CCNA – Show Command Questions
Here you will find answers to Basic Command Questions
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. What can be determined from the output?

A. 192.168.1.2 is local to the router.
B. 192.168.3.1 is local to the router.
C. 192.168.1.2 will age out in less than 1 minute.
D. 192.168.3.1 has aged out and is marked for deletion.
Answer: B
Explanation
The “Age” field in the “show ip arp” command is the age in minutes of the cache entry. A hyphen (-) means the address is local so in this case 192.168.1.1 & 192.168.3.1 are local to this router -> B is correct.
Note: The “Age 0″ means that the address was cached less than 1 minute ago.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. What could be possible causes for the “Serial0/0 is down” interface status? (Choose two)

A. A Layer 1 problem exists.
B. The bandwidth is set too low.
C. A protocol mismatch exists.
D. An incorrect cable is being used.
E. There is an incorrect IP address on the Serial 0/0 interface.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The first part of the “Serial0/0 is down, line protocol is down” indicates a layer 1 problem while the second part indicates a layer 2 problem -> A is correct.
Some popular layer 1 problems are listed below:
+ device power off
+ device power unplugged
+ loose network cable connection
+ incorrect cable type
+ faulty network cable
Answer B “The bandwidth is set too low” will not make a layer 1 problem.
Answer C is a layer 2 problem.
Answer E is a layer 3 problem.
Question 3
Which line from the output of the show ip interface command indicates a layer 1 problem?
A. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
B. Serial0/1 is down, line protocol is down
C. Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up
D. Serial0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Answer: B
Explanation
Same as question 2.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. What is the meaning of the output MTU 1500 bytes?
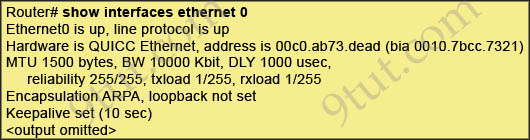
A. The maximum number of bytes that can traverse this interface per second is 1500.
B. The minimum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
C. The maximum segment size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
D. The minimum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
E. The maximum packet size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
F. The maximum frame size that can traverse this interface is 1500 bytes.
Answer: E
Explanation
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) defines the maximum Layer 3 packet (in bytes) that the layer can pass onwards.
Question 5
The network administrator normally establishes a Telnet session with the switch from host A. The administrator’s attempt to establish a connect via Telnet to the switch from host B fails, but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful. What is the issue for this problem?
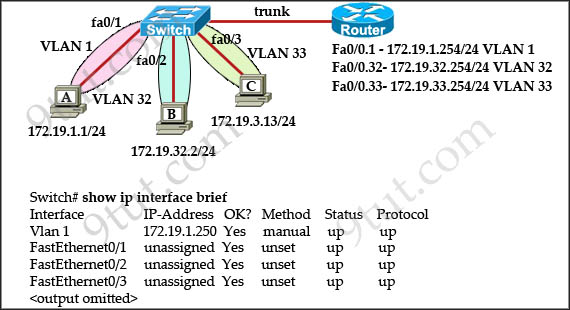
A. Host B and the switch need to be in the same subnet.
B. The switch needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.
C. The switch interface connected to the router is down.
D. Host B need to be assigned an IP address in vlan 1.
Answer: B
Explanation
Host A (172.19.1.1) and the management IP address of the Switch (172.19.1.250) are in the same subnet so telnet from host A to the switch can be successful even if a default gateway is not set on host A.
Although the switch has an IP address in Interface Vlan1 but it does not have a default gateway command pointing to the ip address on interface 172.19.1.254 -> B is correct.
Question 6
Which command displays CPU utilization?
A. show protocols
B. show process
C. show system
D. show version
Answer: B
Explanation
The “show process” (in fact, the full command is “show processes”) command gives us lots of information about each process but in fact it is not easy to read. Below shows the output of this command (some next pages are omitted)
A more friendly way to check the CPU utilization is the command “show processes cpu history”, in which the total CPU usage on the router over a period of time: one minute, one hour, and 72 hours are clearly shown:
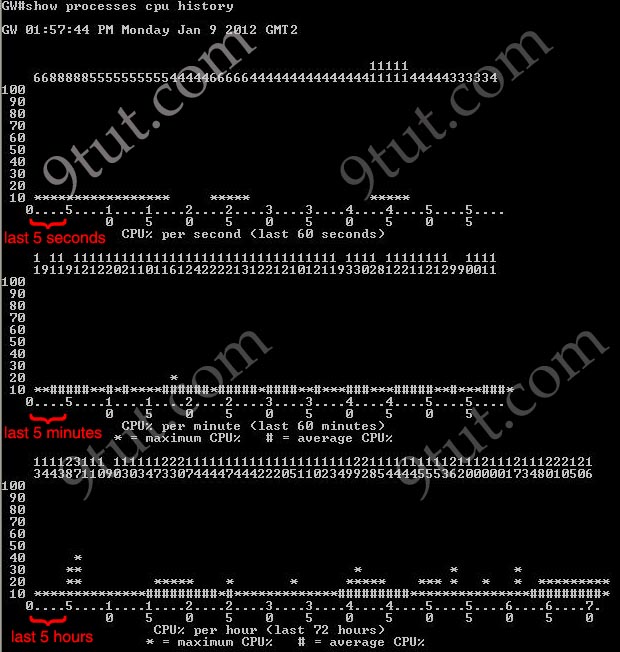
+ The Y-axis of the graph is the CPU utilization.
