CCNA – STP Questions
Here you will find answers to Spanning Tree Protocol Questions
Note: If you are not sure how STP and RSTP work, please read my STP tutorial and RSTP tutorial.
Question 1
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expends the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
E. RSTP use the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
F. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
Answer: A B F
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. blocking
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding but the answers don’t mention about discarding state so blocking state (answer A) may be considered the best alternative answer.
Question 3
Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A
Question 4
At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
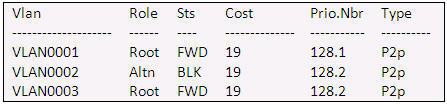
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C
Question 6
Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
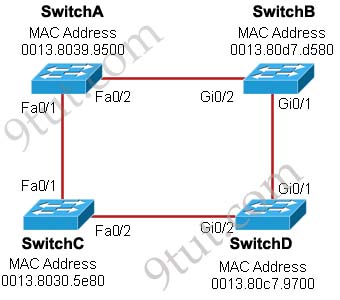
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again
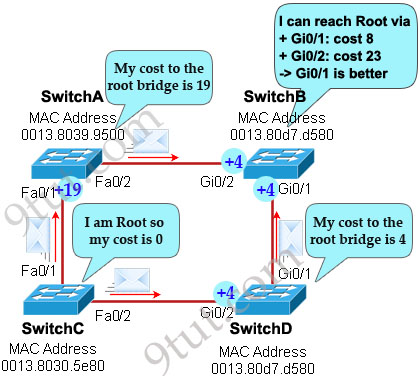
SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and advertises this value (4) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds another 4 and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 8. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 23 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
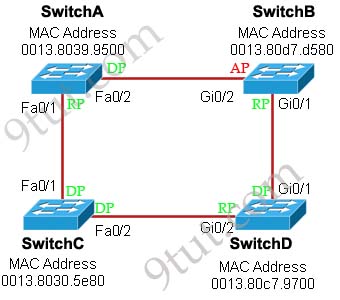
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 8
Which two protocols are used by bridges and/or switches to prevent loops in a layer 2 network? (Choose two)
A. 802.1d
B. VTP
C. 802.1q
D. STP
E. SAP
Answer: A D
Question 9
Which switch would STP choose to become the root bridge in the selection process?
A. 32768: 11-22-33-44-55-66
B. 32768: 22-33-44-55-66-77
C. 32769: 11-22-33-44-55-65
D. 32769: 22-33-44-55-66-78
Answer: A
Question 10
Refer to the topology shown in the exhibit. Which ports will be STP designated ports if all the links are operating at the same bandwidth? (Choose three)
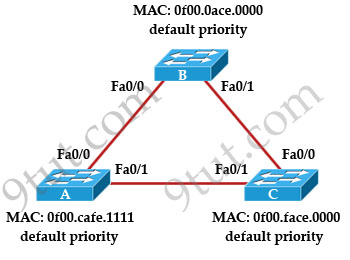
A. Switch A – Fa0/0
B. Switch A – Fa0/1
C. Switch B – Fa0/0
D. Switch B – Fa0/1
E. Switch C – Fa0/0
F. Switch C – Fa0/1
Answer: B C D
Explanation
First by comparing their MAC addresses we learn that switch B will be root bridge as it has lowest MAC. Therefore all of its ports are designated ports -> C & D are correct.
On the link between switch A & switch C there must have one designated port and one non-designated (blocked) port. We can figure out which port is designated port by comparing their MAC address again. A has lower MAC so Fa0/1 of switch A will be designated port while Fa0/1 of switch C will be blocked -> B is correct.



Yes, can someone pls explain answer to Q5.
Thanks.
@mina
if the cost was lower then that of the neighboring switch for that segment it would’ve been “Root/FWD” as seen for vlans 1 and 3
Q10.
What kind of ports would Fa0/0 on switch B and A be considered? I thought designated = forwarding port or am I wrong?
Anon, FA0/0 on A and B would be Root Ports.
@anon
switch B is the root bridge since it has the lowest MAC….
