric=16) instead of marking it down. For example, when network 4 goes down, router C starts route poisoning by advertising the metric (hop count) of this network as 16, which indicates an unreachable network.
POISON REVERSE:
The poison reverse rule overwrites split horizon rule. For example, if router B receives a route poisoning of network 4 from router C then router B will send an update back to router C (which breaks the split horizon rule) with the same poisoned hop count of 16. This ensures all the routers in the domain receive the poisoned route update.
Notice that every router performs poison reverse when learning about a downed network. In the above example, router A also performs poison reverse when learning about the downed network from B.
HOLD DOWN TIMERS:
After hearing a route poisoning, router starts a hold-down timer for that route. If it gets an update with a better metric than the originally recorded metric within the hold-down timer period, the hold-down timer is removed and data can be sent to that network. Also within the hold-down timer, if an update is received from a different router than the one who performed route poisoning with an equal or poorer metric, that update is ignored. During the hold-down timer, the “downed” route appears as “possibly down” in the routing table.
For example, in the above example, when B receives a route poisoning update from C, it marks network 4 as “possibly down” in its routing table and starts the hold-down timer for network 4. In this period if it receives an update from C informing that the network 4 is recovered then B will accept that information, remove the hold-down timer and allow data to go to that network. But if B receives an update from A informing that it can reach network by 1 (or more) hop, that update will be ignored and the hold-down timer keeps counting.
Note: The default hold-down timer value = 180 second.
TRIGGERED UPDATE :
When any route failed in network ,do not wait for the next periodic update instead send an immediate update listing the poison route.
COUNTING TO INFINITY:
Maximum count 15 hops after it will not be reachable.
Configuring RIP
| Router(config)#router rip | Enter router RIP configuration mode |
| Router(config-router)#network <address> | Identify networks that will participate in the router protocol. Notice that you identify networks, and not interfaces. |
NOTE: You need to advertise only the classful network number, not a subnet:
Router(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0
not
Router(config-router)#network 172.16.10.0
If you advertise a subnet, you will not receive an error message, because the router will automatically convert the subnet to the classful network address.
To learn more about configuring RIP, please read my Configuring RIP GNS3 Lab tutorial



@BITE same prob yaar !! i also dint understand debug ip RIP output !
@9tut
Well the explanation about rip is best understood from this website without a doubt.
Just to add, when we see the output of #debug ip rip.
We will never see metric 0!!. I would advise if you make a note of it because when we try to interpret the output of debug ip rip it is really confusing.
@kushal arora
Finally i understood the output.What you can do is use PT, design a network with rip and enable debug ip rip and you will be able to understand.Posting here with the diagram is very hard for me. If you know any site where i can put my network diagram pls let me knoe. If you have an email id i can send you the info
I do not know if this works or not but pls copy and paste the below link. I have explained it to the best of my knowledge Debug ip rip in PT.
http://www.yousendit.com/download/TEhYNnFFdkdEa1UwTWRVag
Please, i need help with using GNS3 as a simulator. Can anyone kindly provide detailed step by step approach to it use? Thanks.
babarindetosin@gmail.com
@Tosain: You should start using GNS3 with my first tutorial: http://www.9tut.com/configure-cisco-router-passwords-gns3-lab
@bite
thnx buddy !! really awesome explanation …i understood now !
“Also within the hold-down timer, if an update is received from a different router than the one who performed route poisoning with an equal or poorer metric, that update is ignored.”
The route is poisoned (16), how can be update with a POOR metric? Or you mean a metric POOR than the metric before poisoning? What happens then if any router other than the one who performed route poisoning will send update with a better metric than “route metric before being poisoned”?
“The route is poisoned (16), how can be update with a POOR metric? Or you mean a metric POOR than the metric before poisoning? What happens then if any router other than the one who performed route poisoning will send update with a better metric than “route metric before being poisoned?”
Sorry, my bad! Now I got it.
Awesome info, thank you 9tut. I got the premium membership for just that reason. Alot of this stuff used to go right over my head but now I’m starting to really understand. Passed ICND1 because of 9tut and I’m getting real confident about ICND2. Packet tracer is also my best friend :-)
Thanks for the help.
Thanks 9tut ,,,,simply great Explaination of RIP……..
Thanks guys
ITS REALLY REALLY GREAT AND YOU CAN SAY BEST ONE SITE…..
THANKS
Great job, thanks so much 9nut
Thanks, nice explanation of Rip
pls anyone clearly tel me about discontiguos network
Vast explanation in a simple way…really great!!
Nice explanation!!!!!!!
Outstanding explanation!!!!!
Taking my CCNA exam June 1st.
Hi 9tut,
I just want to clarify things about split-horizon and poison reverse. if poison reverse breaks the split horizon, it doesn’t make any sense discussing split horizon if it is already superseded. Is split horizon the default config to all routers? when do we use split horizon?
thanks!
can someone email me the latest dumps. Also does anyone know when the CCNA exam is changing?
shahram3272gmail.com
Please send me the latest dumps of CCNA …Thanks in advance ,,,
abhishek.bahuguna9@gmail.com
I’m so sorry , please, could you tell me which three tables include this protocol?
1) Routing table
2) ARP table ?
and the third which table ?
please, send me the answer to internetmiosolo@gmail.com
Thank you in advance.
@9tut I need a tutorial about IP ROUTING PROCESS… & ya thanks for such a great tutorials
Can any one give me the link for IGRP tutorial
Well explained…easy to understand
It is very useful to us!
I have a question…a very serious question but before I ask it, I need to explain why I’m even considering Computer Networking in the first place.
My dad is a certified Cisco guy…he’s somewhere above the Entry Level stage.
I am 25 years old, I’ve NEVER done Computer Networking before, NEVER been interested in it. I’ve never known what to do in life and I’ve already tried several other things that I quit.
My dad seems to believe that I can actually get an ENTRY LEVEL Cisco Network Certification WITHOUT any College education. Like I can just study at home by myself reading 9tut and whatever other online sources I can find.
Is this possible or is my dad crazy?
Thank your Man!!
very good explanation,.. thanx 9tut
contact me for your ccna exam dumps is helpful @ 2go username keleomega tx
thanking you sir. you are awesome
Thank you! it is really very good
thanks alot …….
too good and lucid… thanks
pl any one explain how to config rip
please send fully explanation of ROUTE POISONING and split horizon to
my email babancharak@gmail.com
@9tut,
is GNS3 same as packet tracer or any difference between them ?
very nice site for rip basics… :)
thanx for these
great job! thank you
thank you!
good explaination with diagram
grt
AWESM…….
Great explanation
Good explanation
i am going to give na exam,,,,please send me updated dumps,,if any one hv,,,,,send me on this email id: ihsan_mcitp@hotmail.com