CCNA – WAN 2
Here you will find answers to WAN Questions – Part 2
If you are not sure about Frame Relay, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
Question 1
Users have been complaining that their Frame Relay connection to the corporate site is very slow. The network administrator suspects that the link is overloaded. Based on the partial output of the Router#show frame relay pvc command shown in the graphic, which output value indicates to the local router that traffic sent to the corporate site is experiencing congestion?

A. DLCI=100
B. last time PVC status changed 00:25:40
C. in BECN packets 192
D. in FECN packets 147
E. in DF packets 0
Answer: C
Explanation
First we should grasp the concept of BECN & FECN through an example:
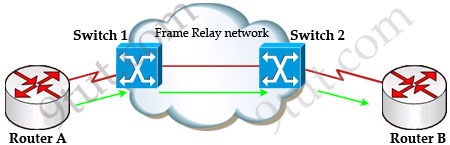
Suppose Router A wants to send data to Router B through a Frame Relay network. If the network is congested, Switch 1 (a DCE device) will set the FECN bit value of that frame to 1, indicating that frame experienced congestion in the path from source to destination. This frame is forwarded to Switch 2 and to Router B (with the FECN bit = 1).
Switch 1 knows that the network is congesting so it also sends frames back to Router A with BECN bit set to 1 to inform that path through the network is congested.
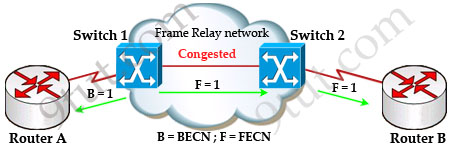
In general, BECN is used on frames traveling away from the congested area to warn source devices that congestion has occurred on that path while FECN is used to alert receiving devices if the frame experiences congestion.
BECN also informs the transmitting devices to slow down the traffic a bit until the network returns to normal state.
The question asks “which output value indicates to the local router that traffic sent to the corporate site is experiencing congestion” which means it asks about the returned parameter which indicates congestion -> BECN.
Question 2
When troubleshooting a Frame Relay connection, what is the first step when performing a loopback test?
A. Set the encapsulation of the interface to HDLC.
B. Place the CSU/DSU in local-loop mode.
C. Enable local-loop mode on the DCE Frame Relay router.
D. Verify that the encapsulation is set to Frame Relay.
Answer: A
Explanation
The first thing when performing a loopback test on a Frame Relay connection is to reconfigure the encapsulation of the interface to HDLC protocol instead of Frame Relay protocol. The main reason is Frame Relay requires a pair of DCE/DTE which cannot be used in a loopback test.
For more information about steps of trouble shooting Frame Relay, please read: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk713/tk237/technologies_tech_note09186a008014f8a7.shtml#topic20
For your information, below is a paragraph quoted from the above link:
“Serial0 is down, line protocol is down”
This output means you have a problem with the cable, channel service unit/data service unit (CSU/DSU), or the serial line. You need to troubleshoot the problem with a loopback test. To do a loopback test, follow the steps below:
1. Set the serial line encapsulation to HDLC and keepalive to 10 seconds. To do so, issue the commands encapsulation hdlc and keepalive 10 under the serial interface.
2. Place the CSU/DSU or modem in local loop mode. If the line protocol comes up when the CSU, DSU or modem is in local loopback mode (indicated by a “line protocol is up (looped)” message), it suggests that the problem is occurring beyond the local CSU/DSU. If the status line does not change states, there is possibly a problem in the router, connecting cable, CSU/DSU or modem. In most cases, the problem is with the CSU/DSU or modem.
3. Ping your own IP address with the CSU/DSU or modem looped. There should not be any misses. An extended ping of 0×0000 is helpful in resolving line problems since a T1 or E1 derives clock from data and requires a transition every 8 bits. B8ZS ensures that. A heavy zero data pattern helps to determine if the transitions are appropriately forced on the trunk. A heavy ones pattern is used to appropriately simulate a high zero load in case there is a pair of data inverters in the path. The alternating pattern (0×5555) represents a “typical” data pattern. If your pings fail or if you get cyclic redundancy check (CRC) errors, a bit error rate tester (BERT) with an appropriate analyzer from the telco is needed.
4. When you are finished testing, make sure you return the encapsulation to Frame Relay.
Question 3
What occurs on a Frame Relay network when the CIR is exceeded?
