CCNA – Access List Questions 2
Here you will find answers to Access list Questions – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about Access list, please read my Access list tutorial.
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What will happen to HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10 if the traffic is processed by this ACL?
| router#show access-lists Extended IP access list 110 10 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq telnet 20 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq smtp 30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http 40 permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any |
A. Traffic will be dropped per line 30 of the ACL.
B. Traffic will be accepted per line 40 of the ACL.
C. Traffic will be dropped, because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
D. Traffic will be accepted, because the source address is not covered by the ACL.
Answer: C
Explanation
The syntax of an extended access list is:
access-list access-list-number {permit | deny} protocol source {source-mask} destination {destination-mask} [eq destination-port]
Notice that in our access list, the network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 is specified as the source but the question asks about “HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10″, which means 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 is the destination network. So in this case there is no match in our access list and the traffic will be dropped because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL. It is surely a tricky question!
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the effect that the Router1 configuration has on devices in the 172.16.16.0 subnet when they try to connect to SVR-A using Telnet or SSH?

A. Devices will not be able to use Telnet or SSH.
B. Devices will be able to use SSH, but not Telnet.
C. Devices will be able to use Telnet, but not SSH.
D. Devices will be able to use Telnet and SSH.
Answer: B
Explanation
Let’s analyze the access list 100:
+ 10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22: allows TCP traffic from network 172.16.16.0/28 to access host 172.16.48.63 with a destination port of 22 (SSH)
+ 20 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet host 172.16.48.63: allows TCP traffic from network 172.16.16.0/28 with a source port of 23 (telnet) to access host 172.16.48.63
Notice that if a device wants to telnet (or SSH) to SVR-A server it must use the destination port of 23 (or 22), not a source port of 23 (or 22).
Access list 100 is applied on the inbound direction of Fa0/0 so it will only filter traffic from 172.16.16.0 subnet to the SVR-A server.
Access list 101 is very similar to access list 100 but it is applied on the inbound direction of Fa0/1 so it will filter traffic from SVR-A server to 172.16.16.0 subnet. In ACL 101:
+ 10 permit tcp host 172.16.48.63 eq 22 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15: allows TCP traffic from host 172.16.48.63 with a source port of 22 (SSH) to access network 172.16.16.0/28.
+ 20 permit tcp host 172.16.48.63 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet: allows TCP traffic from host 172.16.48.63 to access network 172.16.16.0/28 with a destination port of telnet.
Notice that the returned traffic from SVR-A to network 172.16.16.0/28 (resulting from telnet or SSH session) will have a source port of 23 (Telnet) or 22 (SSH)
In conclusion, the first statements of each ACL will allow devices to “SSH” to SVR-A. But they can’t telnet because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
In this question, the second statements of each ACL can be considered “wrong” if we intend to filter telnet or SSH traffic and they have no effect on the Telnet or SSH traffic.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Which three variables (router, protocol port, and router ACL direction) apply to an extended ACL that will prevent student 01 from securely browsing the internet?
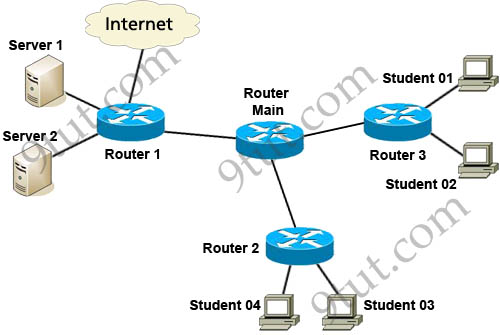
A. OUT
B. Router 3
C. HTTPS
D. IN
E. Router 1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
There are 3 routers we can place this access list: Router 1, Router Main and Router 3 but in theory, an extended access list should be placed close to the source -> Router 3 is the best choice -> B is correct.
The traffic we need to filter here is “securely browsing the internet” so it is HTTPS -> C is correct.
Finally we should apply this access list to the inbound direction so that Router 3 will filter this traffic before making routing decision. It helps save processing resources on Router 3 -> D is correct.
Question 4
Which two statements apply to dynamic access lists? (choose two)
A. they offer simpler management in large internetworks.
B. you can control logging messages.
C. they allow packets to be filtered based on upper-layer session information.
D. you can set a time-based security policy.
E. they provide a level of security against spoofing.
F. they are used to authenticate individual users.
Answer: A F
Explanation
Dynamic ACLs have the following security benefits over standard and static extended ACLs:
+ Use of a challenge mechanism to authenticate individual users
+ Simplified management in large internetworks
+ In many cases, reduction of the amount of router processing that is required for ACLs
+ Reduction of the opportunity for network break-ins by network hackers
+ Creation of dynamic user access through a firewall, without compromising other configured security restrictions
(Reference: CCNA Exploration 4 – Dynamic ACLs)
Question 5
Which command shows if an access list is assigned to an interface?
