CCNA – STP Questions
Here you will find answers to Spanning Tree Protocol Questions
Note: If you are not sure how STP and RSTP work, please read my STP tutorial and RSTP tutorial.
Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
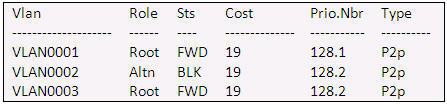
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
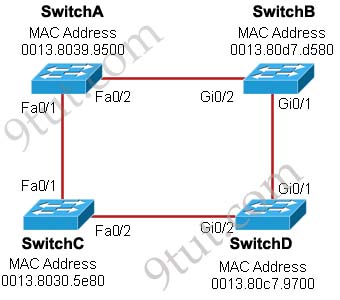
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again
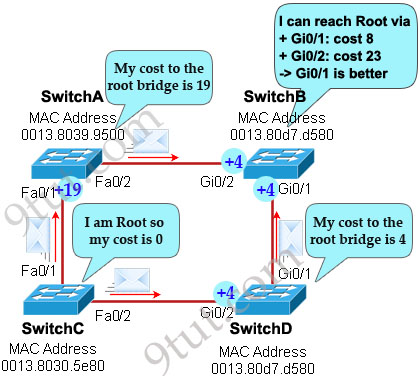
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
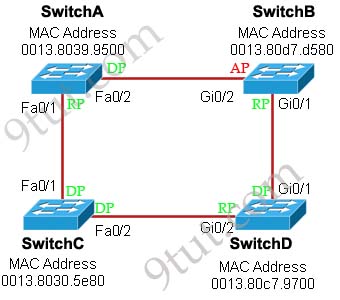
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 8
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 9
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
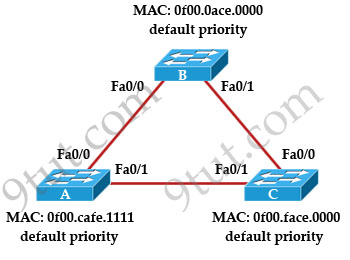
A. Switch A – Fa0/0
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.
On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.



@koffy
My mistake! I noticed now what I was doing wrong! Just like you said simple math :)
thanks.
@9Tut or anyone?
Q2, Isnt the answer B (learning) and D (forwarding), and not A (blocking)? and doesn’t this next question prove it? This is really confusing….
Refer to the exhibit. The output that is shown is generated at a switch. Which three of these statements are true? (Choose three)
A. All ports will be in a state of discarding, learning or forwarding.
B. Thirty VLANs have been configured on this switch.
C. The bridge priority is lower than the default value for spanning tree.
D. All interfaces that are shown are on shared media.
E. All designated ports are in a forwarding state.
F. The switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs on this switch.
Answers A C E.
Q7:
Guys, I don’t think that SwitchB Gi0/2 will be AP but fa0/2 on SwitchA.
Wendell Odom: ICND2 p103.
“Step1 For switches, connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost to reach the root is the DP on that segment.
Step2 In case of a tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the lowest BID becomes the DP”
What do you think?
Thank you
Balazs
Hi 9tut,
In Q7, I agree with the answer. But I dont think the value of cost in your explanation is correct. For example, from Gi0/2 of Switch D to Fa0/2 Switch C, the cost should be 19. Because Gi0/2 of Switch D will reduce its speed to match the Fa0/2 Switch C. Please verify.
Anyway, thank you for providing so much helpful forum.
Kim
@Kim
From which God green earth did you come up with the idea that switch D will reduce its cost to match Fa0/2 of switch C?….Why?……. Can you explain yourself?
The cost will increase because of speed. Usually duplex and speed of the interface will be set autonegotiate by deault. So the two connected interfaces in both sides will have to match the speed and duplex mode, right? And if you force to set 1000MB on Gi0/2 of switch D, it causes the port down because the speed mismatching. Therefore, I think the cost on Gi0/2 of switch D should be 19 instead of 4.
@Kim
This what the question is asking. Why do you insist on adding more to what is required of you?
Please, read the question:
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
So it should use the default configuration. The cost should be 19. That was what I have mentioned. I know this is out of the question. I just want to confirm whether my understanding is correct or not. So what do you think about the cost of Gi02 of Switch D?
lates dumps please kevinbogantes22@hotmail.com
please send me latest dumps on krunal.shah@irwinconsult.com.au. I am sitting in exam on 25th january….
Hi,
Pls share the latest CCNA dumps: azharsrmv@gmail.com
Thanks in Advance, Azhar
Good work! Thanks for nice explanation on Q7 :)
@xallax
which cisco catalyst feature automatically disable the port in an operational PortFast upon of a BPDU
A. backbone fast
B. uplink fast
C. root guard
D. BPDU gaurd
E. BPDU filter
can u answer me
it is D. BPDU gaurd in dump
what is the correct one????
@islam
the BPDU guard feature disables the port if the switch receives frames from another switch on that port
D is correct
Check out some easy explanations on Vambarinc on youtube.
For question two, the answer is C and D
for Q2,
thanks god I passed my exam with 1000, i found this Q in exam and choose C D
Good luck, God bless all of you
Q2 ? what is the answer ?!
@9tut what is the answear for Q2
@adi, @t-one: As I explained, if you don’t see the answer “discarding” in the exam then the best alternative answer is “blocking”
@9tut: As per the above given ex of STP Q7, just want to understand, one port of switch in Fa (Fast Eth) and the connecting other end is of Gig port, but the actual data transmit will be at the spped of Fa (Fast Ether i.e. 100Mbps) correct or not?
So, Total cost of Link will be the 100 Mbps instead of 1gbps. so can we calculate like this or My understanding is wrong??
