CCNA – Access List Questions
Here you will find answers to CCNA Access list questions
Note: If you are not sure about how to use Access list, please read my Access list tutorial
Question 1
Your boss is learning a CCNA training course, refer to the exhibit. The access list has been configured on the S0/0 interface of router RTB in the outbound direction. Which two packets, if routed to the interface, will be denied? (Choose two)
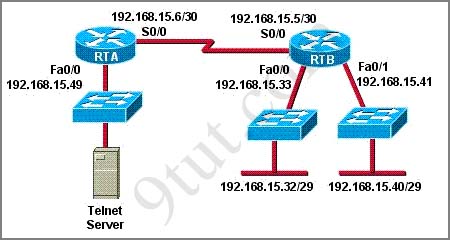
access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.15.32 0.0.0.15 any eq telnet
access-list 101 permit ip any any
A. source ip address: 192.168.15.5; destination port: 21
B. source ip address: 192.168.15.37 destination port: 21
C. source ip address: 192.168.15.41 destination port: 21
D. source ip address: 192.168.15.36 destination port: 23
E. source ip address: 192.168.15.46; destination port: 23
F. source ip address: 192.168.15.49 destination port: 23
Answer: D E
Explanation
First we notice that telnet uses port 23 so only D, E & F can satisfy this requirement.
The purpose of this access-list is to deny traffic from network 192.168.15.32 255.255.255.240 (to find out the subnet mask just convert all bit “0″ to “1″ and all bit “1″ to “0″ of the wildcard mask) to telnet to any device. So we need to figure out the range of this network to learn which ip address will be denied.
Increment: 16
Network address: 192.168.15.32
Broadcast address: 192.168.15.47
-> Only 192.168.15.36 (Answer D) & 192.168.15.46 (Answer E) belong to this range so they are the correct answer.
Question 2
Refer to the graphic. It has been decided that PC1 should be denied access to Server. Which of the following commands are required to prevent only PC1 from accessing Server1 while allowing all other traffic to flow normally? (Choose two)
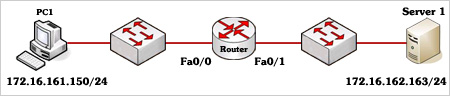
A – Router(config)# interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 out
B – Router(config)# interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)# ip access-group 101 in
C – Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip host 172.16.161.150 host 172.16.162.163
Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
D – Router(config)# access-list 101 deny ip 172.16.161.150 0.0.0.255 172.16.162.163 0.0.0.0
Router(config)# access-list 101 permit ip any any
Answer: B C
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Why would the network administrator configure RA in this manner?

A. to give students access to the Internet
B. to prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA
C. to prevent administrators from accessing the console of RA
D. to give administrators access to the Internet
E. to prevent students from accessing the Internet
F. to prevent students from accessing the Admin network
Answer: B
Explanation
Although the access-list is used to “permit” network 10.1.1.0/24 but the best answer here is “to prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA”. From the picture above, we know that 10.1.1.0/24 is the “Admin” network. This access list is applied to “line vty 0 4″ so it will permit only Telnet traffic from “Admin” to RA while drop all other traffic (because of the implicit “deny all” command at the end of the access list). Therefore we can deduce that it will “prevent students from accessing the command prompt of RA”.
This access list only filters Telnet traffic (because it is applied to vty line) so it will not prevent or allow anyone to access the Internet -> A, D, E are not correct.
C is not correct as this access list allows administrators to access the console of RA.
F is not correct as this access list does not proceed TCP, UDP or IP traffic so the students still access the Admin network.
(Notice that the “command prompt” here implies telnet as telnet is the only way to remotely access RA)
Question 4
An access list was written with the four statements shown in the graphic. Which single access list statement will combine all four of these statements into a single statement that will have exactly the same effect?
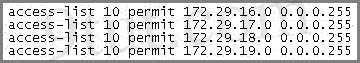
A. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.0.255
B. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.1.255
C. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.3.255
D. access-list 10 permit 172.29.16.0 0.0.15.255
E. access-list 10 permit 172.29.0.0 0.0.255.255
Answer: C
Explanation
Four statements above allow 4 networks (from 172.29.16.0/24 to 172.29.19.0/24) to go through so we can summary them as network 172.29.16.0/22.
/22 = 255.255.252.0 so it equals 0.0.3.255 when converting into wildcard mask -> C is correct.