So, fa0/0 on switchB will be a designated port since a root switch has all its ports as designated
& fa0/0 on SwitchA will be a root port since it is directly connected to the root switch OR in other words fa0/0 on switch A has the lowest cost to reach the root bridge than fa0/1 of switch A………….
i hope i cleared your doubt…….
Question 2: Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? Per Cisco site: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cfa.shtml#states, both disabled and blocking in STP are discarding on RSTP. Some websites have answers as Disabled and Forwarding. Don’t Disabled and Blocking have the same function?
q5 — can someone explain this?– this is show spanning tree for an interface not a vlan
so — we are looking at output for more than 1 vlan
q5 — we have always looked at show spanning tree vlan 1– never used interface — did not know that it could be done –
q6 — defines new port roles and compatible with older version — I dont understand how defining new port roles make it backward compatible — I know that this has been said on cisco site– but I dont understand how they made it work — I have just accepted it
q7– have to find root bridge first before anything can be done — then find which ports are blocked
q7 — I guess that I am used to questions with 3 switches — just need to get into my head that you need a blocked port between A and B — and only 1 blocked port — I would tend to have both blocked — just seems simpler that way — but I am wrong — need to have question with 5 switches — need more practice
q10—- I am confused about root port vs designated port — why wouldnt the port on A be a root port ???– never understood the difference
q10– root ports send towards root bridge and designated ports send away from root bridge — ok — so A has 1 root port and 1 designated port — so the only problem to solve is which is the designated port between A and C and which one is blocked — hmmmm– need more practice with this subject
Q7:
Agree With Koopotang.
iF There r Two Ports
1st: Gigabyte
2nd: Fastethernet
The Negotiation Will Choose The Speed oF The Lower Port Which iS Fasthernet = 100 Mb
Means The Cost oF The 100 Mb = 19
Hope i Made iT Clear…
But That Didnt Mess Up The Solve :D
Thank you Very Much 9tut For Ur Help ^^
Q5:
i Didnt Understand The Explanation Here Exactly Untill i Read That >>>
Per Vlan Spanning Tree (PVST) Maintains a Spanning Tree Instance For Each VLAN Configured iN The Network. It Means a Switch Can Be The Root Bridge oF a VLAN While Another Switch Can Be The Root Bridge oF Other VLANs iN a Common Topology. For Example: Switch 1 Can Be The Root Bridge For Voice Data While Switch 2 Can Be The Root Bridge For Video Data. iF Designed Correctly, iT Can Optimize The Network Traffic.
Now Go Read The Explanation oF Q5. :)
Hope i Was Useful
Q5:
The Other Explanation
“The Port With The Higher Cost iS iN The Blocking State, While The Port With The Lower Cost iS iN The Forwarding State.”
PVST: Per Vlan Spanning Tree …
Read The Name And Now We All Understand..
Thanks 9tut & Everyone Helped!
I THINK QUESTION 7 IS INCORRECT…. ANYONE CARE TO EXPLAIN WHY SWITCH_A PORT FA 0/1 IS A ROOT PORT WHEN IT HAS A PATH COST OF 19 WHILE FA 0/2 AS A CUMULATIVE COST OF 4+4+4 TOTALLING 12…… OR IS IT THAT THE CONFUSION LIES IN THE FACT THAT THE LINK CONNECTION IS FROM A FAST ETHERNET TO A GIGABIT PORT? iF SWITCH_A SEE FA 0/2 AS COST OF 19 THEN THE YOUR ANSWER IS CORRECT.
in question 1′s 1st option it should be like RSTP significantly reduces topology converging time after a link failure. instead of reconverging time
I’d come to see eye to eye with you one this subject. Which is not stimoheng I usually do! I love reading a post that will make people think. Also, thanks for allowing me to comment!
Q2 RSTP doesn’t block, it “discards”
@ Mark Question 7
The Way The Calculate iSn’t Right…
To Make iT Clear ..
iF Two Ports Connected Together For Example ( 1Gi / 1FastE )
The Speed oF The LINK Will Be The Speed oF The Lower PORT
Which iS Fast Ethernet = 100 Mb
So The Cost iS 19
Hope i Made iT Clear.