A. All TCP traffic is marked discard eligible.
B. All UDP traffic is marked discard eligible and a BECN is sent.
C. All TCP traffic is marked discard eligible and a BECN is sent.
D. All traffic exceeding the CIR is marked discard eligible.
Answer: D
Explanation
Committed information rate (CIR): The minimum guaranteed data transfer rate agreed to by the Frame Relay switch. Frames that are sent in excess of the CIR are marked as discard eligible (DE) which means they can be dropped if the congestion occurs within the Frame Relay network.
Note: In the Frame Relay frame format, there is a bit called Discard eligible (DE) bit that is used to identify frames that are first to be dropped when the CIR is exceeded.
Question 4
What are two characteristics of Frame Relay point-to-point subinterfaces? (Choose two)
A. They create split-horizon issues.
B. They require a unique subnet within a routing domain.
C. They emulate leased lines.
D. They are ideal for full-mesh topologies.
E. They require the use of NBMA options when using OSPF.
Answer: B C
Question 5
The output of the show frame-relay pvc command shows ”PVC STATUS=INACTIVE”. What does this mean?
A. The PVC is configured correctly and is operating normally,but no data packets have been detected for more than five minutes.
B. The PVC is configured correctly, is operating normally and is no longer actively seeking the address the remote route,
C. The PVC is configured correctly, is operating normally and is waiting for interesting to trigger a call to the remote router.
D. The PVC is configured correctly on the local switch, but there is a problem on the remote end of the PVC.
E. The PVC is not configured on the switch.
Answer: D
Explanation
The PVC STATUS displays the status of the PVC. The DCE device creates and sends the report to the DTE devices. There are 4 statuses:
+ ACTIVE: the PVC is operational and can transmit data
+ INACTIVE: the connection from the local router to the switch is working, but the connection to the remote router is not available
+ DELETED: the PVC is not present and no LMI information is being received from the Frame Relay switch
+ STATIC: the Local Management Interface (LMI) mechanism on the interface is disabled (by using the “no keepalive” command). This status is rarely seen so it is ignored in some books.
Question 6
Which encapsulation type is a Frame Relay encapsulation type that is supported by Cisco routers?
A. Q933-A Annex A
B. IETF
C. ANSI Annex D
D. HDLC
Answer: B
Explanation
Cisco supports two Frame Relay encapsulation types: the Cisco encapsulation and the IETF Frame Relay encapsulation, which is in conformance with RFC 1490 and RFC 2427. The former is often used to connect two Cisco routers while the latter is used to connect a Cisco router to a non-Cisco router. You can test with your Cisco router when typing the command Router(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay ? on a WAN link. Below is the output of this command (notice Cisco is the default encapsulation so it is not listed here, just press Enter to use it).
![]()
Note: Three LMI options are supported by Cisco routers are ansi, Cisco, and Q933a. They represent the ANSI Annex D, Cisco, and ITU Q933-A (Annex A) LMI types, respectively.
HDLC is a WAN protocol same as Frame-Relay and PPP so it is not a Frame Relay encapsulation type.
Question 7
Router A is unable to reach Router B. Both routers are running ios version 12.0. After reviewing the command output and graphic, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
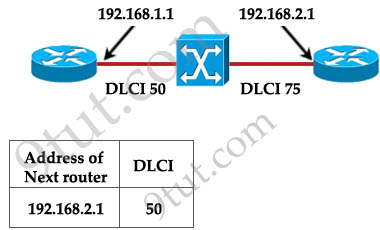
A. incorrect bandwidth configuration
B. incorrect LMI configuration
C. incorrect map statement
D. incorrect IP address
Answer: C
Explanation
With this topology and the DLCI, we can only think of “incorrect map statement”. From the topology we can deduce traffic with a DLCI of 75 will be sent to 192.168.2.1 but the text below wrongly shows “DLCI 50″ for the next router 192.168.2.1 -> C is correct.



@Jeff, my thought exactly ! :) how can they communicate while on different network ? can someone explain ? Also the question is not clear about the origin of the output… :/
q7:what correct answer
ip address
or
map statement
Question 7 the answer is “B. incorrect LMI configuration” because inverse ARP maps a local DLCI to a remote IP address and that mapping is correct in router A.
question no 7 answer d is correct as per me.. since the ip address in different network…
@marcll and @dinesh
u don’t assume anything.the question asked for scenario.they given the ip address and map it means..the map created whilce pvc active only..hence the maping is wrong so the answer ‘c’ is correct…
really i am grateful for you
What is the correct answer for question number 7
Since we have no details about the netmask in use, i do agree with 9tut, and I choose C) Incorrect map statement.
