OSPF Tutorial
In this article we will learn about the OSPF Routing Protocol
Open-Shortest-Path-First (OSPF) is the most widely used interior gateway protocol routing protocol on the world because it is a public (non-proprietary) routing protocol while its biggest rival, EIGRP, is a Cisco proprietary protocol so other vendors can’t use it (edit: EIGRP has become a public routing protocol since 2013). OSPF is a complex link-state routing protocol. Link-state routing protocols generate routing updates only when a change occurs in the network topology. When a link changes state, the device that detected the change creates a link-state advertisement (LSA) concerning that link and sends to all neighboring devices using a special multicast address. Each routing device takes a copy of the LSA, updates its link-state database (LSDB), and forwards the LSA to all neighboring devices.
Note:
+ OSPF routers use LSA (Link State Advertisement)to describe its link state. LSDB stores all LSAs.
+ A router uses Router LSA to describe its interface IP addresses.
+ After OSPF is started on a router, it creates LSDB that contains one entry: this router’s Router LSA.
There are five types of OSPF Link-State Packets (LSPs).
+ Hello: are used to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers. They are also used to elect the Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designated Router (BDR) on multiaccess networks (like Ethernet or Frame Relay).
+ Database Description (DBD or DD): contains an abbreviated list of the sending router’s link-state database and is used by receiving routers to check against the local link-state database
+ Link-State Request (LSR): used by receiving routers to request more information about any entry in the DBD
+ Link-State Update (LSU): used to reply to LSRs as well as to announce new information. LSUs contain seven different types of Link-State Advertisements (LSAs)
+ Link-State Acknowledgement (LSAck): sent to confirm receipt of an LSU message
Key points
+ Is a public (non-proprietary) routing protocol.
+ Is the only link-state routing protocol you learn in CCNA
+ This works by using the Dijkstra algorithm
+ Information about its neighbors (local connectivity) is sent to the entire network using multicasting
+ Routing information is shared through Link-state updates (LSAs)
+ HELLO messages are used to maintain adjacent neighbors. By default, OSPF routers send Hello packets every 10 seconds on multiaccess and point-to-point segments and every 30 seconds on non-broadcast multiaccess (NBMA) segments (like Frame Relay, X.25, ATM).
+ Is a classless routing protocol because it does not assume the default subnet masks are used. It sends the subnet mask in the routing update.
+ Supports VLSM and route summarization
+ Uses COST as a metric which CISCO defines as the inverse of the bandwidth
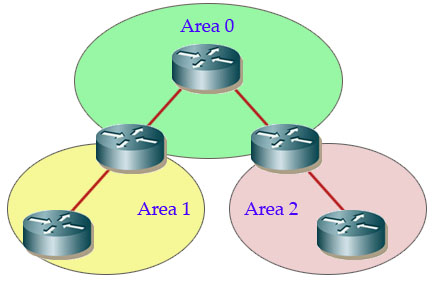
+ Uses AREAs to subdivide large networks, providing a hierarchical structure and limit the multicast LSAs within routers of the same area — Area 0 is called backbone area and all other areas connect directly to it. All OSPF networks must have a backbone area
+ Only support IP but it’s not bad as we are all using IP, right? :)
Area Border Routers (ABR) are any routers that have one interface in one area and another interface in another area
Let’s see an example of OSPF
Suppose OSPF has just been enabled on R1 & R2. Both R1 and R2 are very eager to discover if they have any neighbors nearby but before sending Hello messages they must first choose an OSPF router identifier (router-id) to tell their neighbors who they are. The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router and is chosen using the following sequence:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
+ The router ID can be manually assigned
In this example, suppose R1 has 2 loopback interfaces & 2 physical interfaces:
+ Loopback 0: 10.0.0.1
+ Loopback 1: 12.0.0.1
+ Fa0/0: 192.168.1.1
+ Fa0/1: 200.200.200.1
As said above, the loopback interfaces are preferred to physical interfaces (because they are never down) so the highest IP address of the loopback interfaces is chosen as the router-id -> Loopback 1 IP address is chosen as the router-id.

Suppose R1 doesn’t have any loopback interfaces but it has 2 physical interfaces:
+ Fa0/0: 210.0.0.1 but it is shut down
+ Fa0/1: 192.168.1.2 (is active)
Although Fa0/0 has higher IP address but it is shutdown so R1 will choose Fa0/1 as its router-id.

Now both the routers have the router-id so they will send Hello packets on all OSPF-enabled interfaces to determine if there are any neighbors on those links. The information in the OSPF Hello includes the OSPF Router ID of the router sending the Hello packet.



