CCNA – Show Command Questions
Here you will find answers to Basic Command Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined from the output?

A. 192.168.1.2 is local to the router.
B. 192.168.3.1 is local to the router.
C. 192.168.1.2 will age out in less than 1 minute.
D. 192.168.3.1 has aged out and is marked for deletion.
Answer: B
Explanation
The “Age” field in the “show ip arp” command is the age in minutes of the cache entry. A hyphen (-) means the address is local so in this case 192.168.1.1 & 192.168.3.1 are local to this router -> B is correct.
Note: The “Age 0″ means that the address was cached less than 1 minute ago.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the “Serial0/0 is down” interface status? (Choose two)

A. A Layer 1 problem exists.
B. The bandwidth is set too low.
C. A protocol mismatch exists.
D. An incorrect cable is being used.
E. There is an incorrect IP address on the Serial 0/0 interface.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The first part of the “Serial0/0 is down, line protocol is down” indicates a layer 1 problem while the second part indicates a layer 2 problem -> A is correct.
Some popular layer 1 problems are listed below:
+ device power off
+ device power unplugged
+ loose network cable connection
+ incorrect cable type
+ faulty network cable
Answer B “The bandwidth is set too low” will not make a layer 1 problem.
Answer C is a layer 2 problem.
Answer E is a layer 3 problem.
Question 3
Which line from the output of the show ip interface command indicates a layer 1 problem?
A. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
B. Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down
C. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up
D. Serial0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Answer: B
Explanation
Same as question 2.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. What is the meaning of the output MTU 1500 bytes?
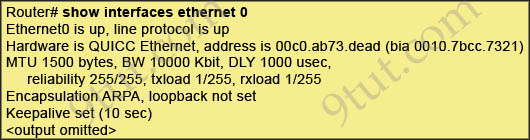
A. The maximum number of bytes that can traverse this interface per second is 1500.
B. The minimum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
C. The maximum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
D. The minimum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
E. The maximum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
F. The maximum frame size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
Answer: E
Explanation
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) defines the maximum Layer 3 packet (in bytes) that the layer can pass onwards.
Question 5
The network administrator normally establishes a Telnet session with the switch from host A. The administrator’s attempt to establish a connect via Telnet to the switch from host B fails, but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful. What is the issue for this problem?
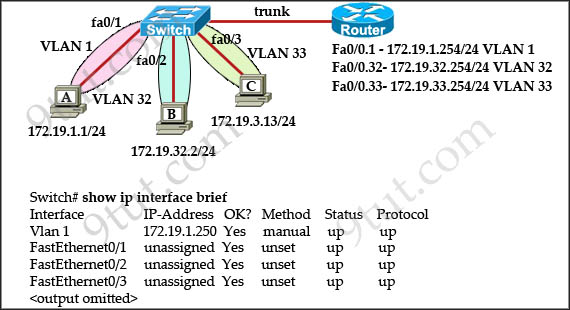
A. Host B and the switch need to be in the same subnet.
B. The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.
C. The switch interface connected to the router is down.
D. Host B need to be assigned an IP address in vlan 1.
Answer: B
Explanation
Host A (172.19.1.1) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are in the same subnet so telnet from host A to the switch can be successful even if a default gateway is not set on host A.
Although the switch has an IP address in Interface Vlan1 but it does not have a default gateway command pointing to the ip address on interface 172.19.1.254 -> B is correct.
Question 6
Which command displays CPU utilization?
A. show protocols
B. show process
C. show system
D. show version
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show process” (in fact, the full command is “show processes”) command gives us lots of information about each process but in fact it is not easy to read. Below shows the output of this command (some next pages are omitted)
A more friendly way to check the CPU utilization is the command “show processes cpu history”, in which the total CPU usage on the router over a period of time: one minute, one hour, and 72 hours are clearly shown:
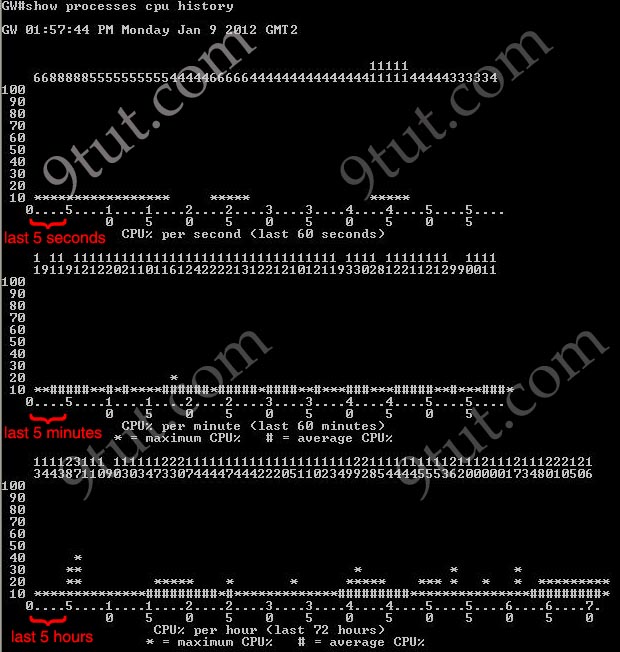
+ The Y-axis of the graph is the CPU utilization.
