CCNA – Access List Questions 2
Here you will find answers to Access list Questions – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about Access list, please read my Access list tutorial.
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What will happen to HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10 if the traffic is processed by this ACL?
| router#show access-lists Extended IP access list 110 10 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq telnet 20 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq smtp 30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http 40 permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any |
A. Traffic will be dropped per line 30 of the ACL.
B. Traffic will be accepted per line 40 of the ACL.
C. Traffic will be dropped, because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
D. Traffic will be accepted, because the source address is not covered by the ACL.
Answer: C
Explanation
The syntax of an extended access list is:
access-list access-list-number {permit | deny} protocol source {source-mask} destination {destination-mask} [eq destination-port]
Notice that in our access list, the network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 is specified as the source but the question asks about “HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10″, which means 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 is the destination network. So in this case there is no match in our access list and the traffic will be dropped because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL. It is surely a tricky question!
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the effect that the Router1 configuration has on devices in the 172.16.16.0 subnet when they try to connect to SVR-A using Telnet or SSH?

A. Devices will not be able to use Telnet or SSH.
B. Devices will be able to use SSH, but not Telnet.
C. Devices will be able to use Telnet, but not SSH.
D. Devices will be able to use Telnet and SSH.
Answer: B
Explanation
Let’s analyze the access list 100:
+ 10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22: allows TCP traffic from network 172.16.16.0/28 to access host 172.16.48.63 with a destination port of 22 (SSH)
+ 20 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet host 172.16.48.63: allows TCP traffic from network 172.16.16.0/28 with a source port of 23 (telnet) to access host 172.16.48.63
Notice that if a device wants to telnet (or SSH) to SVR-A server it must use the destination port of 23 (or 22), not a source port of 23 (or 22).
Access list 100 is applied on the inbound direction of Fa0/0 so it will only filter traffic from 172.16.16.0 subnet to the SVR-A server.
Access list 101 is very similar to access list 100 but it is applied on the inbound direction of Fa0/1 so it will filter traffic from SVR-A server to 172.16.16.0 subnet. In ACL 101:
+ 10 permit tcp host 172.16.48.63 eq 22 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15: allows TCP traffic from host 172.16.48.63 with a source port of 22 (SSH) to access network 172.16.16.0/28.
+ 20 permit tcp host 172.16.48.63 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet: allows TCP traffic from host 172.16.48.63 to access network 172.16.16.0/28 with a destination port of telnet.
Notice that the returned traffic from SVR-A to network 172.16.16.0/28 (resulting from telnet or SSH session) will have a source port of 23 (Telnet) or 22 (SSH)
In conclusion, the first statements of each ACL will allow devices to “SSH” to SVR-A. But they can’t telnet because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
In this question, the second statements of each ACL can be considered “wrong” if we intend to filter telnet or SSH traffic and they have no effect on the Telnet or SSH traffic.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Which three variables (router, protocol port, and router ACL direction) apply to an extended ACL that will prevent student 01 from securely browsing the internet?
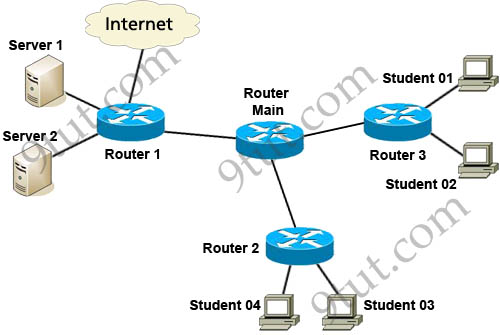
A. OUT
B. Router 3
C. HTTPS
D. IN
E. Router 1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
There are 3 routers we can place this access list: Router 1, Router Main and Router 3 but in theory, an extended access list should be placed close to the source -> Router 3 is the best choice -> B is correct.
The traffic we need to filter here is “securely browsing the internet” so it is HTTPS -> C is correct.
Finally we should apply this access list to the inbound direction so that Router 3 will filter this traffic before making routing decision. It helps save processing resources on Router 3 -> D is correct.
Question 4
Which two statements apply to dynamic access lists? (choose two)
A. they offer simpler management in large internetworks.
B. you can control logging messages.
C. they allow packets to be filtered based on upper-layer session information.
D. you can set a time-based security policy.
E. they provide a level of security against spoofing.
F. they are used to authenticate individual users.
Answer: A F
Explanation
Dynamic ACLs have the following security benefits over standard and static extended ACLs:
+ Use of a challenge mechanism to authenticate individual users
+ Simplified management in large internetworks
+ In many cases, reduction of the amount of router processing that is required for ACLs
+ Reduction of the opportunity for network break-ins by network hackers
+ Creation of dynamic user access through a firewall, without compromising other configured security restrictions
(Reference: CCNA Exploration 4 – Dynamic ACLs)
Question 5
Which command shows if an access list is assigned to an interface?