9tut is a great website…
One useful comment that may or may not have been mentioned in the tutorial. If the router ID is set manually as follows:
router ospf 1
router-id 1.1.1.1
It will take precedence over loopback and local interfaces as the router’s ID, even if it has a lower IP than both of those interfaces.
The easiest way to remember how the OSPF router ID is set is as follows.
1) Uses manually set router-id (if specified)
2) Uses highest loopback interface
3) Uses highest local interface
Could you explain and go into DR/BDR elections for OSPF? I had to use another website to get an explaination for that, and this site would be a one-stop shoping place for learning everything if it was included.
Great information and presentation otherwise! thank you!
Administrative distance of 110…
Thanks for tutorials
This site ROCKS! Thanks for the great information. Very well presented, easy to understand.
Thanks….this site has enlightened me on OSPF…..
9tut is perfect website to learn
Very helpful article. Many thanks to 9tut.com
Does anyone know any engines to run .vce files in that dont require the registration/payment?
very nicely explained :-)
A milioln thanks for posting this information.
thank you 9tut
Boys,Need VCE engine ASAP, email me at vceengineatyahoodotcom. Thanks 9tut!
Great 9TUT…I couldnt read the name of the author anywhere?
But this stuff rocks!!!
@sumit menaria: All the tutorials on this site are written by me so don’t need to put the author name here :)
That’s awesome!!! Great website. Thanks to help us!!!! =c)
Thank You,
You make this lesson more vivid and clear than my instructor.
He is a very good instructor, but the lessons are not that informative or student-friendly:)
This site helpd me a lot in understanding OSPF!
everybody agree that this is the best place to learn but take the time to leave $omething for the people behind it ….
how to measure bandwidth in OSPF
@ 9tut thanx very much
and who are you ? :)
Wonderful site!! It is the best for CCNA certification!!!
Great ….! :D
Very goog explaination!! I´ve got OSPF clearly ;) Can you say something else about DR and BDR role?
help ?? Need explanation for default system originate
There was a question on CCNA that involved it.
Dear friends
I am new in 9tut. I am preparing for CCNA vendor exam. I need the latest dumps questions.
Please help me.
shadat_cs@yahoo.com
Hello 9tut! Great website!
could you please send me the latest dumps of questions to epema.aktobe@gmail.com
Thank you!!
Don’t put your e-mail address in a public forum. Google the latest dumps yourself. Jesus Christ.
please clarify ob your key ospf points below. This almost sounds like periodic updates rather than triggered update. I thought OSPF did not do this?
“The entire routing table is transmitted once every 30 minutes”
@Anonymous: OSPF sends triggered update but it also sends period updates (but only once every 30 minutes).
Thanks for this site
Great work!!!!! and 5***** stars to all those constantly providing insights, valuable resources and clarifications. thankfull n greatfull to all …Mohammed
Thanks 9tut.com
thnx 9tut..this website is great..I wonder if you have video posted..thnx
i am rafi best of luck sallu dont forget me
Dear All.!
How do you identified the Hello interval, Dead interval in question 5 of ccna-ospf-question-2?
Hi, I realized an excel file with a comparison of RIP, RIPv2, IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF. Link to download:
http://matteocappelli.files.wordpress.com/2011/10/compare_rip_igrp_eigrp_ospf_v1-1.xls
Bye!
Hi 9tut. I really admire you or you guys. your work, your patient and knowledge. is 9tut an organization. I love 9tut
Hi 9Tut…
Thanks for your efforts!!
Hi Matteo..
Thanks for the Excel File!..I downloaded it :)
Thanks,
J
Very Helpful dear
OSPF every thing in brief.it’s very helpful revision.Thanks 9tut…
Nice tutorial…………….
Thanx for provide such great information
“The entire routing table is transmitted once every 30 minutes” ?? I thought ospf sends triggered updates on chane, not periodic
ospf sends the UPDATED on change (triggery)
ospf sends the HELLO’s every 10 sec (periodically)
@Odysiuos: Although OSPF is a link-state protocol but it also transmits the whole routing table every 30 minutes (not seconds).
can somebody tell me about Dijkstra algorithm and the Designated Routers(DR) and BDR. I coudnt understand about them
Hey guys ,, this is my understanding hope it helps any of you …!!!!
DR and BDR election is accomplished via HELLO protocol
DR-BDR is selected in the following sequence on the OSPF AREA routers
DR is selected :
1) The router with highest priority is chosen DR.
#IP OSPF priority —- ( by defualt 1, max could be 255 .. also if set to 0 this router won’t
participate in DR0 BDR election )
If the priority of all routers match.
than >>>>>>
2)The router with highest Logical IP address ( loopback ) is chosen as DR
If not assigned
than >>>>>>
3)the Router with highest physical IP address on an interface is selected as DR.
====
*The second ranking Router in the above election b/n OSPF routers is chosen as BDR.
*DR – BDR selection only happnes in B’cast and NBMA networks not in P2P lnks(serial links)
nice one !But what about ABR”s and area concepts?
thnx 9tut..this website is great, thank you 9tut