@ Ali
Yeah i understand it now… Thanks for Clarifying
DID IT!!…854…thx God, thk 9tut!!!!..CCNA certified…good luck to all…can’t stress enough…read EVERY question on this site…
Secret not go nervous.
Congrats Marcelo ..
My exam is on 20th ,
can you pls let me know what simulations are being asked.
Also what are the questions from switching .
My maild ID is mrparab@rediffmail.com
Regarding Q2, it should be listening & forwarding, blocking is NOT a RSTP state…discarding is. Once again…what will CISCO feel is correct?
@Ella Q2
i Agree With u iF u Said “Learning & Forwarding”
The RSTP States r Discarding – Learning – Forwarding
@9tut
Question 2
Can u Plz Confirm The Answer Again With Exaplanation?
Sorry
I just pass CCNA today with 960/1000. FYI, Q2 the option “blocking” has changed to “discarding”. So the correct answers are “discarding” and “forwarding” .
And Sims are the same, ACL, EIGRP and VTP.
Good luck to all!
J&E were the Sims and question covered in 9Tut???
@Archit
All questions are covered in 9Tut, but some place changed, like IP address and host. Don’t worry, if you understand the Sims you will get it.
Thanks to 9Tut’s material and Questions!
Hi xallax,
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
I understand but why cant option A be correct ? Say I have attached two connections between switches to the ports in the same vlan???
Pls explain I am really confused.
@5
it is asking what is the reason why that particular port is not the root port.
A is true but is not what the question is asking
yes, this switch has more than 1 interface that could get to the root bridge but the most likely cause for fa0/10 to be in an alternating state is the fact that it has a higher path cost.
C is correct
Hi Xallax,
Thanks
Spanning Tree 4 life DAWG
Dear 9tut team!
First of all, thank you very much for the great site!
It really does help.
Second, I’d like to pay your attention to Q7 in STP Questions.
I think there are a few mistakes in explanation, while the answer is correct:
- cost of link will be the max cost of two interfaces, e.g. cost between Gi and Fa will be 19 not 4;
- port roles between SwitchA & SwitchB identified by cost to root switch but not the Bridge ID
These issues were checked with PacketTracer (I built the exact topology, except, MAC addresses; I used priorities instead) and I actually received:
- “show spanning-tree” shows max cost of several different interfaces
- port roles assignment is NOT affected by switch priority (in this particular case), but affected by link costs: I changed Fa0/2 to Gi on SwitchC and blocked port moved from of SwB and SwA
Please, check my findings.
Thanks a lot!
P.S. I think Ali raised this topic already.
Corrected:
“I changed the type of interface from Fa0/2 to Gi on SwitchC and blocked port moved from SwB to SwA. I.e. port Fa0/2 on SwitchA became AP”
Q7 is very misleading. Your explanation are unclear and not correct. This could be hard for someone trying to learn from this site.
Here is the correct answers.
Please remember that lowest BID wins the election for the root switch (32768+MAC)(default)
Your cost on the links are incorrect the ONLY link that is +4 is between SwitchB and SwitchD
Corrected costs are
Switch A = 19
Switch B GI0/2 = 38
Switch B GI0/1 = 23
Switch C = 0 (Its the root)
Switch D = GI0/1 = 19
Switch D = GI0/2 = 4
As you can see the answer are still correct BUT for the wrong reason.
“. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.”
This Statement is incorrect, the reason why SwitchA is the DP is because it has a lower cost to reach the Root switch NOT because it’s MAC is lower.
COST IS FIRST! If tie THEN BID.
Please correct this answer as it’s very confusing.
@Glenn: The cost does not determine who is the Root Bridge. You can read here for more information about STP:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_configuration_example09186a008009467c.shtml
This is a paragraph quoted from the link above:
“Before you configure STP, select a switch to be the root of the spanning tree. This switch does not need to be the most powerful switch, but choose the most centralized switch on the network. All data flow across the network is from the perspective of this switch. Also, choose the least disturbed switch in the network. The backbone switches often serve as the spanning tree root because these switches typically do not connect to end stations. Also, moves and changes within the network are less likely to affect these switches.