A. show ip interface [interface] access-lists
B. show ip access-lists interface [interface]
C. show ip interface [interface]
D. show ip access-lists [interface]
Answer: C
Explanation
The output of “show ip interface [interface]” command is shown below:
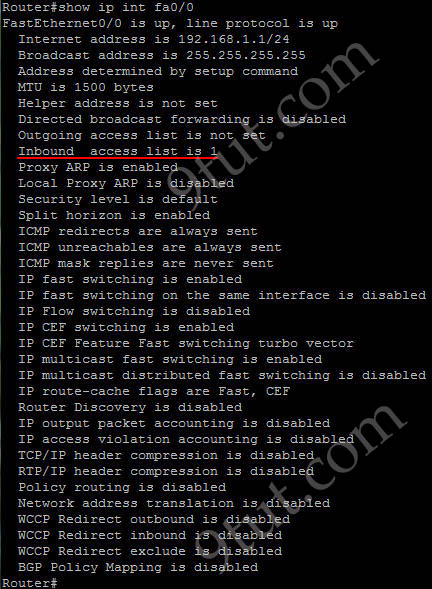
In the output we can see the access list 1 is applied to this interface on inbound direction.
Question 6
Which item represents the standard IP ACL?
A. access-list 50 deny 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.255
B. access-list 110 permit ip any any
C. access-list 2500 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.1 eq 22
D. access-list 101 deny tcp any host 192.168.1.1
Answer: A
Explanation
The standard access lists are ranged from 1 to 99 and from 1300 to 1999 so only access list 50 is a standard access list.
Question 7
Which statement about access lists that are applied to an interface is true?
A. you can apply only one access list on any interface
B. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 3 protocol
C. you can place as many access lists as you want on any interface
D. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 2 protocol
Answer: B
Explanation
We can have only 1 access list per protocol, per direction and per interface. It means:
+ We can not have 2 inbound access lists on an interface
+ We can have 1 inbound and 1 outbound access list on an interface
Question 8
A network engineer wants to allow a temporary entry for a remote user with a specific username and password so that the user can access the entire network over the internet. Which ACL can be used?
A. reflexive
B. extended
C. standard
D. dynamic
Answer: D
Explanation
We can use a dynamic access list to authenticate a remote user with a specific username and password. The authentication process is done by the router or a central access server such as a TACACS+ or RADIUS server. The configuration of dynamic ACL can be read here: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk583/tk822/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094524.shtml
Question 9
Which parameter standard access list takes into consideration for traffic filtering decisions?
A. Source MAC address
B. Destination IP address
C. Destination MAC address
D. Source IP address
Answer: D
Question 10
In which solution is a router ACL used?
A. protecting a server from unauthorized access
B. controlling path selection, based on the route metric
C. reducing router CPU utilization
D. filtering packets that are passing through a router
Answer: D



HI friends can u plz send me the latest dumps to my mail gokulgokz90@gmail.com
In Q3, I really think it should be A C E = OUT HTTPS Router1. Yes extended ACL should be placed close the source as possible but we are talking about Internet traffic here with a destination address of “any” like
access-list 100 deny tcp host D.D.D.D any eq 443
If we place that ACL to Router 1, inbound, the ACL would be denying too much. So I think it should be placed on Router1, on the interface connected to the Internet on outbound direction.
I mean If we place that ACL to Router3, inbound, the ACL would be denying too much.
CAN SB PLS EXPLAIN FURTHER THE Q1 FOR ME
@Vanessa
As a network admin. when placing ACLs you must consider saving processing resources on the routers(overhead). This is the main reason router 3 is chosen, and also an extended ACL must be place close to the source, and apply ACL to the inbound direction.
And lastly, the traffic we need to filter here is “securely browsing the internet” so it is HTTPS.
And, remember you want to keep the student 01 “in”, you don’t want them “out”
I hope this helps.
@usGhana
There is mismatch in the acl statement, and the traffic coming from the internet to its destination.(172.16.12.10)
The Acl statement is pointing to network 172.16.0.0 as the source instead of destination.
Due to the mismatch, and the “deny all” at the end of all acl, the traffic will be dropped.
