CCNA – RIP Questions
Here you will find answers to RIP Questions
Note: If you are not sure about RIP, please read my RIP tutorial.
Question 1
Which statement about RIPng is true?
A. RIPng allows for routes with up to 30 hops.
B. RIPng is enabled on each interface separately.
C. RIPng uses broadcasts to exchange routes.
D. There can be only one RIPng process per router.
Answer: B
Explanation
RIPng is similar to RIPv2 but is used for IPv6. But unlike RIPv1 and RIPv2, RIPng is enabled on each interface separately. For example:
Router(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing (Enables the forwarding of IPv6 unicast datagrams globally on the router)
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ipv6 rip 9tut enable (9tut is the process name of this RIPng)
Question 2
What are two characteristics of RIPv2? (Choose two)
A. classful routing protocol
B. variable-length subnet masks
C. broadcast addressing
D. manual route summarization
E. uses SPF algorithm to compute path
Answer: B D
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Which (config-router) command will allow the network represented on the interface to be advertised by RIP?
| router rip version 2 no auto summary ! interface ethernet0 ip address 10.12.6.1 255.255.0.0 |
A. redistribute ethernet0
B. network ethernet0
C. redistribute 10.12.0.0
D. network 10.12.0.0
Answer: D
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. What information can be gathered from the output?
| RouterA#debug ip rip RIP protocol debugging is on00:34:32: RIP: sending v2 flash update to 224.0.0.9 via FastEthernet8/0 (172.16.1.1) 00:34:32: RIP: build flash update entries 00:34:32: 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.6, metric 1, tag 0 00:34:32: RIP: sending v2 flash update to 224.0.0.9 via Loopback (10.10.1.1) 00:34:32: RIP: build flash update entries 00:34:32: 10.0.0.0/8 via 0.6.0.0, metric 2, tag 0 00:34:32: 172.16.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 00:34:32: RIP: ignored v2 packet from 16.10.1.1 (sourced from one of our addresses) 06:34:33: RIP: received v2 update from 172.16.1.2 on FastEthernet0/6 66:34:33: 16.6.0.0/8 via 6.0.6.6 in 1 hops 66:34:44: RIP: sending v2 update to 224.6.6.9 via FastEthernet0/0 (172.16.1.1) 66:34:44: RIP: build update entries 66:34:44: 10.10.1.0/24 via 0.0.0.0, metric 1, tag 0 |
A. One router is running RIPv1.
B. RIP neighbor is 224.0.0.9.
C. The network contains a loop.
D. Network 10.10.1.0 is reachable.
Answer: D
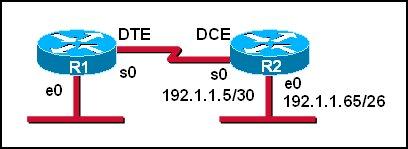
Question 5
Which series of commands will configure router R1 for LAN-to-LAN communication with router R2? The enterprise network address is 192.1.1.0/24 and the routing protocol in use is RIP. (Choose three)
A.
R1 (config)# interface ethernet 0
R1 (config-if)# ip address 192.1.1.129 255.255.255.192
R1 (config-if)# no shutdown
B.
R1 (config)# interface ethernet 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.1.1.97 255.255.255.192
R1 (config-if)# no shutdown
C.
R1 (config)# interface serial 0
R1 (config-if)# ip address 192.1.1.4 255.255.255.252
R1 (config-if)# clock rate 56000
D.
R1 (config)# interface serial 0
R1(config-if)#ip address 192.1.1.6 255.255.255.252
R1 (config-it)# no shutdown
E.
R1 (config)# router rip
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.4
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.128
F.
R1 (config)# router rip
R1 (config-router)# version 2
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.0
Answer: A D F
Explanation
First we notice that the ip address of the E0 interface of R2 is 192.1.1.65/26, which has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.1.1.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.1.1.127
Therefore, the ip address of the E0 interface of R1 cannot belong to this range or the network cannot operate correctly.