@ 9tut
plz refer the link and explain question
http://s1153.photobucket.com/albums/p518/isuru888/STP/?action=view¤t=stp.jpg
Hi all!
In Q.6, Option A: RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
I think RSTP can operate with PVST+, that is RSTP can operate with STP but PVST+ not supports RSTP. So option A is not correct.
please give me some advices.
Thanks so much!
Passed ICND2 2nd time around. Q5, Q7 & Q10 were on it. New OSPF sim and also had a vlan sim. D&D showed up 2 times asking about definitions 4 poison reverse, holdover timer, split horizon etc. Had about 10 new questions that I haven’t seen in the dumps or this site. Used 9tut, Cisco press, Packet Tracer. Study til it hurts!! Thanks 9tut!!
Q1,4 & 6 was there in today’s exam.
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.Acme.640-802.v2012-02-07.by.Arpit.486q.vce.file.html
Most Valid Dump.. All most 99% answers are correct.
Q7: I agree with JEFF.
The Path Cost : 8 and 19 -> so i think B – GI 0/2 is DP .
in Q6
can anyone explain why is it an alternate port?
BLK is still a valid port Status even in RSTP., I have labbed this up
about Q7
Am i correct about the costs of SwitchA’s Fa0/2 and SwitchB’s Gi0/2?
SwitchA’s Fa0/2 = 19 because cost of SwitchA’s Fa0/1 is cost 19
SwitchB’s Gi0/2 = 4 (SwitchB’s Gi0/2) + 19 SwitchA’s Fa0/1 = 23
Q.5 Q5 Question 5
I think, the answer is – A;
Because the answer C cannot be true:
STP puts “Altn” state not only for cost,
but also it considers mac-address and port number
@Aidos
I believe there is not root network segment with two interfaces on one end and one on the other
Segment is one connection between two switches
So i also think C is correct and it implies that root switch and that switch are connected with two segments
But correct me if i am wrong
Q7:
I agree with fatfighter. I think switch B Gi0/2 should be the DP.
Wendell Odom: ICND2 p103.
“Step1 For switches, connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost to reach the root is the DP on that segment.
Step2 In case of a tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the lowest BID becomes the DP”
Which two values used by RSTP bridge to remove stale BPDU information: (choose two)
1. Message Age
2. Forwarding Delay
3. Hello Time
4. Max Age
Thanks.
Q2, Q3, Q10 in exam. 9tut has the best collection and best explanation.
@Sisjun: 1,4
thank you 9tut i got 933 acl2 eigrp switch and multiple choice same as pass4sure corrected by 9tut…………
Q7
Can anybody tell me why the segment between SW A & SW B are not be addressed with cost to the root.
I don’t understand why cost isn’t being used, and we go directly to tiebreaker either. Can someone please elaborate?
Q7.
Root path cost calculation is wrong. The cost is calculated by the link speed of the port & not by the link type. (Explain correctly in the tutorial)
cost to SWA from Root is 19.
Cost to SW B from Root is 23.
– SW C – SW D – Link negotiate to 100Mbps – 19
– SW D – SW B – Link 1GBPS – 4
– Cost = 19 + 4 = 23
So, SW A Fa0/2 – Designated Port
GJ thank you, that was what was missing. Getting the designated bridge relative to the segment of A and B couldn’t have been explained better.
Guys!
I would like to say my views on the Ouestion 7:
1) First of all. When we elect DP for the segment, path cost to Root bridge is MORE preferable than BridgeID. Then bridge with lower path cost to Root will be Designated bridge to that segment and its port will be Designated Port.
2) If the bridges have equal path cost to the Root then comparison their BridgeID – the bridge with lower BID will be Designated bridge for the segment.
3) If BID and path costs to Root are equal then comparison their MAC-address – the bridge with lower MAC will be Designated bridge for the segment.
Now, about Question 7 result:
If we suppose that there are auto-negotiation between links – fa and Gi then Gi has cost which equal the slowest link-type. If our suppose is true – then fa0/2 of SW A will be DP and Gi0/2 of SW B will be AP.
If we suppose that Fa0/2 and Gi0/2 are REAL COSTS i.e. we’ve set costs to port BY FORCE (i.e spanning-tree vlan # cost #) then bridge with lowest path cost will be Designated bridge for the segment!
P.S As you know “spanning-tree vlan # cost #” doesn’t work in PT.
That’s all!
About Q7, maybe this link helps:
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/37645?start=0&tstart=0
It seems than cost calculations are link based, not port based, so in our case, cost SWA-SWB will be 19, as cost SWC-SWD also.
Exam on 19th.. can any one gibe some latest dumps or labs ..
Thanks 9tut!=D
By question 5 why the C is the correct, & not A?
If a switch has in vl X a blocking port, then must be have a root or desg port to.
And, if this switch port has a higher path cost to the root, than the oders, must not be root. Rather desg or blocked, depend the connected other switch bridge priority.
In a CISCO switch if port 1 connected to port 3 how will the STP acts, Can you give an explanation with exmple?
Excellent, Excellent what an Explanation: I just love you GUYS!!!!!!!Q7 Has been bothering for months. But hey now is CLEAR. THANX Alot
Q7:
one end of a cable is connected with fast ethernet port while other one is connected with gig port, i am getting confuse because of both ports bandwidth mis match. kindly someone explain it.
i think we add the cost of any link after completion of paket journey, so from swC to swD cost should be of fast ethernet cable not of gig. am i right?
we consider the Mac add of switches to define port roles if cost become equal on both ends, cost is not same on both ends, i am talking about link b/w swA and swB
thnx in advance
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Why on the earth is answer F correct
If we agree that there is point-to-point link then there is point-to-multipoint links.Between switches is there this kind of connection?