A. show ip interface [interface] access-lists
B. show ip access-lists interface [interface]
C. show ip interface [interface]
D. show ip access-lists [interface]
Answer: C
Explanation
The output of “show ip interface [interface]” command is shown below:
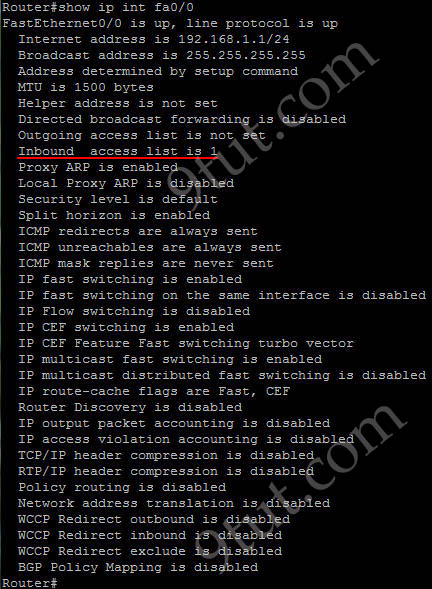
In the output we can see the access list 1 is applied to this interface on inbound direction.
Question 6
Which item represents the standard IP ACL?
A. access-list 50 deny 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255
B. access-list 110 permit ip any any
C. access-list 2500 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 22
D. access-list 101 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.1
Answer: A
Explanation
The standard access lists are ranged from 1 to 99 and from 1300 to 1999 so only access list 50 is a standard access list.
Question 7
Which statement about access lists that are applied to an interface is true?
A. you can apply only one access list on any interface
B. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 3 protocol
C. you can place as many access lists as you want on any interface
D. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 2 protocol
Answer: B
Explanation
We can have only 1 access list per protocol, per direction and per interface. It means:
+ We can not have 2 inbound access lists on an interface
+ We can have 1 inbound and 1 outbound access list on an interface
Question 8
A network engineer wants to allow a temporary entry for a remote user with a specific username and password so that the user can access the entire network over the internet. Which ACL can be used?
A. reflexive
B. extended
C. standard
D. dynamic
Answer: D
Explanation
We can use a dynamic access list to authenticate a remote user with a specific username and password. The authentication process is done by the router or a central access server such as a TACACS+ or RADIUS server. The configuration of dynamic ACL can be read here: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk822/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094524.shtml
Question 9
Which parameter standard access list takes into consideration for traffic filtering decisions?
A. Source MAC address
B. Destination IP address
C. Destination MAC address
D. Source IP address
Answer: D
Question 10
In which solution is a router ACL used?
A. protecting a server from unauthorized access
B. controlling path selection, based on the route metric
C. reducing router CPU utilization
D. filtering packets that are passing through a router
Answer: D



Hi 9tut
Regarding ques 10:
Dynamic ACL is for authentication purpose so ans A ” protecting a server from unauthorized access” can be right in this scenario.
Pls xplain why only ans D is correct and not the ans A.
Here i am talking about TACACS+ authentication.
@kash: Answer A is only correct for dynamic ACL. Answer D is correct for all kinds of ACL so it is the best answer.
Hi 9tut.
Q2.
In the figure we see /20 beeing used.
The ACL are using 0.0.0.15, wich is /28.
So, a device with IP 172.16.16.14 would be allowed to SSH, but a device with IP 172.16.16.17 would not.
Telnet is denied for both.
Since not all devices in the subnet can SSH, the correct answer should be A?
Is this a trick question or just a typo in the figure?
Your thoughts?
@Mike: Yes, I agree with you. Maybe this is a typo in the exhibit. But answer A is also not totally correct because some of the hosts in the 172.16.16.0 subnet can telnet to the server.
Hi 9tut,
For question9, should it be the Destination IP address (B) as the correct answer?
For CCNA point of view:
“Standard near the destination; Extended near the source.”
Please clarify…
@serial: The question just wants to ask which IP address is supported in standard acl. Standard ACL only supports source IP. Below is the full syntax of standard ACL:
access-list access-list-number {permit | deny} source {source-mask}
got it! thanks 9tut! :)
@9tut
regarding Q5 – why B not correct ?
PlZ send me latest dumps
Hossam.saber4@gmail.com
thnx in advance
Here is a good example:
http://www.informit.com/library/content.aspx?b=CCIE_Practical_Studies_I&seqNum=173
@abed
I am not aware option B command exist.
@9tut: Please can you explain this # the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL# in question 1
@kheuche I believe you should read more about ACLs since this is one basic principal, but basically means that whatever you don’t permit in the ACL this traffic will be deny due to the implicit deny at the end of every ACL.
You can read more about this in CCNA Accessing the WAN or in Todd Lammle book (you can download it)
@kheuche
Please tell us that your confusion is because you have issues with the english languaje. If that’s the problem I can explain to you in spanish. But if not, this blog is not just to memorize all questions and go to reach 1000 in the exam. So my recomendation is find a book, get some study an then come back to 9tut.
@9tut
ur ans for qn 4 is wrong please justify..
according to me the ans wud be A and F
@vikas: The question wants to ask about characteristics of dynamic acl. Answer A is also correct but the best answers should be D & F.