In answer A, the ip address of E0 interface of R1 is 192.1.1.129, which does not belong in this range -> A is correct.
In answer B, E0 interface of R1 has the ip address of 192.1.1.97, which belongs in this range -> B is not correct.
The s0 interface of R1 must belong to the same network of s0 interface of R2, which has:
+ Increment: 4 (/30 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1100)
+ Network address: 192.1.1.4
+ Broadcast address: 192.1.1.7
The ip 192.1.1.5 has been used by s0 of R2 so the only suitable ip address of s0 of R1 is 192.1.1.6 -> C is wrong but D is correct.
Now the last thing we must do is enabling RIP. Because e0 interface of R1 and e0 interface of R2 have the same major network (192.1.1.0/24) so we must use RIP version 2 to support discontiguous network -> F is correct.
For answer E, if we configure 2 networks
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.4
R1 (config-router)# network 192.1.1.128
then these networks will be automatically summarized as 192.1.1.0 network.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit. Two routers have just been configured by a new technician. All interfaces are up. However, the routers are not sharing their routing tables. What is the problem?
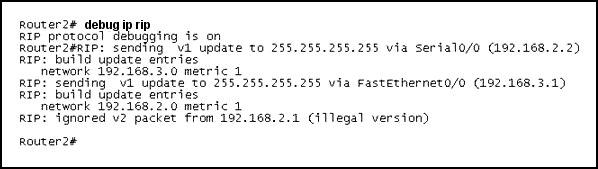
A. Split horizon is preventing Router2 from receiving routing information from Router1.
B. Router1 is configured for RIP version 2, and Router2 is configured for RIP version 1.
C. Router1 has an ACL that is blocking RIP version 2.
D. There is a physical connectivity problem between Router1 and Router2.
E. Router1 is using authentication and Router2 is not.
Answer: B
Explanation
As we can see from the output, Router2 is sending v1 update and ignoring v2 update from neighbor so we can conclude Router2 is running RIPv1. Its neighbor, Router1 (ip address of 192.168.2.1), is running RIPv2.
Notice that router running RIPv2 can “understand” RIPv1 update but router running RIPv1 cannot understand RIPv2 update.
Question 7
What is the default routing update period for RIPv2?
A. 15 seconds
B. 30 Seconds
C. 180 Seconds
D. 240 Seconds
Answer: B
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. The network manager is evaluating the efficiency of the current network design. RIPv2 is enabled on all Layer 3 devices in the network. What network devices participate in passing traffic from the PC at 10.10.1.7 to File Server at 10.20.1.6 in the order that they will forward traffic from source to destination?
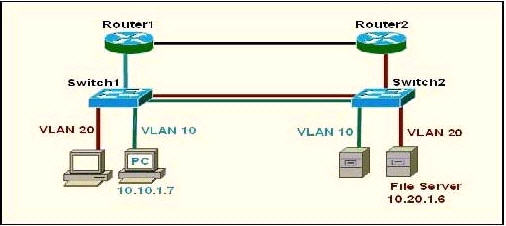
A. Switch, Switch2
B. Switch, Switch2, Router2, Switch2
C. Switch1, Router1, Switch1, Switch2
D. Switch1, Router1, Router2, Switch2
Answer: D
Explanation
The PC and File Server are in different VLANs so surely traffic from PC to File Server must go through Router1 but which path will the packet go next, through Router 2 or Switch1? Well, it is a hard question to answer.
As many comments said “the connection between R1 and Switch is Blue, so that means its under Vlan 10, and R2 to Switch 2 is red. The two routers do not have subinterfaces and are not running router on a stick basing on the color of the links” so D should be the correct answer.
Just for your information, I keep this explanation (which supports answer C) but in the exam you should choose D as your answer!
I haven’t had tested it yet but I guess that because there is a VLAN 20 on Switch 1 so Router1 will try to send that packet back to Switch1. If the link between Switch1 and Switch2 is a trunk link then the returned packet will also be sent to this link. Switch 2 receives that packet and it sends to the File Server at VLAN20. So the path will be Switch1 -> Router1 -> Switch1 -> Switch2.