+ The X-axis of the graph is the increment within the period displayed in the graph
For example, from the last graph (last 72 hours) we learn that the highest CPU utilization within 72 hours is 37% about six hours ago.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. You are connected to the router as user Mike. Which command allows you to see output from the OSPF debug command?

A. terminal monitor
B. show debugging
C. show sessions
D. show ip ospf interface
Answer: A
Explanation
By default, Cisco IOS does not send log messages to a terminal session over IP like Telnet, SSH but console connections do have logging feature enabled by default. To display debug command output and system error messages for Telnet or SSH session, use the “terminal monitor” command in privileged mode.



thank u 9tut, this latest addition is very educative.
Q2:
If (“Serial0/0 is down, line protocol is down” indicates a layer 1 problem while the second part indicates a layer 2 problem) & (Answer C is a layer 2 problem.).. doesnt that means that A & C are the right answers??
please.. someone explains
FOr Q2: If serial0/0 is down, means there is a layer 1 problem. If serial0/0 is down, then automatically line protocol will be down.
If it was like this
‘Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down”, then C could have been the answer
@arun
if there were a protocol mismatch (serial is up, line is down) then the physical layer was all good.
the exhibit shows “serial is up, line is down” which a result of no connectivity at all or the usage of a wrong cable
Hi all!
I confused about Q.5, please explain for me.
Thanks so much!
Q.5
to connect two devices which are in different network addresses ( subnets ) you need to configure the default gateway , which it make devices to reach router , cuz router know all the routes of the entire network (check this command #show ip route ) . in Q5 host B network is ( 172.19.32.0) which is different from switch network (vlan1) ( 172.19.1.250) , so host B will reach switch network through it’s default gateway (router) , and switch will response host B through it is default gateway router so we need to give the switch a default gateway ( command # ip default-gateway 172.19.1.254 )
one more thing in Q5 is that the default gateway for host c is wrong it should be 172.19.3.254
Q5
I’m not sure if I get this right. If there was no default gateway set on host B, then how would B be able to ping A and C? Since B can ping them, it should be able to communicate with the management interface as well, shouldn’t it?
I’m wondering about the way that the answer (“B. The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.”) differs from the explanation (“…so host B needs a default gateway to telnet to the switch”). Who needs to default gateway – is it B or the switch? Where do I configure it and how?
Cheers!
@ ET switch needs a default gateway ( command # ip default-gateway 172.19.1.254 )
@ALsindi
thanks so much!
Why does #4 have the same answer multiple times (B &C) and (D & E)
@Me: They are different answers. B & C are about “segments” (layer 4) while D & E are about packets (layer 3).
On #4 the answers for both B & C are exactly the same:
B. The minimum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
C. The minimum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
need ccna latest dump ambition11111@gmail.com
QUESTION NUMBER 5:
The question states that:
“pings from host B to other two hosts are successful”
so the answer explanation need not include:
“so host B needs a default gateway to telnet to the switch. The default gateway on host B should be 172.19.32.254.”
Because host can already ping devices in other network.
The answer is: “B. The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.”
And the solution would be issuing ip default-gateway on the switch to route back the packets.
i have ccnp Routing 50 exact questions in my exam – ciscolikesme@gmail.com
need ccna latest dump detekto@inbox.lv
Question 5
reponse is D
@someone
STATUS Serial0/1 line Protocol
port operational UP UP
L2 PROBLEM UP Down
L1 PROBLEM/INCORRCT CABLE Down Down
Port disabled Adm- Down Down
All the questions are very helpful.
Can somebody send me few dumps on my email address so that i can practise. i want to pass the ccna exam in first attempt. please help
nitinstu@yahoo.co.in
q.7 i got for today xam
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this Feb. Please send me latest dump so that I will have an idea for the exam.. rico.blake@ymail.com
Thanks Guys!
Hi ,
for Q5, if the host B can ping other hosts, wouldnt it need a default gateway to be assigned.
other hosts are in different vlans.