Hi Guys I am preparing for CCNA exam, So how many question will be appear of WAN on the exam? need to lab practice of WAN? pls share your experience
To everyone confused about question 7:
I was also confused about this so I did some research. On a point to point link, the DLCI has global significance. You cannot use the statement ‘frame-relay map ip x.x.x.x dlci’ on a frame-relay point-to-point link. It took me a while to actually figure this out, and even after reading a good bit and following 9tut’s link I still couldn’t not get a definitive answer. It wasn’t until I opened packet tracer and fooled around that I found this out. On a point-to-point frame-relay link you simply set your encapsulation, interface IP, and set the interface-dlci for that interface. Now on a point to multi-point frame-relay link, you DO use the ‘frame-relay map ip x.x.x.x dlci’ which DOES have local dlci significance. This took me a good 2 hours to figure out which is complete crap. This question is very confusing, but I hope I was able to help some out.
@Euphoria
at first u understand the dlci number and ip address..here dlci 50 contains ip 192.168.1.1 and dlci 75 contains ip 192.168.2.1..remeber map generate only pvc active here pvc can’t active at first bcz he route is wrong..
There are a few errors ovlearl:#3 should be The mapping between DLCI 100 and 172.16.3.1 was learned through Inverse ARP. DLCI’s refer to frame relay and do not use DHCP. #19 should be They begin with the FE80::/10 prefix. and They are assigned to a host by a stateless autoconfiguration process. The keyword is local The second answer is missing from #41 and should be Telnet to 172.16.20.0/24 is denied. #50 should be access-list 10 deny 192.168.16.32 0.0.0.15 the .32 subnet with a wildcard mask 0.0.0.15 (255.255.255.240 if it were subnet mask) will cover 192.168.16.32 through 192.168.16.47
It it simple,
the 2 interfaces are not in the same network so this 2 router could not talk to his peer router.
there is o informations about some “ip route” to permit a real connectivity between this 2 router but, the frame relay mapping is correct.
DLCI 50 well describes the link to 192.168.2.1 (from 192.168.1.1)
and DLCI 75 well describes the link to 192.168.1.1 (from 192.168.2.1)
So the good answer is “D”
But where did you see that the netmask is /24 ?
it totally can be /16.
Since we have no precisions about this, ” Incorrect map statement” is still the good answer.
TY 9tut.
Today I have passed the CCNA. (860/825)
50 questions 3 labs (VTP, EIGRP, ACL). 35 from 9tut.
Also thanks a lot Brar and Sekhar (still valid from examcollection)
Ty again 9tut
Normally, for class C address we consider /24, not /16.
It it simple,
the 2 interfaces are not in the same network so this 2 router could not talk to his peer router.
there is o informations about some “ip route” to permit a real connectivity between this 2 router but, the frame relay mapping is correct.
DLCI 50 well describes the link to 192.168.2.1 (from 192.168.1.1)
and DLCI 75 well describes the link to 192.168.1.1 (from 192.168.2.1)
So the good answer is “D”
“q7″ “B is the correct”
“q7″ “D is the correct” lo siento lo najallin se pega. jajaja
Q7-Original anwer C is correct. Because when you config Router B , you map the right ip address to wrong Dlci #. In real work area, when you sign a contract with service provider, they give you DLCI # . You should map your ip address with this DLCI # correctly .If not in the Show frame-relay command , you will message “PVC STATUS=DELETE or INACTIVE.”
esse questão esta totalmente errada. Porque se isso for um ponto-a-ponto, o valor do DLCI teria que ser o memso, e estar na mesma rede, mas não podemos ver nessa questão a maskara de rede, se for um /24 esta muito errado e se for /16, esta errado por causa do DLCI que tem que ser o mesmo num ponto-a-ponto. Se for um multi-ponto o mapeamento esta correto ,pois o mapeamento DLCI mapeia um end remoto para a DLCI local. que nessa questão esta coerente.
Espero que na prova real não caia uma questão confusa como essa!!!
Question 7:
As we know OSI model has been created for one single reason, just to simplify works of network stack. We know that none of this layer interrupt on each others works!