There are some debates about this question but if the routers are properly configured then the packets can go from Switch1 -> Router1 -> Router2 -> Switch2 (D answer) so D can be a correct answer.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. Router A has interfaces with addresses 192.168.1.1 and 172.16.1.1. Router B, which is connected to router A over a serial link, has interfaces with address 172.16.1.2 and 10.1.1.2.
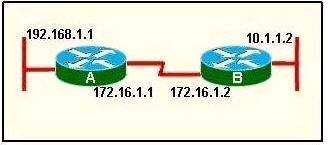
Which sequence of commands will configure RIPv2 on router B?
A.
B( config)# router rip
B(config-router)#version 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
B(config-router)# end
B.
B(config)# router rip 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
B(config-router)# end
C.
B(config)# router rip
B(config-router)#version 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
B(config-router)#end
D.
B(config)# router rip version 2
B(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
B(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
B(config-router)#end
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. S0/0 on R1 is configured as a multipoint interface to communicate with R2 and R3 in this hub-and-spoke Frame Relay topology.
While testing this configuration, a technician notes that pings are successful from hosts on the 172.16.1.0/24 network to hosts on both the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks. However, pings between hosts on the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are not successful. What could explain this connectivity problem?
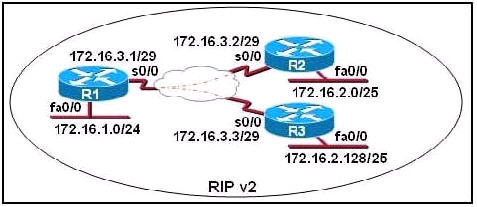
A. The ip subnet-zero command has been issued on the R1 router.
B. The RIP v2 dynamic routing protocol cannot be used across a Frame Relay network.
C. Split horizon is preventing R2 from learning about the R3 networks and R3 from learning about the R2 networks.
D. The 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are overlapping networks that can be seen by R1, but not between R2 and R3.
E. The 172.16.3.0/29 network used on the Frame Relay links is creating a discontiguous network between the R2 and R3 router subnetworks.
Answer: C
Explanation
The “ip subnet-zero” allows the use of the first subnet but it doesn’t cause this problem and we don’t have that first subnet (like 172.16.0.0/24) so we can’t confirm if the “ip subnet-zero” was used or not -> A is not correct.
Frame-Relay can use RIPv2 with no problem if we configure it correctly -> B is not correct.
In the exhibit above we notice that the s0/0 interface of R1 has not been divided into sub-interfaces so the split horizon will prevent updates from R2 to R3 and vice versa. The split horizon rule states “A router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came”. In this case R2 send an update to S0/0 of R1 so R1 cannot send that update back on S0/0 -> R3 will not learn about networks of R2 (and vice versa) -> C is correct.
172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are not overlapping networks. They are two different sub-networks -> D is not correct.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol so it supports VLSM and discontiguous networks -> E is not correct.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. After a RIP route is marked invalid on Router_1, how much time will elapse before that route is removed from the routing table?
| Router_1# show ip protocols Routing Protocol is “rip” Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 8 seconds Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240 Outgoing update filter list foe all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Router 1# |
A. 30 seconds
B. 60 seconds
C. 90 seconds
D. 180 seconds
E. 240 seconds
Answer: B
Explanation
The question reads: After a RIP route marked invalid on Router_1, how much time will elasped before that route is removed from the routing table.
The word “REMOVED” in the question means “FLUSHED”
Carefully look at the Router_1 show ip protocol output:
Invalid is 180 secs.
Flushed is 240secs.
RIP route marked invalid (180secs.)
Time elasped before route is removed (Flushed 240secs.)
The difference is 60secs……..240-180=60. Actually is 180+60=240.
Please notice that the invalid timer, hold down timer and flush timer start counting at the same time.