+ The X-axis of the graph is the increment within the period displayed in the graph
For example, from the last graph (last 72 hours) we learn that the highest CPU utilization within 72 hours is 37% about six hours ago.
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. You are connected to the router as user Mike. Which command allows you to see output from the OSPF debug command?

A. terminal monitor
B. show debugging
C. show sessions
D. show ip ospf interface
Answer: A
Explanation
By default, Cisco IOS does not send log messages to a terminal session over IP like Telnet, SSH but console connections do have logging feature enabled by default. To display debug command output and system error messages for Telnet or SSH session, use the “terminal monitor” command in privileged mode.



Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this march. Please send me latest dumps to enable me prepare.. dmosabi@gmail.com
Thanks Guys!
Hi 9tut… Hi Guys! Can you please help me… I will take exam this march. Please send me latest dumps to enable me prepare.. dmosabi@gmail.com
Thanks Guys!
can any 1 explain Q4
@rock says
MTU represents the maximum size a PDU can have while passing from one OSI layer to the next.
or, as 9tut explains: “The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) defines the maximum Layer 3 packet (in bytes) that the layer can pass onwards.”
read more on MTU here: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maximum_transmission_unit
Hey guys.. the answer for Q.5 is incorrect.. the correct answer should b “D. Host B need to be assigned an IP address in vlan 1.” for telnet to work from Host B.. or u need to assign an ip address for vlan2 (which is nt in the opt.).. as far as i ‘ve read u cannot assign a default gateway for a switch… so go with D opt.
@Vishal…
you are incorrect in your thinking thus far. Keep reading up and you will find that you can in fact give a switch a default gateway…
I vote for 9tut.com being correct on this one.
download packet tracer 5 or better yet GNS3 and test this out. GNS3 is far better than PT5 due to the fact that we are using actual IOS’s and have full functionality…
@Anonymous ..
hey thanx for correcting me.. well i guess i was wrong abt going with opt. D.. well its not completely wrong though.. u cn do dat aswell… bt the best answer is “B”.. but the default gateway u need to set for the switch ‘ll b obviously from one of the ip address assignd to a sub-interface of the router.. correct me if i am wrong..
Q5
this question has mistakes as I feel.
1)host C was assigned a wrong IP address which is not in the VLAN 33.(default gateway and host C’s IP address is not in the same subnet.).so I can’t even think of pinging from host B to host C.but question says so that “but pings from host B to other two hosts are successful”
2)without correct default gateways are assigned pings from host B to other two hosts should not successful.so the answer for this question can’t be accepted.and other answers are also can’t be accepted.
As I understood by going through 9tut tutorials I suggest such this answer for this question.”telnet access from host B is denied by ACL of the router”
isn’t that a nice answer…..:D ?
9tut:
The explanation under Q3 says “Same as question 1″. After reviewing the explanation for Q1, it doesn’t seem as though there is any correlation whatsoever.
Thank you
@moncho: Q3 is same as Q2. Thanks for your detection. I updated it.
hi guys need latest dumps pls send to pveleng@gmail.com
@Udana and anyone else asking about Q5. If I am understanding it right, and I looked at it with a puzzled face the first time!!! The reason host B cannot Telnet the switch is….
1) The switch doesn’t have an IP assigned to it from host B’s subnet.
2) The switch doesn’t have a default gateway assigned.
In this matter you have to look at the travel of the data as it goes through the network when host B starts a request to Telnet to 172.19.1.250.
1. Host B realizes 172.19.1.250 is not in local network and therefore sends frames to default gateway of 172.19.32.254/VLAN32 DFGW/Fa0/0.32 on the router.
2. Router finds destination in it’s routing table, sends data down to 172.19.1.250 (Switch Vlan1 Management IP).
3. Switch receives data.
4. Switch wants to send reply and realizes 172.19.32.2 isn’t in the local network (VLAN1) so sends to it’s default gateway.