Need CCNA Latest Dump. meraja19@gmail.com
je suis une jeune centrafricaine agé de 21ans, je dois passer mon ccna dans 3semaine, svp aidez moi pour des questionnaires en français pour le ccna, qui est ce que vous me conseillez pour ma reussite?
carine 21ans
In the examination of LAB SIM, can we go for TAB or ? for next command?? or we have to type full command for executing the practical.
Q:5
The host B can ping all host because inter vlan.
The host B can use telnet if only he is in the vlan 1, same ip gateway host A and same network.
I do not see just reponce
@boby
Q5
Yes, host B can ping all host because inter vlan (sub-interfaces)
The reason A is able to telnet switch and B is not able is, A’ s IP address share the same subnet with Vlan1-management Vlan(1.1 and 1.250), and B’s IP address does not share the same subnet with Vlan1(32.2 and 1.250). Therefore, B’s needs to have a default gateway to telnet switch.
Host A IP address 172.19.1.1 and Host B IP address 172.19.32.2
Management IP address 172.19.1.250………check Switch# show IP interface brief
Hope this help.
Nice questions 9tut :)
regarding Q5
Explanation
Host A (172.19.1.1) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are in the same subnet so telnet from host A to the switch can be successful even if a default gateway is not set on host A.
But host B (172.19.32.2) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are not in the same subnet so host B needs a default gateway to telnet to the switch. The default gateway on host B should be 172.19.32.254.
the answer wasn’t included in the choices so answer A may be correct or PLZ add this answer:
host B needs a default gateway should be 172.19.32.254
thanks alot
latest dumps :-
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.PrepKing.640-802.v2012-01-03.by.DHARANI.615q.vce.file.html
&
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2011-07-09.by.Collisio.486q.vce.file.html
I passed ccna today 973 guys regarding Q7 showed up in my exam but as multiple qnswer where i sould choose 2 answer one of them was for sure terminal monitor and the others i ve no clue about it , except this question all the rest question was from 9tut and acme dump.
good luck
@Xallax @9tut
In the examination of LAB SIM, can we go for TAB or ? for next command?? or we have to type full command for executing the practical.
Please assist
@arpit
you get to use tab and ? on some questions but i’d recommend you avoid using TAB as it could change the highlighted item to Next question and that would be in your disadvantage.
just learn the syntax :)
Q7, I had this on the ICND2 test and they wanted 2 answers. I atleast one was Terminal Monitor but im not sure about the second.
just seen your post mouradteleco, what options did u pick?
Hello
Can anyone tell what means “local to the router” in Q.1??
@ Smaug
Local to router means, the ip address 192.168.3.1 is belongs to one of the router’s interface
regards
@Isuru
thank you.
@9tut
I am wondering if the answer to this question in the question dump is wrong.
Which command will show the MAC addresses of stations connected to switchports?
A. show mac-address
B. show arp
C. show table
D. show switchport
My answer was A but their answer was B. Please explain it the answer in the dump is right.
If anyone else knows please explain the aswer why the aswer is not A .
Which command will show the MAC addresses of stations connected to switchports?
A. show mac-address
B. show arp
C. show table
D. show switchport
who wants cake?
Q3!
Which line from the output of the show ip interface command indicates a layer 1 problem?
A. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
B. Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down
C. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up
D. Serial0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
option A also correct, in the case missing clock rate on DCE.
please give me some advices,
Thanks!
@kindrock
the clock rate operates under the LLC which is a part of the Data Link Layer.
A is incorrect
@xallax
thanks!
but I think you wrong, because in ICND1, clock rate related to OSI layer 1 (page 80)
and in ICND2 mentioned of Troubleshooting Serial links in layer 1 (page 446).
please give me some advices.
sorry because my Eng.!
@kindrock
voltage is related the L1, not clock rate…
may i know from which book did you get the reference?
maybe i got it wrong…
anyway, it says “Serial0/1 is up…”, that means there’s no problem at L1
@xallax
I read the books: CCNA ICND1&2 Official Exam Certification Guide Second Edition.(Wendell Odom)
thanks so much!
@kindrock
mister odom states:
“Interestingly, one other common physical layer problem can occur that results in both
routers’ interfaces being in an up/down state. On a back-to-back serial link, if the required
clock rate command is missing on the router with a DCE cable installed, both routers’
serial interfaces will fail and end up with a line status of up but a line protocol status of
down.”
i’m still dazzled…
found this on the net, doesnt say much
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1915.html
they say somewhere that “Verify that the correct cable is being used.
If the line protocol is still down, there is a possible hardware failure or cabling problem. Insert a breakout box and observe leads.”
you must be right, it could be correct if it were a DCE device.
yet we pick the most obvious one, down/down
@xallax
thanks! :)
@s4cnc
Thanks! :-)