Question 12
Refer to the graphic. Host 1 cannot receive packets from Host 2. Assuming that RIP v1 is the routing protocol in use, what is wrong with the IP configuration information shown? (Choose two)
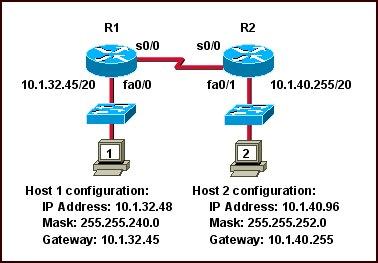
A. The fa0/1 interface of router R2 has been assigned a broadcast address.
B. The fa0/1 network on router R2 overlaps with the LAN attached to R1.
C. Host 2 has been assigned the incorrect subnet mask.
D. Host 1 has been configured with the 255.255.248.0 subnet mask.
E. Host 2 on router R2 is on a different subnet than its gateway.
Answer: B C
Explanation
The fa0/1 interface of R2 is assigned an IP address of 10.1.40.255/20. It seems to be a broadcast address but it is not. If we calculate the range of this network we will understand why:
Network 10.1.40.255/20
Increment: 16 (/20 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 0000.0000 0000)
Network address: 10.1.32.0
Broadcast address: 10.1.47.255
-> 10.1.40.255/20 is an usable host address -> A is not correct.
The IP address of host 1 (10.1.32.48) belongs to the range of interface fa0/1 on R2 as shown above -> B is correct.
In the topology above, all subnet masks are /20 (255.255.240.0) excepting the subnet mask of Host 2 (255.255.252.0) so C can be incorrect.
The subnet mask of Host 1 is 255.255.240.0, not 255.255.248.0 -> D is not correct.
Host 2 is not on a different subnet than its gateway even if the subnet mask 255.255.252.0 is used. Let’s analyze the range of Host 2 network:
Network 10.1.40.96/22
Increment: 4
Network address: 10.1.40.0
Broadcast address: 10.1.43.255
Its gateway (10.1.40.255) is still belongs to this range -> E is not correct.
Note: In this question, C is the best suitable answer after eliminating A, D, E answers. But in fact Host 2 can ping its gateway because they are on the same subnet.
Question 13
What two things will a router do when running a distance vector routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. Send periodic updates regardless of topology changes.
B. Send entire routing table to all routers in the routing domain.
C. Use the shortest-path algorithm to the determine best path.
D. Update the routing table based on updates from their neighbors.
E. Maintain the topology of the entire network in its database.
Answer: A D
Question 14

Use the output from the router shown in the graphic above to determine which of the following are correct. (Choose two)
A. Router John uses a link-state routing protocol.
B. Router John will receive routing updates on the Serial0/0 interface.
C. Router John will receive routing updates on the Serial0/1 interface.
D. Router John will send routing updates out the Serial0/0 interface.
E. Router John will send routing updates out the FastEthernet0/0 interface.
F. Router John will send routing updates out the Serial0/1 interface.
Answer: B D
Explanation
As you can see under “Routing for networks”, network “10.0.0.0″ is advertising. The IP address of S0/0 is 10.168.11.17 which belongs to 10.0.0.0 network -> RIP is running on s0/0 interface only, not s0/1 -> S0/0 will send and receive RIP updates.
Question 15
What can be determined from the line of show ip route output shown in the exhibit? (Choose two)
R 10.10.10.8 [120/2] via 10.10.10.6,00:00:25, Serial0/1
A. The next routing update can be expected in 35 seconds.
B. The IP address 10.10.10.6 is configured on S0/1.
C. The IP address 10.10.10.8 is configured on S0/1.
D. This route is using the default administrative distance.
E. The 10.10.10.8 network is two hops away from this router.
Answer: D E
Explanation
From the output, we can see 2 parameters [120/2]. The first is the administrative distance of the routing protocol being used. In this case it is RIP (symbolized by the letter “R”). Because 120 is also the default administrative distance value of RIP -> D is correct.
In RIP, the metric is hop count so “2″ means the network 10.10.10.8 is two hops (routers) away from this router.



Q 11.
Why will be remove in 60 seconds?
