CCNA – STP Questions
Here you will find answers to Spanning Tree Protocol Questions
Note: If you are not sure how STP and RSTP work, please read my STP tutorial and RSTP tutorial.
Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
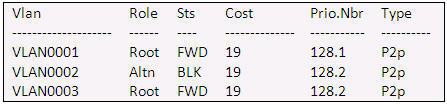
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
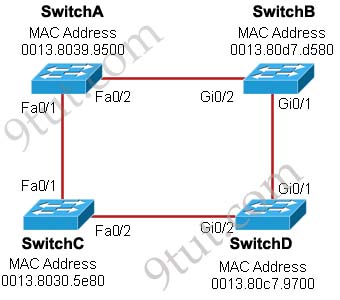
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again
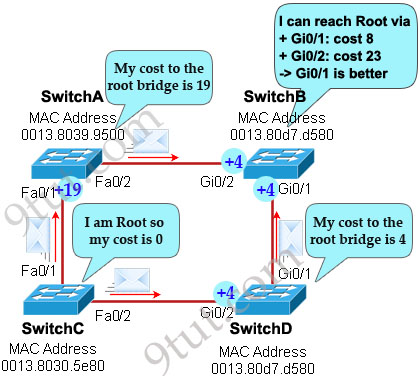
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
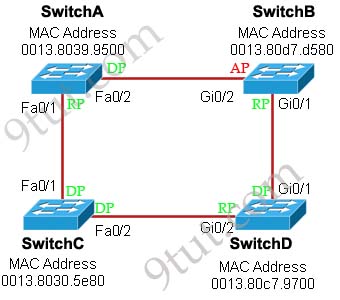
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 8
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 9
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
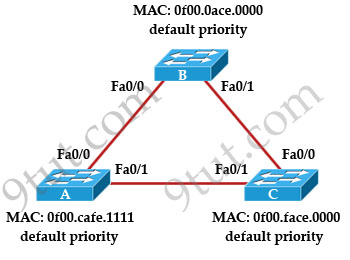
A. Switch A – Fa0/0
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.
On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.



Amazing explanation 9tut well done
@Misha
for reference plz visit the following link and read Table 9.8 Spanning tree tie breaker criteria.
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=426642&seqNum=3
Now according to the rule:(consider Q7) i will go step by step.
1: Switch C is the Root Bridge as it has the lowest Mac Address and its both ports will be in Forwarding state.
2:Switch A’s F0/1 is Directly Connected to the Root Bridge having path cost of 19 and is Root Port.
3: Switch D’s Gi0/2(cost 4) is Directly connected to Root brigd’s Fo/2(cost 19) and is the root Port but have path cost of 19 not 4.
4: SWITCH B is Connected to SWITCH A’s F0/2 port via its Gi0/2 port and again the cost will be 19 and its second Gi0/1 port is connected to SWITCH D’s Gi0/1 port having path cost of 4.
Now SWITCH B CAN REACH Root Bridge via both switches but it will choose for the lowest cost ie is via SWITCH D (TOTAL COST 4(SWITCH B TO SWITCH D) + (SWITCH D TO SWITCH C)19= 23)
5::: Here comes the Critical and confusing part according to the 9tut (SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port ) IS WRONG:
HERE IS THE RIGHT ANSWER
Its True that SWITCH A is lower than SWITCH B but according to the rule number 2 SWITCH B has a root path cost of 4+4=8 and SWITCH A has a root path cost of 19 so the Gi0/2 port of SWITCH B will become Designated port and SWITCH A’s port Fa0/2 will be blocked. This can be checked in packet tracer as well and for a reference please visit the STP video link.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y-SppCHx1Qs
Q2: The answers don’t mention about discarding state because “the name blocking is used for the discarding state in Cisco implementation”: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cfa.shtml
@Muhammad Arshad
Absolutaly agree with you. Nevertheless based on your explanation there are only two answers: B F
But it requires to choose three!
9tut please conclude.
Excellent article! Very accurate.
Newbs, always remember:
1) Every non-root switch has a root port, so, label all those first. (Use bridge ID w/MAC, etc. to find root switch.)
2) Every segment has a designated port, so, label those next. (Use cost and/or bridge ID w/MAC, etc.)
3) After the 2 process above, you are left with an alternate port(s), (or blocking, if STP).