A, B, D are not correct as their wildcard masks are false. For example:
Answer A allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.16.255
Answer B allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.17.255
Answer D allows from 172.29.16.0 to 172.29.31.255
Both the network address and wildcard mask of answer E are false as it allows the whole major network 172.29.0.0/16 to go through.
Question 5
A network administrator wants to add a line to an access list that will block only Telnet access by the hosts on subnet 192.168.1.128/28 to the server at 192.168.1.5. What command should be issued to accomplish this task?
A – access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 23
access-list 101 permit ip any any
B – access-list 101 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.240 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 23
access-list 101 permit ip any any
C – access-list 1 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.5 0.0.0.0 eq 21
access-list 1 permit ip any any
D – access-list 1 deny tcp 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 host 192.168.1.5 eq 23
access-list 1 permit ip any any
Answer: A
Explanation:
First the question asks to block only Telnet access so the port we have to use is 23 -> C is not correct.
Next we need to block traffic from hosts on the subnet 192.168.1.128/28, which is 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.15 if we convert to wildcard mask (just invert all bits of the subnet mask,from 0 to 1 and from 1 to 0 we will get the equivalent wildcard mask of that subnet mask) -> so B is incorrect
In this case, we have to use extended access list because we need to specify which type of traffic (TCP) and which port (23) we want to block -> so D is incorrect because it uses standard access list.
Question 6
As a network administrator, you have been instructed to prevent all traffic originating on the LAN from entering the R2 router. Which the following command would implement the access list on the interface of the R2 router?
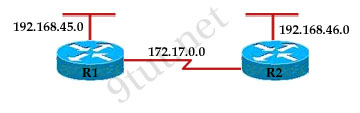
A – access-list 101 in
B – access-list 101 out
C – ip access-group 101 in
D – ip access-group 101 out
Answer: C
Question 7
The following access list below was applied outbound on the E0 interface connected to the 192.169.1.8/29 LAN:
access-list 135 deny tcp 192.169.1.8 0.0.0.7 eq 20 any
access-list 135 deny tcp 192.169.1.8 0.0.0.7 eq 21 any
How will the above access lists affect traffic?
A – FTP traffic from 192.169.1.22 will be denied
B – No traffic, except for FTP traffic will be allowed to exit E0
C – FTP traffic from 192.169.1.9 to any host will be denied
D – All traffic exiting E0 will be denied
E – All FTP traffic to network 192.169.1.9/29 will be denied
Answer: D
Explanation:
There is always an implicit “deny all” command at the end of every access list, so if an access list doesn’t have any “permit” command, it will block all the traffic.
Note: This access list is applied on outbound direction so only packets exiting E0 will be checked. Packets entering E0 will not be checked and they all are allowed to pass through.
Question 8
The access control list shown in the graphic has been applied to the Ethernet interface of router R1 using the ip access-group 101 in command. Which of the following Telnet sessions will be blocked by this ACL? (Choose two)
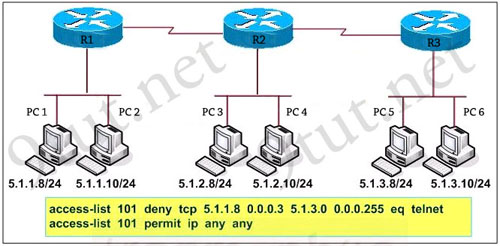
A – from host PC1 to host 5.1.1.10
B – from host PC1 to host 5.1.3.10
C – from host PC2 to host 5.1.2.10
D – from host PC2 to host 5.1.3.8
Answer: B D
Explanation
Below is the simple syntax of an extended access list:
access-list access-list-number {deny | permit} {ip|tcp|udp|icmp} source [source-mask] dest [dest-mask] [eq dest-port]
Notice that this access list is applied to the Ethernet interface of R1 in the “in direction” so in this case, it will filter all the packets originated from E1 network (host PC1 and PC2) with these parameters:
Source network: 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 which means 5.1.1.8/252 (just invert all the wildcard bits to get the equivalent subnet mask) -> Packets from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 will be filtered.
Destination network: 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 which means 5.1.3.0/24-> Packets to 5.1.3.0/24 will be filtered
Therefore packets originated from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 and have the destination to the host 5.1.3.x (via Telnet) will be denied.
Question 9
The following configuration line was added to router R1
Access-list 101 permit ip 10.25.30.0 0.0.0.255 any
What is the effect of this access list configuration?