I think should be in 240 (Flushed)
Agreed, routes will stay in a routing table for a total of 7 minutes with Rip. The first 180 seconds (3 minutes) tick down to mark the route invalid. Once this has been done, the route will then take another 240 seconds to actually flush from the routing table.
Correction, the answer is indeed 60 seconds. The flush timer and the invalid timer start at the exact same time, so 60 seconds after its marked invalid, it will be flushed. This was confusing to me because I believe there is a bug in PacketTracer. Simulating this in packet tracer takes a full 7 minutes for the route to drop out of the table but simulating this in GNS3 only takes the 240 seconds. I’m inclined to believe GNS3 simply because it utilizes actual Cisco IOS.
@Claudio form Chile
Regarding Q11.
Well, notice it says “AFTER a RIP route is marked invalid on Router_1″ so it isn’t “invalid” until after 180 seconds. The hold down timer has expired at that time too because it also has been 180 seconds. So then 60 seconds later its flushed at 240 seconds.
Make sense.
I asked this same question to my instructor and this is how it was explained to me.
i cant find networkfundamental questions
Q8 & Q11 was confusing question but answer were more confusing.
Q8: Refer to the exhibit. It show connectivity between Switch 1 to Switch 2 without Router 1
and if we have only 1 Router we can to from Vlan 10 to Vlan 20.
Guide me Plz
If i configurate RIP v2…… i should put network or subnetwork address?
Why never can we put no auto-summary summary when there are subnetworks”
Can you explain me?
@claudio from chile
we use *no auto-summary* when we have discontinuous networks.
discontinuous networks:
R1 connects to 10.100.5.0/24 and to 10.107.1.64/27
if i do this:
R1(config)# router rip
R1(config-router)# version 2
R1(config-router)# network 10.100.5.0
OR
R1(config-router)# network 10.107.1.64
both above network commands are equal to *network 10.0.0.0*
then R1 will think it has connection to all 3 networks: 10.0.0.0/8, 10.100.5.0/24 and 10.107.1.64/27
this is because auto-summary is in effect by default and the router will summarize to the classful IP (which is 10.0.0.0/8 – class A IP)
now think that there is another router, R2, that connects to 10.100.6.0/24 and 10.108.1.32/27.
if we connect both routers and try to send packets from on router’s LAN to the other’s we would have problems because both routers think the packets are destined for 10.0.0.0/8 and both of them think they are connected to everything that is within 10.0.0.0 ~ 10.255.255.255
if we had different networks we would’ve had no problems with the summarization.
let’s say R1 connects to 192.168.1.0/28 and 192.168.2.240/28
and
R2 connects to 192.168.3.0/24 and 192.168.120.64/27. there would be no problems at all to send packets between the LANs.
bottom line: use *no auto* when you use subnets that belong to the same classful IP range
Q14..I think bro..Routing for network is only network 10.0.0.0 classfull because Rip v1 used.
int s0/1 was passive interface and not updated in 192.168.11.0 in routing network.This is Classfull Rip v1.So only s0/0 is optional which 10.168.11.17 is included in 10.0.0.0..Help me if Im wrong..thanks
going for certification next week, plz help if u got anything. send it to my email.
jkwok1@aol.com . thhx all
q5 correction in the question. RIPv2 is used ;) . I believe its a typewriting mistake :)
@sando
nope, no mistake there. when you say “RIP” you refer to either v1 or v2.
Hi all,
i will take CCNA certification and i’m a bit lose in this website (i don’t know which to review for CCNA certification) kindly help me. T_T .
thanks you in advance guys/gurls
In CCNA Exam ask broadcast address RIPng….What is it?
hi there..
in question no.2, it’s answer is B and D, but wen i checked lammle’s 6th edition book (page no.444, ).. it says tat RIPv2 does not support route summarization… so, according to the book, correct answer shud be A and B.. right….???
can someone explain me question 12? I thought the correct answer was C and E
@alex
“Host 2 on router R2 is on a different subnet than its gateway”
10.1.40.0/22 is part of 10.1.40.0/20 so the computer can send packets to the router with no problem.
option E can be ruled out.
host subnet mask should reflect the mask configured on the default gateway.
guys, how many questions do they ask in ccna cert n how much time do they provide?