After you decide on the root switch, set the appropriate variables to designate the switch as the root switch. The only variable that you must set is the bridge priority. If the switch has a bridge priority that is lower than all the other switches, the other switches automatically select the switch as the root switch. “
@9tut
Correct. As quoted from my post “Please remember that lowest BID wins the election for the root switch (32768+MAC)(default)”
This wasn’t my issue with your explanation. It was how you added up the cost. Which was incorrect, also Cost IS the fact on all non-root switches .
TY 9tut.
Today I have passed the CCNA. (860/825)
50 questions 3 labs (VTP, EIGRP, ACL). 35 from 9tut.
Also thanks a lot Brar and Sekhar (still valid from examcollection)
Ty again 9tut
from here Q 3
Dear 9tut and all
I was confusing of these two commands between the “spanning tree@ global config” and “spanning tree @ interface config.I don’t know what command to be use for spanning tree in several vlan
Can anyone help me ;)
@9tut
Question 2
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged?
As we can see here : http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cfa.shtml#states
For RSTP , we can have 3 states : Discarding, Learning, Forwarding.
So, the good answer is : B D .
@DERK: The “spanning tree” in global config is used to enable STP for all ports in all VLANs while the “spanning tree” in interface/vlan config is used to enable STP on an individual Port/vlan.
Note: By default, spanning tree runs on all ports of a Cisco switch.
@Kahlan: The question asks “when RSTP has converged” but Learning is not a state when RSTP has converged.
9tut !
Of course ! thank you !
Q10 how to calculate lowest mac-add?
Had Q5 Today!!!
HI
Can somebody explain question 10?
Thanks
Q10 explained…
The first task is to determine the root. We start with the priority, which in this case are equal on all switches. Next we examine the MAC addresses. Remember a MAC address consists of a 48 bit address written in two byte blocks separated by a decimal point (.). So looking at the MAC addresses you’ll notice the first two bytes (0f00) are the same. The third byte is different and by defination the lowest MAC address (0a < ca < fa) becomes the ROOT. Hence Switch B becomes the ROOT Bridge. As a result both of Switch B's ports are Designated Ports and are in the forwarding state. Since Switch B's F0/0 port connects to Switch A's F0/0 port, Switch A's F0/0 becomes a ROOT port and is placed into a forwarding state. Switch B's F0/1 port connects to Switch C's F0/0 port so Switch C's F0/0 port becomes a ROOT port and enters into a forwarding state.
Next we need to determine which port, ether Switch A's F0/1 or Switch C's F0/1, will become the designated port. Since all links between the switches are the same bandwidth and default priority, we begin by examining the MAC addresses of Switch A and Switch C. The lowest MAC address wins. In this case Switch A is lower, so Switch A's F0/1 port becomes the designated port and Switch C's F0/1 becomes a blocking port.
Hope this helps.
Qno 7:
what if we swape Switch A with Switch B then which port will be blocked. ?
in packet tracer it will block switch B’s GI0/2 and if these switches will be swaped then switch A’s Gi0/1 will become A/P. while switch A’s Bridge ID is lower then Switch B.
Q7:
in my opinion following last step will not occure BECAUSE I HAVE TESTED THAT IN PACKET TRACER AND AS SOON AS IT DECIDES WHICHT PORT IS THE ROOP PORT THE SWITCH BLOCKS ITS PORT CONNECTING TO SWITCH A REGARDLESS OF ITS MAC ADDRESS.
(“Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.)
@Muhammad Arshad
As reported in CCNA ICND 2 Official Guide, in STP Troubleshooting (page 103):
“step1: for switches connected to the same LAN segment, the switch with the lowest cost to reach the root is the DP on that segment.
step2: in case of tie, among the switches that tied on cost, the switch with the lowest BID becomes the DP”
In this scenario, the bid is not important and will not be considered,because the root path cost of switch A is lower than the root path cost of switch B