@Muhammad Arshad
in 4: the cost for switch B to reach the root bridge through switch D is 23, I agree
however in 5: you write that this cost is 8 (4+4), while it should be 23 I guess, so FA 0/2 will be the DP in this segment in my opinion
Q9′s Answer I think should be C because between 66 for A and 65 for C, 65 is the lowest value and in the selection process of a root bridge, the lowest mac-add is selected.
sorry didnt check the priority. A is correct.lol
@ElToroLoco::
my explanation and answer was based on facts and rules while you are giving an opinion
Try it in packet tracer and you will then come to conclusion and also please visit the links which i have mentioned in my previous post.
Thanx 9tut for the great site and help i have successfully passed CCNA today with 881/1000 .
next is for CCNP. Best of luck for others who are going to take the exam.
@Muhammad Arshad
4) Now SWITCH B CAN REACH Root Bridge via both switches but it will choose for the lowest cost ie is via SWITCH D (TOTAL COST 4(SWITCH B TO SWITCH D) + (SWITCH D TO SWITCH C)19= 23)
5) but according to the rule number 2 SWITCH B has a root path cost of 4+4=8
So what is exactly the root cost from switch B to switch C? 23 or 8? :)
@eltoroloco::
Lowest Cost is defiantly 8:
Plz Consult the links below for better understanding:
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=426642&seqNum=3
and a video about STP
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y-SppCHx1Qs
@Muhammad Arshad
I understand well enough ;) what I mean, is that in point 4 you write that the cost from SW B through SW C to SW C is 23, whereas in point 5 you write that this cost is 8, so please make up your mind and decide, whether it is 8 or 23?!
and no hard feelings of course :)
@eltoroloco::
a typo mistake but the point is at last which switch is going to block its one port is Switch A’s Fa0/2.
Ref Q7, the question that needs to be answered first before everyone shoots their mouth off about what the cost really is at SwitchD Gi0/2 is: The interface will be running at 100 Mbps even though it’s a Gigabit interface. What’s it’s cost – is it based on what it’s capable of or what it’s running at?
Valid Que :D
Q:7
VALID QUESTION ON CCNA EXAM
Q#8
Hi,
I still don’t get Question 5
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2
that must be true, although it may or may not considered to be an answer.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
How can we know that? maybe other switch has a interface with a higher path than this one and is also blocking it’s port, for a given topology, more than one ports may be in blocking state.
If the answer would be “… than another in the switch” that would be right, but for the given “topology”, other switches may be blocking some ports.
Also, if you see the other vlans, the cost is the same (19 = 100 Mb/s ), so why will we assume that this port has a higher path?
Thanks.
@Muhammad Arshad & @eltoroloco
Just to clear up the confustion about path cost (Q7)
I’ve tested this in my lab between a gig port on a 2950 and 100Mb on a 3550, and the output is as follows:
2950-2#sh spanning-tree interface gigabitEthernet 0/1 cost
VLAN0001 19
VLAN0033 19
VLAN0040 19
So it seems that the cost is based on the negotiated link speed, not the interface rated speed, which makes the most sense.
So the explanation here is incorrect. Both switch b gi0/2 and switch d gi0/2 have a cost of +19.
Very good.
I think the dump by shikhar is enough to take preparation of ccna.
One more thing on question 5
the image must be wrong, because the column Prio.Nbr should be:
128.10
128.10
128.10
and not as it is now.
wait! Q5: A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN2.
what is root network segment? <= I think this is the reason A is wrong!
Q.2 :
I think the answer is: BD
From the Official CCNA Academy Material:
-Discarding:This state is seen in both a stable active topology and during topology synchronization and changes.
-Learning:This state is seen in both a stable active topology and during topology synchronization and changes.
-Forwarding:This state is seen only in stable active topologies.
So There’s no blocking state in RSTP,, and the learning state can be seen in a stable network
On Question 4 on the exam instead of “blocking” I found “discarding”. It’ a valid question I found in today exam
@9tut
Q7, explanation regarding DP selection is incomplete.
Based on Wendell Odom CCNA ICND2 book (Cisco official guide), page 70, “the DP on each LAN segment is the switch port that advertises the lowest cost HELLO on to the LAN segment. In effect, the switch with the lower cost to reach to the root, among all switches connected to a segment, becomes the DP on that segment. If the advertised cost tied, the switches break the tie by choosing the switch with the lower bridge ID.”
Based on this explanation, on the segment between Switch A and Switch B, Switch A advertises 19 to reach root, whereas Switch B advertises 23 to reach root. Therefore Switch A Fa0/2 becomes DP.
When you think about it, that’s got to be the right aneswr.