Frame-relay is Layer 2 communication technology, which emulates leased line topology. In a point-to-point connection, both ends device has to be in same subnet. As we can see the ip addresses of those devices are not in same subnet, if we take default classful subnet mask.
for this reason answer could be : D
Question 7 is ambiguous.
q7 i have test this aproach in GNS3 both C & D is not write beacuse it is fram-replay point-to-point this mean it do’t requited same subnet is theory says as i did practical
in fram relay we use frame-replay interface-dlci 50 to use pvc as this is my uploads my test
using each steps
[IMG]http://i46.tinypic.com/dvhea1.jpg[/IMG]
[IMG]http://i46.tinypic.com/24e1g15.jpg[/IMG]
[IMG]http://i46.tinypic.com/20535gn.jpg[/IMG]
[IMG]http://i45.tinypic.com/1zz6uyc.jpg[/IMG]
ok guys same thing in packet tracer not working
if ip is same subnet it is working
or
make a static route then it is working even it is not in same subnet
QUESTION 7: The phrase “command output” in the question may be the key to the solution.
I looked at the two labs (one for multipoint the other for point to point) I created before.
I issued “show frame-relay map” command on both scenarios and observed the following output.
MULTIPOINT, IP’s are on the same subnet.
R1#show frame-relay map
Serial0/0 (up): ip 192.168.5.2 dlci 503(0x1F7,0x7C70), static, broadcast, CISCO, status defined, active
POINT TO POINT, IP’s are on different subnet.
R1#show frame-relay map
Serial0/0.503 (up): point-to-point dlci, dlci 503(0x1F7,0x7C70), broadcast status defined, active
Comparing these two outputs are telling me that if I see a DLCI number and and IP address in the output, then we have multipoint configuration.
Maybe this is why we can say that the ip’s are on the same subnet (even though there is no information in the question regarding what the subnet mask is).
Now, the output in the question is telling me that if you want to get to remote IP 192.168.2.1, use local DLCI 50, so this output show the result of “show frame-relay map” issued on Router A, and it indicates Multipoint configuration.
If router A (192.168.1.1) pings router B (192.168.2.1), router B gets the ICMP echo message, this direction works.
But then, router B needs to send echo-reply back to A. If there is a mapping problem on router B (if they did not map remote ip 192.168.1.1 to local DLCI 75) then Icmp-echo would not be able to get back to router A. Then router A would say he can’t reach router B. (Again, router A would not be able to know if he made it to Router B, unless he gets a reply from router B).
So, there must be a mapping configuration issue on router B. Therefore, I would choose “C. Incorrect map statement” as the answer.
@Cevo, Thats what i call a deep analysis. This guy is right C is the way to go.
@Civo
Question states ‘Router A unable to reach RouterB’. According to ur analysis “If routerA(192.168.1.1) pings routerB (192.168.2.1), routerB gets the ICMP echo message, this direction works”, this means RouterA is able to reach RouterB, just that RouterB is unable to reach RouterA. As we know from the question that RouterA is unable to reach RouterB. So ‘C’ cannot be the answer
I tried few scenarios packet tracer, ill share what i observed,
1) configured both router with the ip add in the question and assigned 16 bit mask. I could ping successfully
2) I changed mask to 24 bit( now both router in different subnet), RouterA cant reach RouterB(I assume this is because RouterA detected the network different)
3)Configured a frame relay map with wrong dlci on RouterB( wrong frame map statement). RouterA can reach RouterB, but RouterB cant reach RouterA)
)Configured a frame relay map with wrong ip and correct dlci on RouterB( wrong frame map statement). RouterA can reach RouterB, but RouterB cant reach RouterA)
4) Configured RouterB with different LMI type, Router A still can reach RouterB but RouterB couldnt reply back, because different lmi type caused line protocol down.
5)Configured RouterA with different LMI type, line protocol went down, now RouterA cant reach RouterB
So its possible that wrong LMI type on Router A or both interfaces are on different subnets
Hi, Can someone please send me latest dumps to my eamil ID? It’s shwetatrivedi.1489@gmail.com.
Thanks in adv!!
Q7:
For me, the answer is D – incorrect IP address.
All interfaces in a network should belong to the same network address in a frame-relay multipoint or point-to-point configurations. Local DLCI should always be mapped to the remote interface IP address (Statically or Dynamically). This is a layer 2 protocol. The mapping is correct as shown in the table above but still connectivity failed due to suspected incorrect ip address. This is a more valid reason why connectivity fails.
Subnet mask is not given in the problem but both are class C addresses which has a default SM of /24.