@9tut
i think the correct answer for Q7 should will A
can you explain plz
@jawad: The answer A is mean that you have only 1 acl per interface. Answer B is mean that you may have 1 inbound acl and 1 outbound acl per interface (you may total 2 difference direction acl per interface). Sorry for my Eng :(
@9tut
for q4 the (d) option corresponds to time-based access list isnt it.
Plz update the ans
@9tut
Q4
Correct answers are: A and F
–>CCNA Exploration 4.0–>Accessing the wan–>ACL’s–>5.4.2.1
Thanks very much for your great job!!
@vikas, @Pasanisi: Yes, thanks for your detection. I updated it!
@9tut
thanks and i cleared ccna yesterday thanks for providing such a valuable support
@ vikas
congr !! any new question ? N sim?
@ zallax
Q:2
i think that we should use mask \20 = 0.0.15.0 as i think
instand of mask \28 = 0.0.0.15 so shat you think about that ??? asap plz
sorry /28 Instead of /20
@mohamed
yes sir, i agree with you
@9tut
regarding 2nd question
can you please take a second look at it?
the wildcard would allow traffic for 172.16.16.0/28, not for “/240″
@ xallax wanna know if /20 is also right as a majour network or what ?????? thx
@mohamed
/20 would refer to 172.16.16.0 ~ 172.16.31.255
that’s 16*256 IPs
if we use that wildcard provided above (0.0.0.15) we would only filter the first 16 IPs of that subnetwork leaving 16*255 IPs unfiltered
the exhibit has something wrong in it
@xallax: Yes, thanks for your detection. I updated it!
@xallax
regarding Q1.
Since Acl statement is pointing to network 1722.16.0.0 as the source instead of destination.
How should statement be written to point to network 172.16.0.0 as the destination.
I guess you gonna have to create a source ip address(server), since there isn’t one.
I have a vague idea, but just wanna check with you…..second opinion so to say.
Can you kindly help, if you don’t mind.thanks.
access-list ### permit/deny SOURCE_ADDRESS_START __ SOURCE_ADDRESS_WILDCARD __ 172.16.0.0 __ WILDCARD_HERE
as an example:
access-list 100 permit 10.10.0.80 _ 0.0.0.15 _ 172.16.0.0 _ 0.0.255.255
this would allow everybody in the range of 10.10.0.80 ~ 10.10.0.95 to access the classful network of 172.16.0.0
@xallax
Thanks.
@franco
thanks man :)
Q7
The explanation, means:
ip access-list 10 permit ip ………
ip access-list 10 permit ipx……..
ip access-list 10 permit Apple Talk……
Three Layer 3 protocols need three different vlans, one per direction
Question 9
Which parameter standard access list takes into consideration for traffic filtering decisions?
A. Source MAC address
B. Destination IP address
C. Destination MAC address
D. Source IP address
Answer: D
How can D be correct. With standard ACL’s, we set them up close to the destination. And with extended ACL’s, they are put close to the source. So the correct answer should be B.
Does anyone agree? If not, please explain why?
@jimi
standard ACL example:
access-list 7 permit 192.168.1.5
i am allowing traffic from 192.168.1.5
access-list 2 deny 172.31.6.6
i am denying traffic from 172.31.6.6
the rule of thumb says that the standard access-list should be placed as close to the destination as possible (sane logic dictates it too).
maybe i want to place it half-way… i will still filter traffic from those sources.
Thanks for the comment xallax. I know now, I was reading it wrong. The parameter uses only the source ip address but the acl is initiated close to the destination.
Please, could someone send me the latest dumps to guzmonne@hotmail.com??? Best Regards.
Q1:
traffic coming from the internet should not be affected by the extended access list because I suppose it was applied outbounds on the interface, right?
plse,add more ,Thanks.
i hv an exam after a week .
Thanks 9tut. i jst passed my ccna now with 854. sim is vtp, accesslist and nat tranlation. GOD BLESS YOU REAL GOOD
Hi all,
Regarding Question 3. I think A, C and E is more appropriate for this question. The goal is to deny student 01 to access the internet securely! With answer B, C and D, the student will be prevented to communicate with HTTPS to all destinations. Example, if there is secured web page in one of the servers, student 01 can not access to it.
What do you think??
@xallax
I can not find ACL 2 sim, can you give me the link ?
@anonymous
http://www.9tut.com/78-ccna-access-list-sim-2
@Tun_CCNA
You are correct, but thinking too deep. The question doesnt mention web pages on other servers, so we can ignore that. All we need to do is locate an ‘extended’ ACL, as per cisco reccommendations and that is as close to the source as possible.
I think the trick behind most CCNA questions is just to work with what they provide in the question and make no other assumptions, unless its hinted at, in the question.
I hope that makes sense.
@Anonymous,
You are right! I think we have to stick to the question and not thinking too deep!
Thanks
Can any one explain more on Question 2, why the answer is B. I kind of got confused with the extended ACLs given in exhibit.