I hope this helps.
hi all
@ Q4 : is D correct too?
hello 9tut
pls where can i download the latest cisco packet tracer online..wil appreciate ur assistance.Thanks
hello 9tut
regarding Q2 , traffic should all be denied since implicit deny all applies,
there is no deny command at the end of the list ,,, is this answer correct ? i think it should be A
@NATZ: Implicit deny is a default behavior for ACL i.e. if packet don’t match no record and if ACL haven’t “permit ip any any” in the end of ACL then will be used “deny ip any any”.
@9TUT
Please confirm the answer for Q4 as I have seen ‘D’ also as the answer…can any1 clarify??
Can someone help me understand how to decide if ACL is to be applied in/out . I’m confused very much.Urgent please
Which two statements apply to dynamic access lists? (choose two)
A. they offer simpler management in large internetworks.
B. you can control logging messages.
C. they allow packets to be filtered based on upper-layer session information.
D. you can set a time-based security policy.
E. they provide a level of security against spoofing.
F. they are used to authenticate individual users.
*** THE ACME 486 DUMP SAYS THAT D & F ARE THE ANSWERS … CAN SOMEONE EXPLAIN TO ME WHATS GOING ON ?? ***
hey .. can anybody explain me more about Q1 ???? i’ve a confusion because at the end the line is permit any . why it will denied all traffic due to the implicit deny rather than we already type permit any ??? plzzzzzzzzzzzz tomorrow is my exam
hey .. can anybody explain me more about Q1 ???? i’ve a confusion because at the end the line is permit any . why it will denied all traffic due to the implicit deny rather than we already type permit any ??? plzzzzzzzzzzzz tomorrow is my exam
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What will happen to HTTP traffic coming from the Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10 if the traffic is processed by this ACL?
router#show access-lists
Extended IP access list 110
10 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq telnet
20 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq smtp
30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http
40 permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any
A. Traffic will be dropped per line 30 of the ACL.
B. Traffic will be accepted per line 40 of the ACL.
C. Traffic will be dropped, because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.
D. Traffic will be accepted, because the source address is not covered by the ACL.
Answer: C
@Suhail
There is mismatch in the acl statement, and the traffic coming from the internet to its destination.(172.16.12.10)
The Acl statement is pointing to network 172.16.0.0 as the source instead of destination.
Due to the mismatch, and the “deny all” at the end of all acl, the traffic will be dropped.
I hope this helps.
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
hi somebody can bring me the latest dump
please
about20@yahoo.fr
I hope this helps.
@9tut ! Have you made mistake in answer of Q4 , because in dumps I studied the best 2 choices are D and F but you have selected A and F?
I am going to take CCNA exam this month so I want the latest dumps for the same. Please someone send me the latest dumps so that I can clear my exam. My E-mail is (parvin_kumar333@yahoo.com). It would be so kind of you.
question 4
i think d and f
because question 8
@9tut
Q2:if /28 is used,then how can we assign the broadcast address to the server.so the typo error in acl.the wcm should be 0.0.15.255 instead 0.0.0.15.if i am wrong please correct me
@Raj: The wildcard mask of the server is /20 (not /28) so 172.16.48.63/20 is not a broadcast address and can be assigned to the server. Only devices on the left use the wildcard mask of /28 (maybe the exhibit is wrong about the wildcard mask).
nice questions BTW :)
latest dumps :-
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.PrepKing.640-802.v2012-01-03.by.DHARANI.615q.vce.file.html
&
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2011-07-09.by.Collisio.486q.vce.file.html
very helpful.
many thanks 9tut.
Question6 Explanation
The standard ACL range is 1-99 and 1300-1399 not 1300-1999
The Extended ACL range is 100-199 and 2000-2699
Q4
I also think it’s D&F
HI Maja, re: q4 please see page 263 and 264 or Wendell Odom CCNA ICND2 (2nd Edition) for explanation for answer being A and F. Time-based ACL’s correctly defing answer D.
Hi Friends i have finished CCNA i need CCNA recent Dump Quetions anybody have pls send me to my mail id:p.g.esavan@gmail.com
Hi Friends i have finished CCNA i need CCNA recent Dump Quetions anybody have pls send me to my mail id:p.g.kesavan@gmail.com
Which two statements apply to dynamic access lists? (choose two)
A. they offer simpler management in large internetworks.
B. you can control logging messages.
C. they allow packets to be filtered based on upper-layer session information.
D. you can set a time-based security policy.
E. they provide a level of security against spoofing.
F. they are used to authenticate individual users.
*** THE ACME 486 DUMP and Pass4Sure SAYS THAT D & F ARE THE ANSWERS … CAN SOMEONE EXPLAIN TO ME WHATS GOING ON ?? ***
I failed in my CCNA exam @ 815/1000, and I am re-taking the exam end of the week, are there any surprises I should know about? Any advice?