@rohit_goa
please read here:
http://www.9tut.com/ccna-faqs-a-tips
q14
Can anybody tell me why f0/0 isn’t included in the section below.
edistributing: rip
Default version control: send version 1, receive any version
Interface Send Recv Key-chain
Serial0/0 2 1 2
Serial0/1 2 1 2
just curious because f0/0 isn’t listed it led me to think s0/1 shouuld be included in the answer.
@rogues pierre
the command used was “network 10.0.0.0″.
interface f0/0 does not have an IP that resides on this network. it is configured with an IP from the 192.168.18.0 network
pay attention to details such as this one. a simple question can become your nightmare if you try to read it to fast
In respect to Q8. In a sense the configuration is acting like a longer version of router on a stick, without subinterfaces. Basically, frames are been sent from switch to router to router to switch to destination. Since we can’t be cetain which links are trunk, then we can’t send frame from switch to router and back to switch to switch to destination. This is just a thought. Does it make any sense?
3. (router—-router).3
1 to 2 to 3 to 3 to 2 to 4 .
2. (switch—-switch).2
1. (source—destination).4
hi all,
why you keep asking for updated ccna exam dump?
isn’t 9tut not updated anymore? T_T
please do advice
By default, RIPv2 sends and receives only version 2 updates. If a network must use both versions of RIP, the network administrator configures RIPv2 to send and receive both versions 1 and 2. By default, RIPv1 sends version 1 updates, but receives both versions 1 and 2. So RIPv1 and 2 are completely compatible.
Going by this fact, explanation to Answer B, in Question 6 is not correct.
Hi, Appreciate if someone could send me the latest dumps at treepanel.ken@hotmail.com , i plan to take the exams at the end of sep.
Thanks.
can somebody plz explain how to calculate subnet mask in question 12) :(
Many thanks for detailed replying! Amasing God Bless You
can anyone tell me which exam collections are more needed,,,i mean the author
I will be taking the test at the end of the SEP. Could someone pls send me the latest dumps to big_boy99_01@yahoo.com.
@ anyone can u send me the latest CCNA actual exam?
please send it to sab3001@hotmail.com
Appreciate anyone who will share it. Thanks!
@jon:
The subnet mask provided is /20 which is 11111111 11111111 11110000 00000000. When you add the the 3rd octet (11110000) you get 240 (128+64+32+16). 256-240 = 16 (or 15.255) which will cover the following IP’s:
10.1.32.0 – 10.1.47.255.
In Q12s case the address used on fa0/0 of R1 is 10.1.32.45/20. The fa0/1 address of R2 is 10.1.40.255 which as you can see above overlaps with the 10.1.32.0/20 subnet.
A. The fa0/1 interface of router R2 has been assigned a broadcast address. (No because 10.1.32.0 – 10.1.47.255)
B. The fa0/1 network on router R2 overlaps with the LAN attached to R1. (Yes based on explanation above)
C. Host 2 has been assigned the incorrect subnet mask. (Yes, inherently wrong because of the overlapping subnet with R1. Plus we had to choose two answers and this is the only other choice)
D. Host 1 has been configured with the 255.255.248.0 subnet mask. (No because its part of the 10.1.32.0 – 10.1.47.255 subnet therefore it’s assigned 255.255.240.0 subet)
E. Host 2 on router R2 is on a different subnet than its gateway. (No because its part of the 10.1.40.0 – 10.1.43.255 subnet)
Answers B, C
i need the latest dumps please!!!!!!!!! send to patkiwanuka@yahoo.com
can someone clarify this for me pls ?