5. OH NO, WAIT, Switch doesn’t have a default gateway assigned so can’t reply to any traffic outside of VLAN 1.
Note to self that probably won’t be on CCNA but good working knowledge. If you assign a switch a management VLAN IP you should also assign that switch a default gateway that is within the same subnet as the switch’s management IP.
@9tut. I think this is correct to the best of my knowledge. Please correct me if I’m wrong.
Taking Exam Tomorrow wish me luck!!! Thanks for all the help 9TUT!!!
hi xallax, Ive been using your vce dump to study for ICND2 just wanted to let you know that question 4 above is on the dump and the answer given is frame size answer#4. The expanation given says: notice we are dealing with ethernet which is frames-also arpa encapsulation.
Can you doublecheck this one please? Thanks, appreciate all the time you spend here.
@joe
this questions has been discussed at: http://www.sadikhov.com/forum/index.php?/topic/185144-what-is-the-meaning-of-the-output-mtu-1500-bytes/ in detail.
some go for packet, some for frame.
i’d go for packet is it goes down the OSI layer.
the 1.0944 practice questions are based on actualtests. they took out the frame size option to remove ambiguity.
MTU can refer to both frame and packet. maybe 9tut could lighten us up on this
thank you for asking :) cheers
guys, please send me latest dumps.. I’ll take my ccna exam this coming April 13, 2012.. here’s my email add anjoy_galope@hotmail.com
I scored 933 thanks to 9tut :) good luck for all inshallah
Q7 in today’s exam. 9tut is the best.
guyz plz anyone can tel me that how can we find default gateway’s address?(.254)
Hi. Who got the Q7 on the exam with 2 answers, what was the second cmd or what the possible choices in the answers, if you remember? Thanks.
Q4. MTU is the maximum frame size…http://www.answers.com/topic/mtu
So the correct answer is F
MTU is in the role of ethernet, so it must be talking about layer 2..CMIIW
Does 9Tut like bodi2009′s March 14th, 2012 response to Q5?
thank u 9tut very very good
thanks you 9 tut :)
thanks lot
Hi, could any one explain me the Q.8.
what do the numbers 2122876755437323445566778976000 indicate…in the screen shot?
@umesh show run commad
Dear all,
you may also want to check below site for some useful resources. Good luck to all of us!
careercert.info
I know that this is probably the wrong category – but — Can anyone simplify the explanation of : ip default gateway vs. ip default network vs. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
and here is cisco site that goes into the explanation == http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094374.shtml
Here is another one that could be made easier to understand — default information originate ??!!!
ok — at the bottom of explanation is — summary — use ip default gateway when ip routing is disabled on cisco router. Use ip default network and ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 to set the gateway of last resort that have ip routing enabled.
Now I am finding ip route vs. ip default gateway — about switches — ip default gateway is only used when switch is in L2 and you can use ip route or default network at L3. -HUH??!!
What??
Here’s more — ip route is local on the router — and has admin distance of 1
where ip default network is advertised with the routing protocol — interesting!
ok??!!— you can have more than 1 default network (?), so gateway of last resort is determined according to the metric
Here’s more — ip default gateway is used to enter router’s default gateway
ip route is used to create static routes
or we can tell the router which gateway it must use in order to reach specific networks
I think that for CCNA purposes we are interested in manually assigning ip information to a switch —- 1. enter interface configuration mode — interface vlan 2. enter ip address and subnet mask 3. exit or go to global configuration mode 4. ip default gateway
summary: once default gateway is configured, the switch has connectivity to remote networks with which it needs to communicate — any comments or more explanation??
@9tut
the answer to Q5 is clearly troublesome, it would have been nice if you clarified or corrected.
Hi Friends
I am planning to CCNA in 2 weeks time. Can you please send me latest dumps please at ahm_1_001@hotmail.com?
Thanks
@geedub
1>ip default gateway is use for switch
2>ip default network is use for router.
Hi all, I am taking CCNA 640-802 exam first time on 30/05/2012. Could anyone please send me latest dumps which are valid for UK? My e-mail address is puneet_gill84@yahoo.co.uk. Many thanks.
Am having my CCNA exams this week. Can any one please send me latest dumps at yuflink@yahoo.co.uk.
Thanks
yes, raja —- ip default gateway is used on a switch and ip default network is used on a router — still a lot of simplification — no details with that explanation
Hey Help qith question:::
Based on the input below:
OMCorp#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “rip”
Sending updates every 30 seconds, next due in 0 seconds
Invalid after 180 seconds, hold down 180, flushed after 240
After a RIP route is marked invalid on Router OMCorp, how much time will elapse before that route is removed from the routing table?