@9tut @ Xallax: I have some confusion on Q.4 the answer should include D. you can set a time-based security policy.
Todd Lamle Edition 6. Page No: 637 (Dynamic ACL) 4th Line “This causes traffic to be allowed through for a specific amount of time..
kindly explain the same
@arpit
“time-based security policy” means “between hour A and hour B allow traffic from X to Y”
dynamic ACLs don’t deal with time-based rules, QoS does
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk543/tk759/technologies_tech_note09186a00801aa69d.shtml
dynamic ACLs allow traffic for “a specific amount of time” (quoting from your own quote)
http://www.informit.com/library/content.aspx?b=CCIE_Practical_Studies_I&seqNum=168
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2012-02-07.by.Arpit.486q.vce.file.html
Most Valid Dump.. All most 99% answers are correct.
9tut plz help me.as u had chosen the answer option C) Traffic will be dropped, because of the implicit deny all at the end of the ACL.but in collision and testinside dump the answer is option A) Traffic will be dropped per line 30 of the ACL.
Which is the correct answer as i m really confused.
Q: Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the effect that the Router1 configuration has on devices in the 172.16.16.0 subnet when they try to connect to SVR-A using Telnet or SSH.
Router1#show ip access-lists
Extended IP access list 100:
10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22
20 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet host 172.16.48.63
Extended IP access list 101:
10 permit tcp 172.16.48.63 eq 22 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15
20 permit tcp 172.16.48.63 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet
Router1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router1 (config)# int fa0/0
Router1 (config-if)# ip access-group 100 in
Router1 (config)# int fa0/1
Router1 (config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
Router1 (config-if)
A. Devices will not be able to use Telnet or SSH.
B. Devices will be able to use SSH, but not Telnet.
C. Devices will be able to use Telnet, but not SSH.
D. Devices will be able to use Telnet and SSH.
Answer is B>…..I don’t know why.. Who can explain this Question… Please explain me…
@thura
Extended IP access list 100:
10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22
allows traffic from the subnet to the server on SSH port (OK)
20 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet host 172.16.48.63
allows traffic that originates on telnet port (here’s the problem) and goes to any port on the server
Extended IP access list 101:
10 permit tcp 172.16.48.63 eq 22 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15
allows traffic from server ssh to the subnet (OK)
20 permit tcp 172.16.48.63 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet
allows traffic from the server to the subnet. it can originate on any port on the server and can only access telnet on the subnet. this is a misconfiguration yet again
@xallax
thank a lot
there is a new question on the order of how permit and deny statements of Extended ACLs should be arranged.
@xallax
have you tried this on packet tracer? instead of making SSH work, I tried making telnet work. Works fine using access list 100 line 10, But as soon as I added access list 101 line 10 using 23 instead of 22 i cant telnet to 172.16.48.63 anymore.
Q2.
Can You Explain the meaning of 10 in the sentence :
10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22
Thnx,
R
@derp
please mail me the PT file to contact@ciscovce.com . ill give it a look
thanks
@anonymous
it’s the line number.
in access-list edit mode you can actually number the access-list lines as you wish so that you can easily modify them afterwards or add lines in-between
@xallax
Ok Thnx Xallax.
But, Can you give me how about place the line number command in the extended acl?
Router(config)#Access-list 100 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22
Thank’s
@anonymous
read a bit here:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/secursw/ps1018/products_tech_note09186a00800a5b9a.shtml#editacls
cheers
@Xallax
Very helpfull..:)
Thnx
@thura
Understanding the question is the first part. Its asking about network 172.16.16.0 and not 172.16.48.0 so the second extended access-list(101) isn’t a factor and should be ignored. The problem with line 20 is that the syntax is incorrect, look at where the [eq telent] is placed on the line. So the SYNTAX is the problem with line 20.
Extended IP access list 100:
10 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 host 172.16.48.63 eq 22
allows traffic from the subnet to the server on SSH port (OK)
20 permit tcp 172.16.16.0 0.0.0.15 eq telnet host 172.16.48.63
Can anybody please explain me more about question on the link bellow.
http://dl.dropbox.com/u/59575250/Q30.JPG
Thnx before.
nazty
@Nazty
take a look Q3 here
http://www.9tut.com/70-ccna-access-list-sim#more-39