Question 1,5 on CCNA 2nd try today
thanks 9tut u are a truly helpful i take the exam on 26 march and i passed 894/1000
switching , VTP , STP and wan are the same ,also the sim ques. except for the eigrp the as is 112 and there are new questions in vlan and routing about 4 ques i cann’t recall.
Regarding question #7 I would have to agree with Paul above. SwitchA Fa0/2 will advertise onto the segment a cost to the root switch of 19 and SwitchB gi0/2 will advertise a cost of 23. That will make fa0/2 the DP and gi0/2 blocking.
Reason being is that although the default cost of a gig link is indeed 4, the operating cost of SwitchB gi0/2 in real life will actually be 19 because the links on the segment will autonegotiate to fastethernet 100 megabit speed since one side is a gig link and the other side is only a fastethernet.
I verified this by setting up the scenario in Packet Tracer and indeed SwitchB gi0/2 autonegiated down to 100 megabit. Hope this clarifies things further to you all =)
Hello everybody… Let´s check the question 7
On the first part of the explanation said:
“The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.”
On the final of the sentence said the letter E is correct. so this really correct?
Because on SW C F0/2 port is a DP (designated port) I´m right???
Have good wind´s from Brazil =)
Thiago E is definitely incorrect. All ports on the root bridge become DP’s, not root ports.
please send me latest ccna questions semo2003@hotmail.com
passed icnd 2 today and got Q7 in the exam
Q7 WAS ON EXAM TODAY
Q2 answers are learning and forwarding states on prepking dump.it is written on description part that blocking state is not valid state for RSTP.but here answers are blocking and forwarding..what answers should i choose if i meet this question on real exam?
Q.7 so confused -_- if port Gi & Fa is auto negotiate why not expand the answer “SwitchA has
cost to root lower than SwitchB” but they say “MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of
SwitchB” that it means cost to root between SwitchA & SwitchB are equal ????
(Sorry my English is not strong)
Question #2, one of answers is definitely D, the other answer is Discarding which is not listed(question flagged?), RSTP has Discarding, Learning, and Forwarding port roles, so when is converged you will see ports in forwarding and discarding, you will not see learning else is not converged yet.
q1,q4 n q8 in today exam
q10 in exam last week
Q2 i know RSTP have 3port roles which are discarding, forwarding, learning and of which in cisco network Academy exploration 3 three port state of STP which are blocking listening and disabled make up one port state in rstp which is the discarding state i think the answer should be A$D even C pls i`m still confuse !
i really enjoy the explaination thanks to 9tut.com
Q6.
PVST+ option do not supports RSTP for that,
RSTP cannot operate with PVST+ is correct too
Answer: A B E
Q7
@gobregon: exactly! when a GIG and a FastEthernet port are connected the maximum transmission speed is 100Mbps… because the GIG link negotiates the speed and also “becomes” a FaE port the link cost is 19 NOT 4 !!!
nevertheless, the solution is rigtht, just the explanatation is a little bit bugged ;)
Pliz i will sit for the CCNA exam next month, can someone send me the latest dumps on email: olesimbe@yahoo.com
QUestion 7 is valid, it was in my exam last week!! I got 986/1000
Q5 explanation:
the questions asks, “the most likely reason not to be the root port”
A -> there is another port
(just the presence of another port in the same vlan doesn’t make this port ALT BLK)
C -> the cost is higher (this does)
hope this helped somebody
Referring Q7: Since, by your diagram, the switch A has a cost of 12 to the root bridge via fa0/2. So, shouldn’t it be the root port of Switch A instead of fa0/1 which has a cost of 19 to the root bridge?
I think the Gigabit interface should negotiate with the bandwidth of fast ethernet. How can a fast ethernet interface have a speed of 1Gbps?
famous explanation
Q7 – If port Gi connect to Port Fa, transmit cost of this port`s is same. (19) Cause, this ports are both operate on FastEthernet speed.
Sorry for my bad english. Just from Russia.
q2 q7 in exam today
@9tut
Q2: there is no blocking , but discarding is available
What will be in the following situation ?
<— cost to root is 8
SWITCH A Fa0/1 Gi0/1 SWITCH B
MAC ADDRESS ——————— MAC ADDRESS
0013.8039.9500 0013.80d7.d580 |
| | | cost to root is 8
| Gi0/1 | Gi0/2 | but port is lower
| | V than Gi/1
| |
| |
| |
| Fa0/1 | Gi0/1
| |
SWITCH C Gi0/2 Gi0/2 SWITCH D
MAC ADDRESS ———————- Mac Address
0013.8030.5e80 0013.80c7.9700
Root bridge
Will the low speed path preferred against Gi path ?