Hi,
someone plz mail me the latest dumps…@ mittal2sneha@gmail.com
thanxx :)
can anybody tell me which questions belong to lab question give me a reference plz
I agreed with Eydz, the correct answer is D. Because the DLCI is always local and map to the remote IP address. Thus, the map statement is correct!!!
hello can u help i downloaded the sekhar and brar from exam collection but i cannot open to my vce….im preparing for exam this april and can someone send me tne latest dump altura_rex08@hotmail.com….tnx….and is 9tut worth it if the brar and sekhar not work in my vce…..tnx
the answer is incorrect ip…even the 9tut tutorial clearly explained it…wonder why they gave the wrong answer
the answer is C “incorrect IP address”, the map statement is OK because we define the far ip address and the local DLCI.
ex. frame-relay map ip 192.168.2.1 50 broadcast
This is for those who needs latest dumps. This dumps and 9tut, its enough for you to pass exam. just remember me in your prayers. Best of luck…..
http://www.examcollection.com/cisco/Cisco.ActualTests.640-802.v2012-07-15.by.Sekhar.697q.vce.file.html
It’s not even funny how incorrect the given answer to question 7 is.
The correct answer is D.
You can set GNS3 to run exactly like the diagram in the picture complete with frame-relay switch. If you configure it like the question’s example it won’t work. But if you use 192.168.1.11 instead of 192.168.2.1 then it works. It doesn’t matter which one is Router A and Router B, it still won’t work without the IP addresses configured correctly. I know the subnet mask isn’t stated but because this is the case your only option is to go with a classful mask, which is protocol for any question that doesn’t explicitly state the mask, with that said it also forces you to recognize classful boundaries, which is a bonus evaluation for the question.
Hi guys ,i looking for the latest ccna exam dump .would you please help out ?my e mail is titykn@gmail.com
Im still confused on question 7. As long as I know the default for a class C IP address is/24
If they are on different subnet, they can’t communicate.
The map statement is also wrong, but…
DLCI number misconfiguration is an L2 issue, different IP subnet is an L3 issue.
The question states that RA can’t “reach” RB, which kind of tells me that it is a L3 issue.
My other problem with this question is that what if the 0 subnet is not enabled? That means the IP address is a network address, 1 more reason why I think the answer is D, even though SEKAR and most 9tut ppl say C is the correct. Any thoughts?
Q 7 is wrong (in real world, in exam is a wrong answer/question issue, we always assume a 192.168.x.0 as /24 in ccna)
our perspective is Router A (as is the one is being stated as having no access to Router B) IF we assume that Router A is the one to the left!!:
1) assuming a mask /22 (instead of /24)
map is ok:
to go to 192.168.2.1 you need to use DLCI 50
2)if mask is /24 (what we usually assume from that kind of ip) they won’t be able to connect because they are in different subnets.
3) If “output” (that’s a lousy output, no command will give you that “output) for the map is wrong it should be “75″ instead of “50″ then, answer C will be the way to go.
Anyway, if that’s the real question/graphic, Cisco made another big mistake there…
1) wrong (or waaay misleading) ip scheme
2) wrong map statement
3) no labels on routers
I hope we won’t find that kind of question in an exam because who wants to pay for an exam with that many mistakes?
Question 7 on CCNA 2nd try today exact
Number 13, has one more answer• The LCP niaitegtoon phase is complete.Number 14, the correct answer is• Frame Relay at R3 and R2 should be tested to narrow the scope of the problem.• An ACL entry error could cause the failure at Layer 4 in either R3 or R2.There you go and you should had 100% by following the correction that i made.
@9tut
|| Question 7 ||
I have information that all interfaces that participate in Frame Relay should be in the same network subnet.
But now in Q7 they are not in the same network. And map statement needs remote ip and local DLCI.
I think at now the problem can be clear with Subnet mask specifiying.
DO you think we should answer this question in exam.
Q.7 on the exam today.
totally confused by this answer! I thought that in frame relay you map the remote ip 192.168.2.1 using the local DLCI 50. so why is C correct?
I need help to open the dump spike or shekter getting only 5 trial copy pls .
9 tut or other reviewers . Please Give me any information about Q7 because I think of this answer as A.Sh . Please help I will take examination tomorrow
A.Sh March 30th, 2013 @9tut
|| Question 7 ||
I have information that all interfaces that participate in Frame Relay should be in the same network subnet.
But now in Q7 they are not in the same network. And map statement needs remote ip and local DLCI.
I think at now the problem can be clear with Subnet mask specifiying.
DO you think we should answer this question in exam.