A – permit all packets matching the first three octets of the source address to all destinations
B – permit all packet matching the last octet of the destination address and accept all source addresses
C – permit all packet matching the host bits in the source address to all destinations
D – permit all packet from the third subnet of the network address to all destinations
Answer: A



@ Claudio from Chile
“prevent all traffic originating on the LAN from entering the R2 router”. You need to block the R2 LAN (192.168.46.0) from entering the router. You need to block traffic that is going inbound to the router. You need to place the ACL as “in” so it will filter inbound traffic.
Q6.
Friends….question don´t say where put access-group command….question is not clear….
hi all am about to write my CCNA i really need your Mentorship to pass this please help my email address is tebogobareng@yahoo.com please send me all the recent dumps you have,
your assit will be highly appretiated
hello cisco everybody. i am taking ma exams in ten 15 days please can somebody send me the latest dumps.? waiting
@bangs
you can try my VCEs at this link:
http://www.tinyurl.com/xallaxvce
cheers
To Claudio from Chile:
Why not? All is clear.
We have extended ACL (ACL number 101), so we have to place this ACL closest to the _source_ of traffic. The place closest to source => in for int E0.
Hi all, i saw that the Exam questions was changed 30% can somebody tell me about the Exam or that the exam was changed? or can tell me list of the Simulations or how many simulation are in the exam?? Plz help me i am highly appreciated you all.
Hi Mr CHris, could plz tell me what type of simulations did you see in your exam yesterday
i would like to write my exam after this week.
Can any one explain how to calculate subnet mask of 192.168.1.5 or 192.168.1.97 ?
or how I will calculate the subnet mask by giving only ip address i.e without giving subnet mask like /24 or /25 or /29 etc.
Please help me out
“Can any one explain how to calculate subnet mask of 192.168.1.5 or 192.168.1.97 ?” be more specific please
“how I will calculate the subnet mask by giving only ip address i.e without giving subnet mask like /24 or /25 or /29 etc.”
think like this:
8 bits is 255.
7 bits is 254
6 bits is 252
5 bits is 248
4 bits is 240
3 bits is 224
2 bits is 192
1 bit is 128
0 is 0…
let’s take /24:
24 = 8 + 8 + 8 + 0
255.255.255.0
/25:
8 + 8 + 8 + 1
255.255.255.128
/29:
8+8+8+5
255.255.255.248
/15
8+7+0+0
255.254.0.0
hope this is helpful :)
there is a script that generates subnetting questions that comes with any of the icnd1/icnd2/ccna downloads. visit this link:
http://www.tinyurl.com/xallaxvce
Hi all,
i will take CCNA certification and i’m a bit lose in this website (i don’t know which to review for CCNA certification) kindly help me. T_T .
thanks you in advance guys/gurls
Thanks xallax, for helping me but my question was , is ther any way that I could find out mac address by using ip address but not using subnet mask?
for an example 192.168.1.97 /28, using subnet mask /28 I know the mac address would be 255.255.255.240 but if subnet mask is not given then how I’ll find out Mac address only using IP address?
If any one knows then help me out with my doubt.
Thanks
@tuhin
255.255.255.240 is not a mac address. its also the subnet mask
255.255.255.240 is the same as /28.
255= 8 bits hence 240 = to the first 4 bits of the 4rth octet of the subnet mask.
Therefore you have 255.255.255.240 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000
count all the 1`s then put a “/” in front of it, you should get “/28″
Let me just highlight the 4rth octet .11110000
the bit value is as follows {128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1 } respectively
so: .11110000 = 128+64+32+16+0+0+0+0
therefore: .11110000 = .240
hope this helps
@tuhin
also if the subnet mask is not given consider the other given values, such as the number of host needed or the number of subnets required. That should give you an idea what the subnet mask is.
If there is no other given values then consider it as a classful address.
1 – 126 – Class A SM= 255.0.0.0 = /8
128 – 191 Class B SM= 255.255.0.0 = /16
192 – 224 Class C SM= 255.255.255.0 = /24
FYI
1, 126, 128, 191, 192, and 224 are the first octet value of an IP Add
Eg: 192.168.1.1 etc…
@ stantheman
thanks for explaining me the subnet mask. sorry I just mixed up subnet mask with mac address.
actually my question is how I will get subnet mask using only IP address if there is no host or subnet mention?
for an example could you please explain me how I will get subnet mask of the IP address 192.168.1.97 or 172.16.192.29
thanks in advance.
@tuhin
If there are no other given values then consider it as a classful address.