Q15 RIP
R 10.10.10.8 [120/2] via 10.10.10.6,00:00:25, Serial0/1
Serial0/1 here mean the local interface of the router witch learn the RIP route, right ? It also mean if local router need to send to destination 10.10.10.8, pass it to Serial0/1 which how to know to get to 10.10.10.6
I post this on rip gns3 page have not got any feedback, i am repost it here :
can anyone comment on GNS3 and Packet Tracer, I am new to both
GNS3 seems more powerful, if i load, say, a c1700 IOS, does it allow me to use other series feature or it is very specific ?
Packet Tracer seem no need to deal with IOS but I am having hard time to make it to work, (using version5.3) like the lab here. I also not able to make the Frame Relay cloud work. (although no problem for all commands)
Any good tutorial on Packet tracer ? thanks
q 12
i think answers A,C are correct chek it
explain 15th question
@satish: I added the explanation for Q12 & Q15, please read it again.
Question 12 is a mess? how does a host do to find-out
if a destination belongs to the same subnet or not? it does an AND
between its subnet mask and the destination IP and then compare it
to its own network address, if they are equal then it will assume
that the host belongs to the same subnet, even if it isn’t. That
situation is arrisen because of wrong subnet addressing and
overlapping and shouldn’t occure in reality I suppose. That is what
I think anyway. I haven’t tested and verified it.
Question 14′s out put for the command SHOW IP PROTOCOLS seems to be faulty. What is the serial interface 0/1 doing in the out-put. That interface doesn’t belong to 10.0.0.0 so how did it came there in the first place??? Please help if you know???
question 14′s answer is correct, review the output and the answer list please.
@9tut
about question 11, some review materials saying it should be d.240 seconds, can you please verify? thanks.
q 5 in RIP v2 we must put Mask
so i think E is correctly
About Q14:
According to the picture:
show ip int bri
IP address S0/0: 10.168.11.17
IP address S0/1: _192_.168.11.21
show ip pro
Routing for networks: 10.0.0.0
Interface Send Recv
Serial 0/0 1 12
Serial 0/1 1 12
Why is S0/1 interface in this list? It has ip address 192.168.11.21
Misprint?
Hi Guys
I’M taking my CCNA exam on oct 3, 2011, please help with latest dumps
this is my email Address : risdiholic@yahoo.co.id
many many thanks!
hey guys i hav to giv my ccna exm in october, please help with latest dumps
my id-mansi0105@rediffmail.com
thanks!!
hey i hav not understood q14..can u help??
@summer
A. Router John uses a link-state routing protocol.
rip is not a link-state protocol, ospf ad eigrp are. false
B. Router John will receive routing updates on the Serial0/0 interface.
s0/0′s IP address is part of the 10.0.0.0 routed network. true
C. Router John will receive routing updates on the Serial0/1 interface.
this interface’s IP address is not part of a network that is routed by this router. false
D. Router John will send routing updates out the Serial0/0 interface.
true – same reason as B
E. Router John will send routing updates out the FastEthernet0/0 interface.
false – same reason as C
F. Router John will send routing updates out the Serial0/1 interface.
false – same reason as C
About Q14:
According to the picture:
show ip int bri
IP address S0/0: 10.168.11.17
IP address S0/1: _192_.168.11.21
show ip pro
Routing for networks: 10.0.0.0
Interface Send Recv
Serial 0/0 1 12
Serial 0/1 1 12
Why is S0/1 interface in this list? It has ip address 192.168.11.21
Misprint?
i am agree with dems
reply pls 9tut!!!
Q14.
This is one of the easiest to solve, if one follow router output and analyze it well.
Deault gateway is 10.168.11.14
Se0/0 int. is 10.168.11.17
The question ask:
Use the output from the router shown in the graphic above to determine which of the following are correct.
Out of the six options given, only two options conforms. B&D
Obviosly sending updates and recieving update will be via serial interface 0/0.
I hope my analysis make sense.
@koffy
u r right thay s0/0 is receiving and sending the update but if we r considering the output in the figure then:
Interface Send Recv
Serial 0/0 1 12
Serial 0/1 1 12
why we can not consider the s0/1 as receiving and sending the update!!!
think both s0/0 and s0/1 both r the true as an answer!!!!
help pls 9tut~~~