A. 30 Sec
B. 60 Sec
C. 90 Sec
D. 180 Sec
E. 240 Sec
According to the examen I was looking at, the answer is E., however, what I think is this… The question says, after a route is marked invalid (that means 180 sec have passed already) how much time will elapse to flush the route (that means that from the time it was marked invalid (180) to the time it will be flushed, it will have passed 60 sec…
I want to hear your comments….. Please
if there are multiple vlans on a switch, and hosts from each vlan need to access the vlan 1 management interface, then does the switch need multiple “ip default-gateway” command, one for each vlan (since subnets for each vlan will be different)?
I PASSED CCNA EXAM TODAY THANKS TO ALL MIGHTY ALLAH
960/1000
can someone send ccna latest dumps to firegoblets@gmail.com ? pls
@jpmarinm : the answer is 60 sec and ur reasoning is right
Hi, Im Priya from Kerala(India).Im taking ccna exam on 30th June.Really im fed up.Can any one plz send me latest dumps to my email priya.ccna@yahoo.in Love you all .God Bless ..Thanks
priya
Q5
@bodi2009
YOU ARE ABSOLUTLY RIGHT. Thnx!
I have just tested on Packet Tracer. Host B can reach the Switch, but Switch can’t respond to the ping, becouse there is no default gateway set.
From PT simulation:
****************************************************************************
1. The destination IP address is not in the same subnet and is not the broadcast address.
2. The default gateway is not set. The device drops the packet.
****************************************************************************
Default gateway for Switch should be: 172.19.1.254
The question 5 in “Show command questions” explanation is confusing. The answer said
B. The SWITCH needs an appropriate default gateway assigned.
but the explanation said:
“host B needs a default gateway to telnet to the switch. The default gateway on host B should be 172.19.32.254.”
And by the way I think host B already got the right default-gateway because it could ping other hosts from different VLAN from the beginning.
Can someone explain this thoroughly?
Hi all, I am having my CCNA (640-802) exams this week. Can anyone please send me latest dumps: allient@post.sk
Thank you ;)
Question 5 is complicated by the answer where it states that Host B needs a default gateway assigned rather than explaining why the switch needs a default gateway.
A switch is a layer-2 device and moves traffic from port to port using MAC addresses rather than IP addresses, so, in effect it does not know a router connected to one of its ports from a workstation or printer. So how do devices on a network determine where to send traffic? First, they apply their subnet mask to their address to determine if the intended recipient is on their own network or not. Then, if the recipient is in their network they ARP for its MAC address and send their traffic directly to the recipient aided by the switch which knows which port the recipient is attached to. But, if the intended recipient is in another network, the traffic needs to be forwarded to the nearest router interface for layer 3 routing to a distant network. This nearest router port is defined as the “forwarding gateway.” A switch without a forwarding gateway defined is unable to determine the “nearest router” and is therefore unable to forward any traffic to any other network other than its own. Hence, while Host A can communicate with the switch (same network) Host B will be unable to communicate with the switch because it does not know where to send traffic destined for another network. In point of fact, Host B has no trouble getting traffic to the switch (the router takes care of that), it’s the switch itself that can’t determine where to send its traffic so that it can be forwarded to another network.
If you think about the ARP process it’s easy to see that you first need an IP address to resolve; without a forwarding gateway assigned to the switch it simply doesn’t know how to send traffic to another network.
The part of the answer regarding a forwarding gateway being needed on Host B is at best, a misprint. That Host B can successfully ping to two other hosts is ambiguous since it is not known whether those other two hosts are on the same or different subnets. In this case it’s important to remember that “different VLANs” and “different subnets” or “different networks” all amount to the same thing: they all require a router to route traffic between them; a switch is incapable making layer 3 routing decisions since it “lives” at layer 2, and even though we can point to the cable connecting the switch to the router, the switch is too dumb to know that it can send traffic for forwarding to that port without a statement defining the IP address equating to “it’s a forwarding gateway” with the emphasis on “forwarding,” which it can then ARP to get the MAC address and Port ID of the forwarding port. Only then can it get its own traffic forwarded to other networks, VLANs and subnets.
Forget the second part of the answer; the correct, most feasible and most practical answer is that no forwarding gateway IP address was assigned to the switch, given the information provided in the question and graphic. Answers A & D are ruled out because they both essentially say the same thing, and answer C, while possible would manifest problems for all users traversing that router interface. Therefore B is the most likely right answer.
I passed my ccna exam today Praise be to God! Thank you Jesus! and thanks to 9TUT for the tutorials and explanations, great site and thanks to xallax for your explanations to questions and thanks to http://www.examcollection.com for the dumps. Pls guys lets donate and help to keep this site up!
48 ques for exams including 3 simulation, I had EIGRP, Acesslist2 and VTP . Make sure you practice the simulation, use packet tracer or gns3. Best wishes to all!
Am taking mi CCNA exam the end of this month so can any one help mi with latest CCNA dump..mi mail rnldkblkgsmr770@gmail.com