1 – 126 – Class A SM= 255.0.0.0 = /8
128 – 191 Class B SM= 255.255.0.0 = /16
192 – 224 Class C SM= 255.255.255.0 = /24
192.168.1.9 belongs to class C SM = 255.255.255.0 = /24
172.16.192.29 belongs to class SM = 255.255.0.0 = /16
Hello All, i am going to get my CCNA Exam two weeks later, i have get some dumps from Examcollection.com i am not sure that the exam was changed if you have any idea about the exam or any one has the latest dumps pzl send it to this Email: Mohamed.ahh@hotmail.com thank you all for your everythink
Thanks stantheman. I got my answer. thanks a lot.
Friends
What do you do for internet users see privatte address?
Should i configure a default static route to the private network or NAT 1-1 from Internet?
@claudio
at hope i have a little router (dlink…) and my ISP assigned me 1 IP. I have a PC and a laptop. my neighbor connects her laptop to my WLAN too (i don’t mind, just being friendly cause she’s old and helps everybody).
I can’t use nat 1-1 because i would end up with only 1 host accessing the internet.
so… i use PAT (all hosts use the same public IP from my ISP, but on different ports).
i do want to access my main computer from anywhere when i go to someone and have to retrieve files or use my software. i do that by having my computer as the only DMZ device, i use a no-ip.org name and i connect via Remote Desktop Connection (windows xp+ has it by default).
on your home router you don’t set up anything static unless you are sure those things would never change (my PCs IP is static, the other devices get configured via DHCP)
Yes there should realize the reader to RSS my feed to RSS commentary, quite simply
/29 is 255.255.255.248 but you wrote 255.255.255.240 why?
PLZ help its Question1 its say /29 so it must be 255.255.255.248
Please help me to get the following answer clarified.
Please help me with the following question.
What will happen to the HTTP traffic coming from Internet that is destined for 172.16.12.10, if the traffic is processed by this ACL?
Extended IP access list 110
10 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq telnet
20 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq smtp
30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http
40 permit tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any
ANSWERS
A. Traffic will be dropped per line 30 of the ACL
B. Traffic will be dropped per line 40 of the ACL
C. Traffic will be dropped, because of the implicit deny all at the end of ACL
D. Traffic will be accepted, because the source address is not covered by the ACL
ACME dumps show Answer “C” as correct.
My doubt is, How that answer can be correct when the question is talking about the traffic DESTINED for 172.16.12.10 host but not traffic ORIGINATING from 172.16.12.10 host.
As a whole what the above ACL does is to block telnet, smtp and http traffic coming from 172.16.0.0 subnet that is going to any destination host while allowing all other traffic from the same subnet to any destination host.
Even if this ACL applied to either on “IN” direction or “OUT” direction, there is not possible way that implicit deny can come in to play as the question is asking about the traffic “Destined for 72.16.12.10″. That is my understanding and I believe answer “D” should be the most relevant one.
Please provide your views. Thanks in advance!
Osman
you have .32/29 and .40/29
I think it’s the same with .32/28 if you do the summary
Auger3
you forget that the implicit deny is: deny ip any any
and the ip cover all protocols,so answer C is correct.
Can anyone send me the latest dumps for CCNA at ibatros4@yahoo.fr
many thanks
No 123 it cant its /29 but he wrote /28 i think i problem is with the diagram maybe plz 9tut respond
@123
Thanks for your answer. Yes “C” is correct.
Can any body plz send me latest dump?i will b highly oblige to u plz
masud139@yahoo.com
hi all,
why you keep asking for updated ccna exam dump?
isn’t 9tut not updated anymore? T_T
please do advice
123. In auger 3′s question. Why would answer A not be enough to block http?
30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http
A. Traffic will be dropped per line 30 of the ACL
Thanks in advance.
Found this explanation.
Well in an access list, “Source” IP address and port come first and then “destination” IP Address and port come after it…
As line 30 says..
30 deny tcp 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq http
deny – denies the packet that matches this rule
172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 – source IP address
any – destination IP address
eq http – matching http
This rule means http traffic coming from “172.16.x.x networks” will be dropped….
The question was about the internet as the source. Which 30 would not block.
Hi, Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps at treepanel.ken@hotmail.com , i plan to take the exams at the end of sep.
Thanks.
can anyone tell me which exam collections are more needed,,,i mean the author
@ anyone can u send me the latest CCNA actual exam?
please send it to sab3001@hotmail.com
Appreciate anyone who will share it. Thanks!
pls can some 1 explain y the /24 was change to /22,in ques 4
@captain:
The reason it was changed to a /22 from a /24 was because it became a summary route. The question asks us to create a single access list statement instead of having 4 access list statements. So instead of the router first checking to see if the packet came from 172.29.16.0/24 and then 172.29.17.0/24 and the 172.29.18.0/24 and finally 172.29.19.0/24 it can now check to see if it came from 172.29.16.0/22 (which is a summary of networks 172.29.16.0-172.29.19.0).
Hope that helps!
can someone explain question 8 ? I think answer should be “D”, Not “B and D”
“access-list 101 deny tcp 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 eq telnet”
if we reverse wild card to subnet mask, it become 255.255.255.252 or /30
increment is 4
8-11 is ip range
so valid IP are 5.1.1.9 and 5.1.1.10
5.1.1.8 is network number (cannot be used) this mean PC1 is invalid IP
5.1.1.11 is broadcast (cannot be used)
Isn’t it true we often use netmask 252 or /30 for serial line because they provide exactly 2 valid ip address ?
why answer of question 8 include PC 1 (5.1.1.8) ?
@nc
actually, we use 0.0.0.3 to permit/deny a block of 4. we don’t care if those are valid IPs or the broadcast address on a subnetwork.
please take a look at the subnet for that network on which PC1 resides: it is /24 (255.255.255.0)
the wildcard mask will not transform 5.1.1.8 into a subnetwork with a /30 mask.
by using that wildcard mask we say “don’t allow anyone in this range to do this”
answers B and D are correct. please review the question
@xallax
thank you for explain that. I got it.
I wonder what will happen in such scenario
1)if PC 1 and PC2 Do have /30 as subnet mask (5.1.1.8/30 and 5.1.1.10/30)
2) instead of deny in the question, access-list 101 is to permit
Would PC 1 able to pass through the access-list 101 ?
@nc
nope, PC1 would be configured with an invalid IP and traffic wouldn’t happen.
at auger question..
I would go on Answer C:..
the trick there was the way the acl arrange it was intended to reverse the source and destination instead of 172.16.0.0 be a destination they put it into source just to confused us. I guess.
and secondly you cannot have an 172.16.0.0 as a source if coming from the net as this address is Private. (Just my though )
Hi to everyone,
please send me the latest dump @ abmmejia@yahoo.com I’m planning to take the exam this coming October.
Thank you so much.
Hi guys, I having trouble determining how to identify the outbound and inbound direction of an access list when looking at a figure… any tips?
@ken
INbound on interface s0/0 <- gets into the router on interface s0/0. it will filter only what comes in
OUTbound on interface s0/0 <- leaves the router on interface s0/0. it will filter only what goes out
@xallax
Thanks! btw do you know if theres any difference when when i just leave out the “host” word in the ACL commands?
Thanks in advance!
@ken
if you use the word “host” then it’s implied that you are using the wildcard 0.0.0.0
if you don’t use the word “host”, but you want your access-list to apply to traffic for a single host, then you must use the wildcard 0.0.0.0 after that particular host’s IP
i.e.:
access-list 100 permit ip host 10.1.1.5 10.1.23.8 0.0.0.7
access-list 100 permit ip 10.1.1.5 0.0.0.0 10.1.23.8 0.0.0.7
Below is the simple syntax of an extended access list:
access-list access-list-number {deny | permit} {ip|tcp|udp|icmp} source [source-mask] dest [dest-mask] [eq dest-port]
Notice that this access list is applied to the Ethernet interface of R1 in the “in direction” so in this case, it will filter all the packets originated from E1 network (host PC1 and PC2) with these parameters:
Source network: 5.1.1.8 0.0.0.3 which means 5.1.1.8/252 (just invert all the wildcard bits to get the equivalent subnet mask) -> Packets from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 will be filtered.
Destination network: 5.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 which means 5.1.3.0/24-> Packets to 5.1.3.0/24 will be filtered
Therefore packets originated from 5.1.1.8 to 5.1.1.11 and have the destination to the host 5.1.3.x (via Telnet) will be denied.
Question 9
The following configuration line was added to router R1
Access-list 101 permit ip 10.25.30.0 0.0.0.255 any
What is the effect of this access list configuration?
A – permit all packets matching the first three octets of the source address to all destinations
B – permit all packet matching the last octet of the destination address and accept all source addresses
C – permit all packet matching the host bits in the source address to all destinations
D – permit all packet from the third subnet of the network address to all destinations
tell me how to find this,,,,?just help me any one…